Sodium is cheap and abundant, but the batteries can’t quite match lithium cells—so far.


A breathtaking new image of the RCW 38 star cluster showcases a cosmic nursery bursting with color, light, and energy.
Located 5,500 light-years away, this region teems with young, newly formed stars and swirling clouds of glowing gas. The European Southern Observatory’s powerful VISTA telescope cuts through the dust to reveal hidden celestial wonders, offering astronomers a rare glimpse into the chaotic beauty of star birth.
A stunning glimpse of RCW 38.
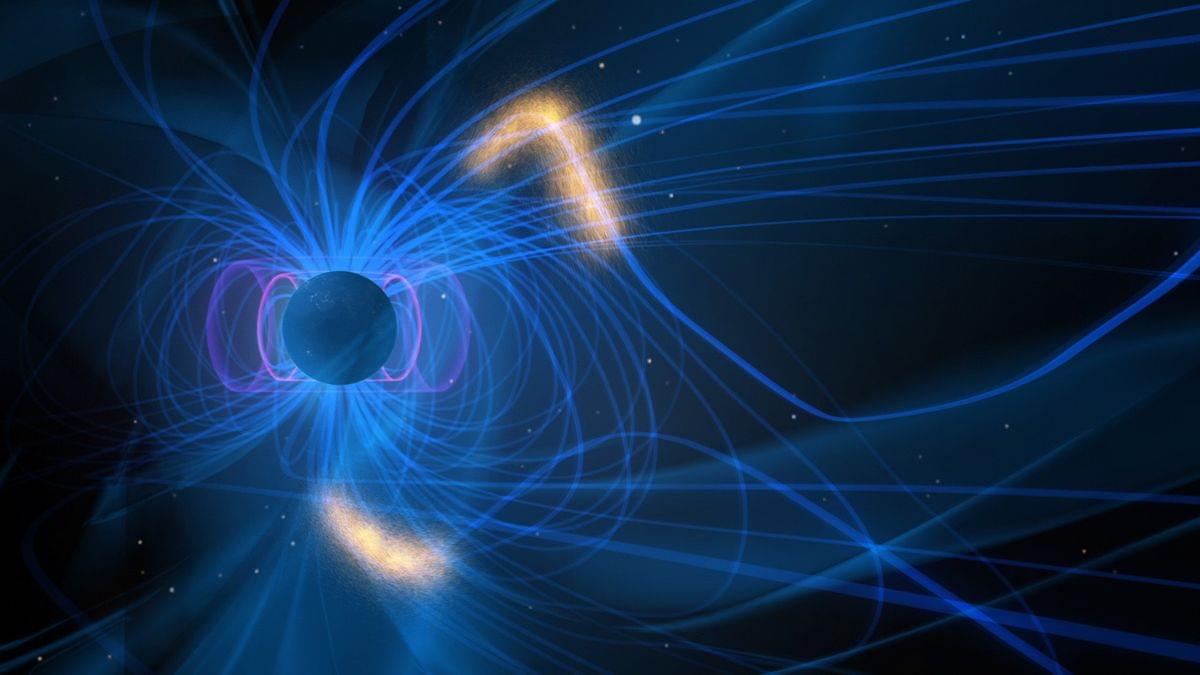
And understanding these waves a little better could help scientists better predict when and where they’ll happen, as well as how strong they’ll be. That could be vital to the safety of satellites orbiting our planet, which are vulnerable to solar storms and other sudden bursts of radiation from deep space.
“These high-energy electrons are known as ‘killer electrons’ because they have damaged several satellites, costing hundreds of millions of dollars,” wrote Horne. “Chorus waves are now included in forecasting models that are designed to protect these satellites.”
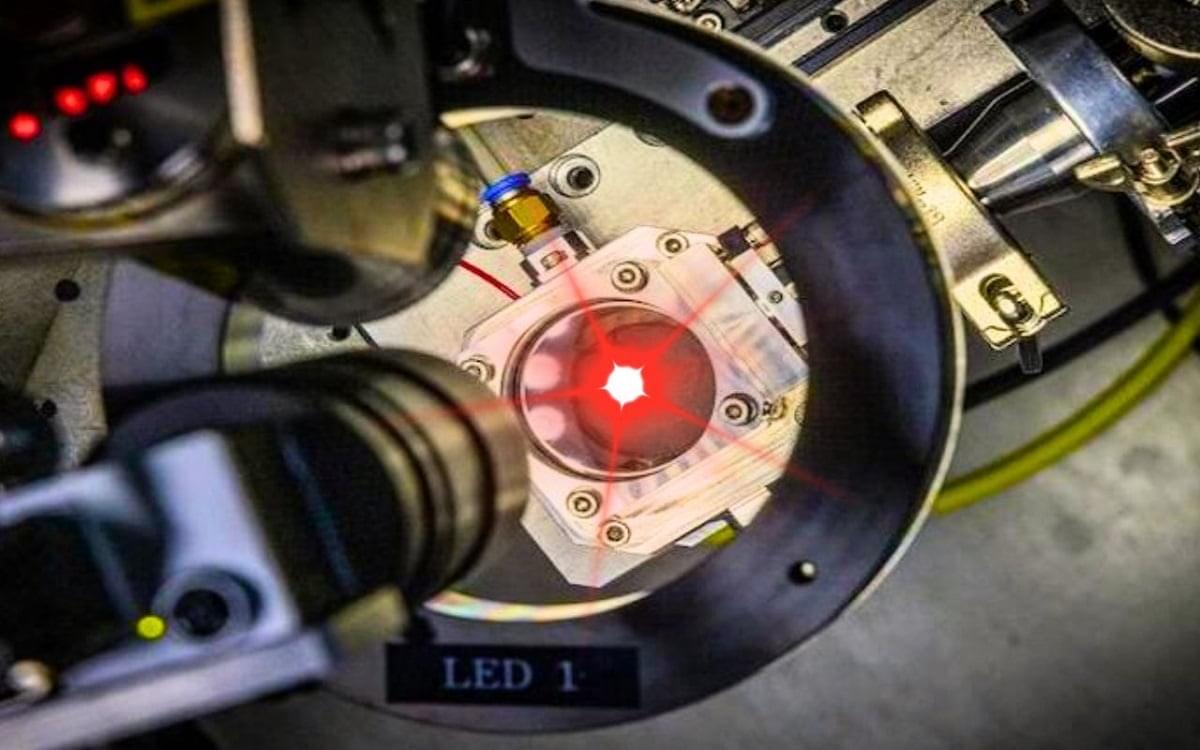
In a major leap forward for energy storage technology, a team of researchers from South Korea has developed a groundbreaking method that could revolutionize the manufacturing of sodium-ion batteries. This innovation not only promises to enhance battery efficiency but could also reshape how we think about energy storage and its future applications in various industries.
At the Korea Electrotechnology Research Institute (KERI), a team led by Dr. Kim and Dr. Park has achieved a breakthrough in the production of hard carbon anodes for sodium-ion batteries. By using a method that involves microwave induction heating, they are now able to prepare these anodes in just 30 seconds —a dramatic improvement over conventional methods. This quick processing technique could significantly reduce manufacturing times and costs, potentially making sodium-ion batteries a more viable option for widespread use.
The research team’s approach has already gained considerable attention in the scientific community, as it marks a significant step toward the commercialization of sodium-ion batteries, which are seen as a safer, more sustainable alternative to lithium-ion batteries.

Life on Earth has always existed in the flux of ionizing radiation. However, fungi seem to interact with the ionizing radiation differently from other Earth’s inhabitants. Recent data show that melanized fungal species like those from Chernobyl’s reactor respond to ionizing radiation with enhanced growth. Fungi colonize space stations and adapt morphologically to extreme conditions. Radiation exposure causes upregulation of many key genes, and an inducible microhomology-mediated recombination pathway could be a potential mechanism of adaptive evolution in eukaryotes. The discovery of melanized organisms in high radiation environments, the space stations, Antarctic mountains, and in the reactor cooling water combined with phenomenon of ‘radiotropism’ raises the tantalizing possibility that melanins have functions analogous to other energy harvesting pigments such as chlorophylls.
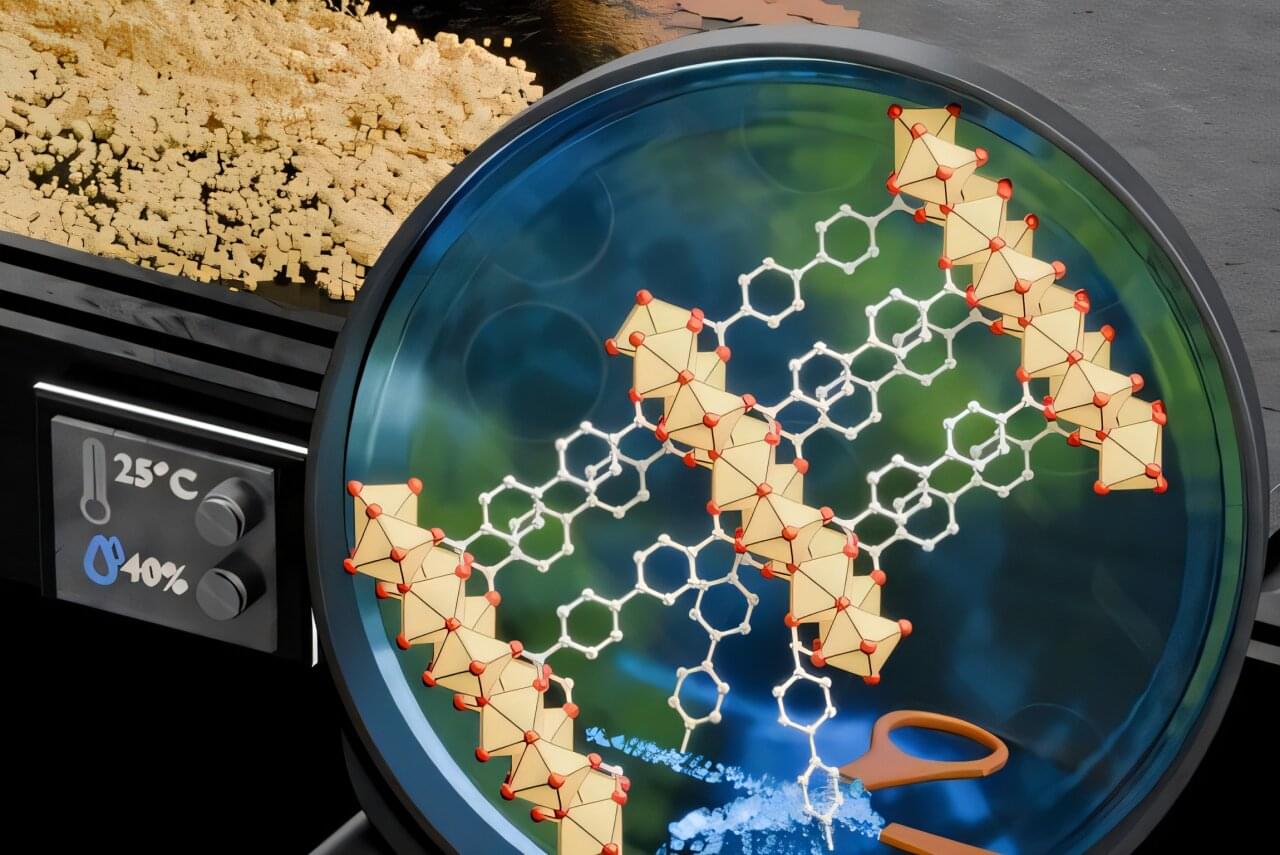

Finding the right lubricant for the right purpose is a task that is often extremely important in industry. Not only to reduce friction, overheating and wear, but also to save energy. At TU Wien, the research groups of Prof Carsten Gachot (Tribology, Mechanical Engineering) and Prof Dominik Eder (Chemistry) are therefore working together to develop innovative, improved lubricants.
The team has now presented a new type of material with special properties: The lubricant COK-47 is not liquid like lubricating oil, but a powdery solid substance. On a nanoscale, it consists of stacks of atomically thin sheets, like a tiny stack of cards.
When the material comes into contact with water molecules, these platelets can slide past each other very easily—a so-called tribofilm is created, which ensures extremely low friction. This makes COK-47 a highly interesting lubricant in humid conditions.

A collaborative study published in Nature reveals an innovative strategy to enhance energy storage in antiferroelectric materials.
The study, conducted by researchers from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Tsinghua University, Songshan Lake Materials Laboratory, and the University of Wollongong, introduces the antipolar frustration strategy, which significantly improves the performance of dielectric capacitors that are crucial for high-power devices requiring fast charge and discharge rates.
Antiferroelectrics, which feature an antiparallel polarization configuration, are emerging as promising materials for energy storage due to their phase transition from antiferroelectric to ferroelectric under an electric field. This transition provides high polarization strength and near-zero remanent polarization, ideal for energy storage.

Ugly.
Job losses are always terrible. This will be a dark and painful day at a space agency that brings so much light and joy to the world. Many of the probationary employees are just starting out their careers and were likely thrilled to land a job at NASA to explore the universe. And then all of that youthful energy and hope was extinguished this week.
It’s possible to view these losses through a couple of lenses.
Yes, NASA is clearly losing some capability with these latest cuts. Many of these hires were likely being counted on to bring new energy into the space agency and become its future discoverers and leaders. And their jobs are being sacrificed for no clear purpose. Is it to increase funding for the military? Is it to pay for tax cuts for the rich? There is a lot of anger that the relatively thin budget line of NASA—less than one-half of 1 percent of the federal budget—is being sliced for such purposes.
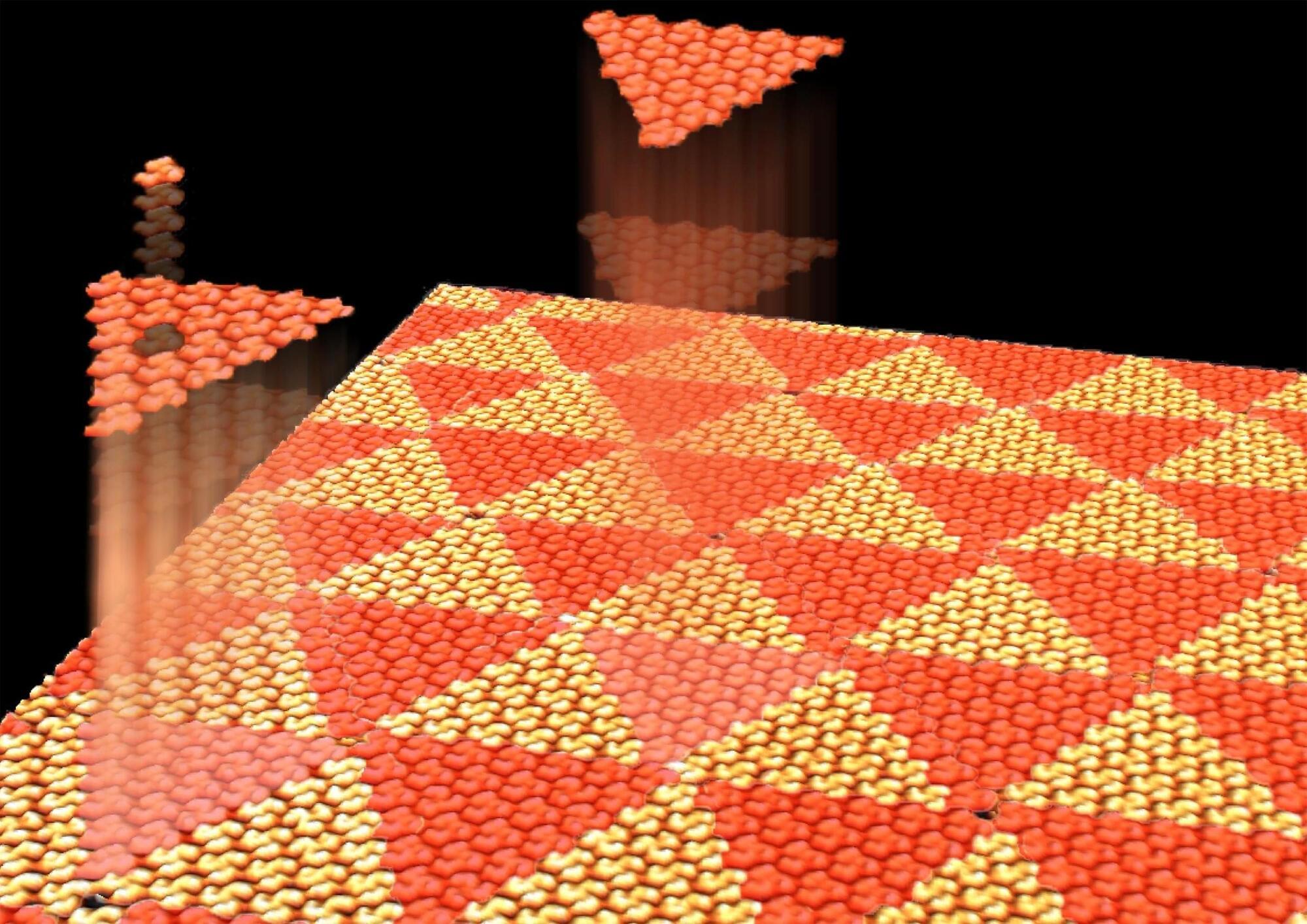
A strange molecular pattern, first mistaken for an error, led researchers to an unexpected discovery: molecules forming non-repeating structures similar to the einstein tiling problem.
This phenomenon, driven by chirality and energy balance, could pave the way for novel insights into molecular physics.
At the crossroads of mathematics and tiling lies the einstein problem—a puzzle that, despite its name, has nothing to do with Albert Einstein. The question is simple yet profound: Can a single shape tile an infinite surface without ever creating a repeating pattern? In 2022, English amateur mathematician David Smith discovered such a shape, known as a “proto-tile.”
In this video, we break down the Cahill Cycle, also known as the Glucose-Alanine Cycle, a crucial metabolic pathway that helps transport nitrogen from muscles to the liver while maintaining glucose balance! 🧬🔥
You’ll learn:
✅ How alanine plays a key role in nitrogen transport 🏋️♂️
✅ The step-by-step process of the cycle 🔄
✅ Why this process is energy-intensive for the liver ⚡
Join this channel to get access to perks:
/ @easypeasylearning.
Thank You For Watching.
Please Like And Subscribe to Our Channel: / easypeasylearning.
Like Our Facebook Page: / learningeasypeasy.
Join Our Facebook Group: / 460057834950033
Support Our Channel: / supereasypeasy.