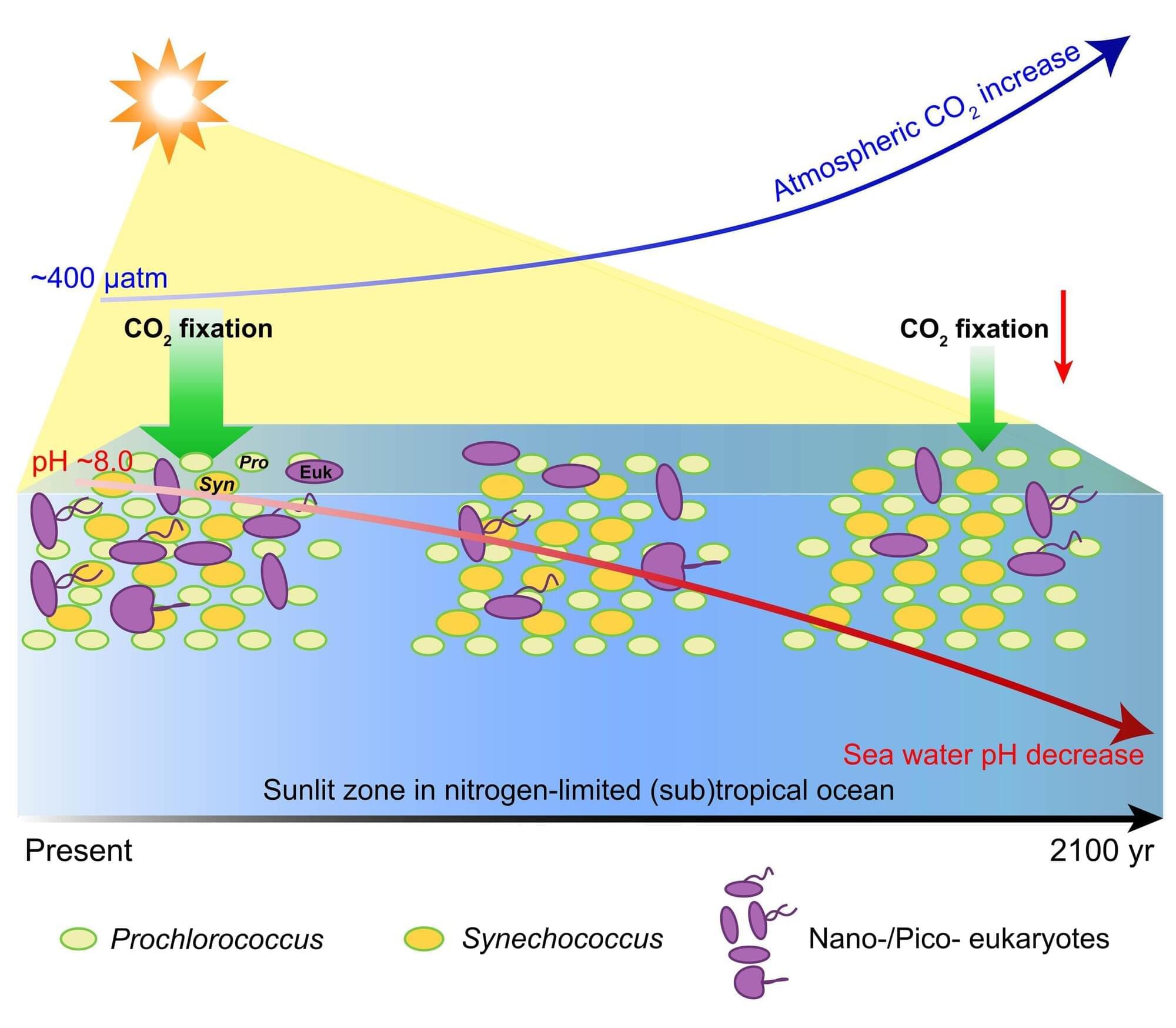
To fuel the future advancement of the electronics industry, engineers will need to develop batteries that can be charged quickly, have higher energy densities (i.e., can store more energy) and last longer. Among the most promising alternatives to lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries, which power most devices on the market today, are lithium-metal batteries (LMBs).
As suggested by their name, LMBs have an anode (i.e., negative electrode) made of Li metal. Compared to Li-ion batteries, which have graphite or silicon-based anodes, LMBs can exhibit significantly higher energy densities.
Despite their potential, LMBs have been found to exhibit slow redox kinetics and poor cycling reversibility. These limitations tend to adversely impact their performance, reducing their charging speed and their efficiency over time.