Discover the Future of Sustainable Energy: Harnessing Kinetic solutions for a Brighter World. Explore Energy Floors’ Innovative Kinetic Tiles Today!



Unlock the future of energy! Discover how abundant thorium and advanced Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) could power our world and humanity’s pioneering Moon base, offering a safer, cleaner path to net-zero.
If you liked this video, please show it to a friend who hasn’t heard of us yet! Also, please leave a comment below. Thanks for watching!
🚀 New mind-blowing episodes every week!
Link to Best Telescopes at the website: https://apollo11space.com/best-telesc… website: https://apollo11space.com 🌠 Join our constellation of curious minds: Facebook: / apollo11space11 Pinterest:
/ tranquilitybase784 Instagram:
/ apollo11spacechannel X (Twitter):
/ apollo11space69 Reddit:
/ orbitingapollo Copyright Title 17, US Code (Sections 107–118 of the copyright law, Act 1976): This website uses all media for the purpose of review and commentary under the terms of fair use. All footage and images used belong to their respective companies. #thorium #materialscience #space.
My website: https://apollo11space.com.
🌠 Join our constellation of curious minds:
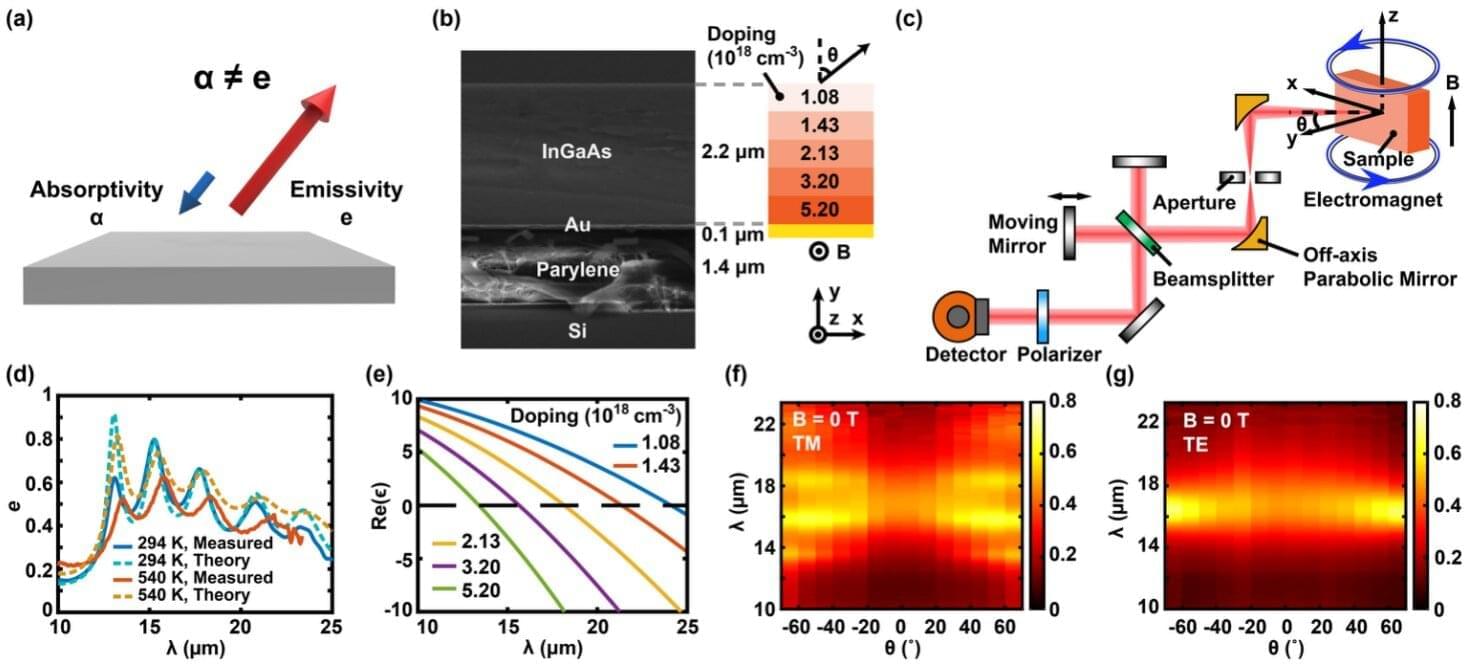
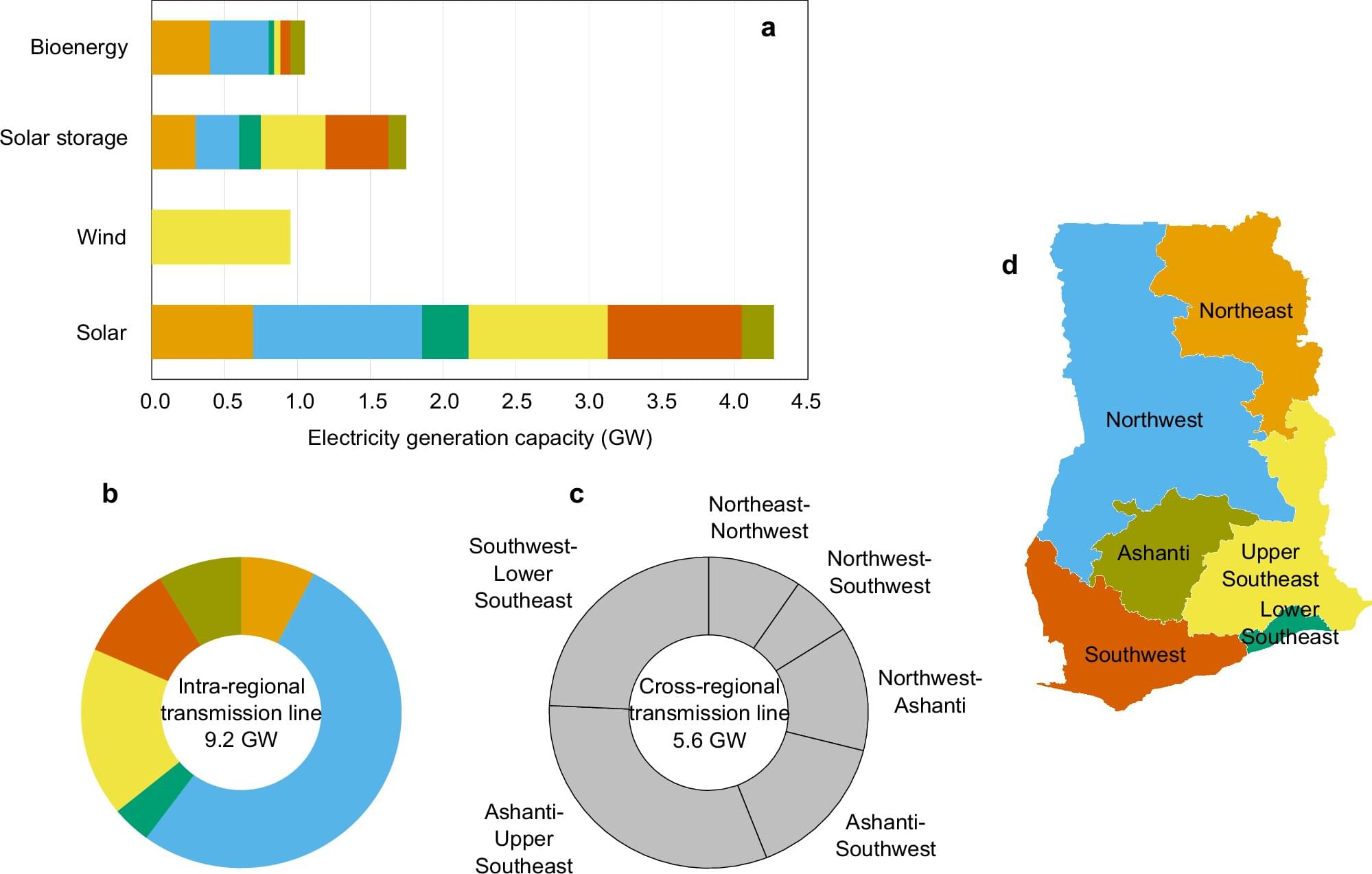
In the building sector, which accounts for approximately 40% of global energy consumption, heat ingress through windows has been identified as a primary cause of wasted heating and cooling energy.
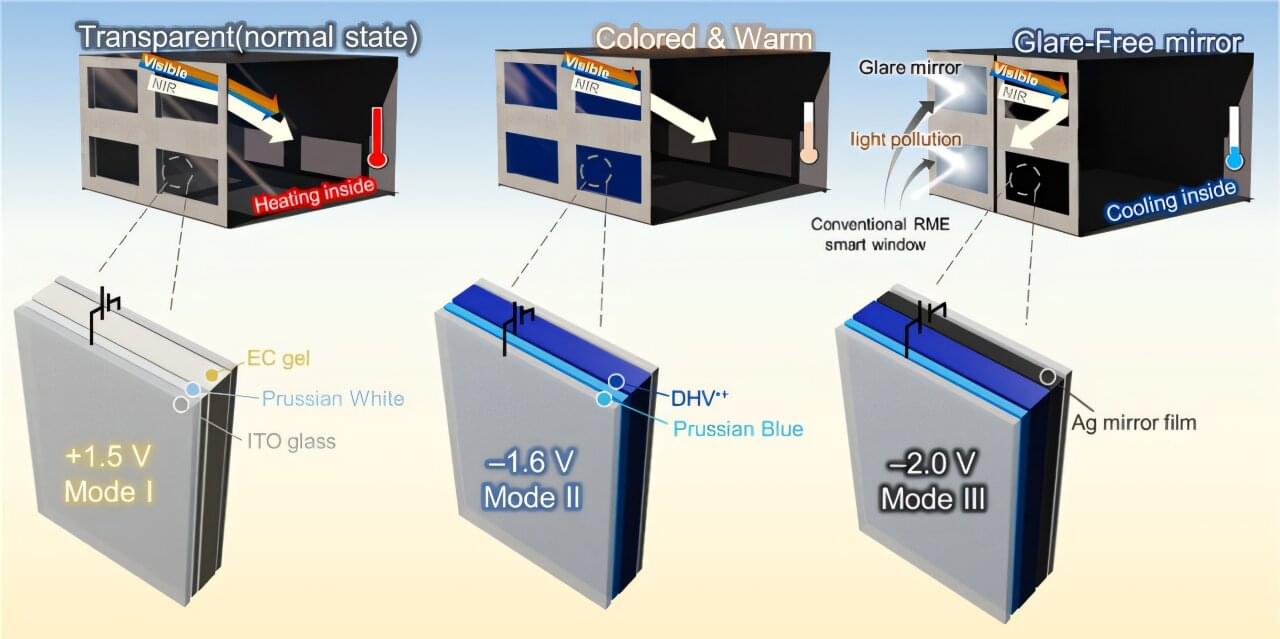
A KAIST research team has successfully developed a ‘pedestrian-friendly smart window’ technology capable of not only reducing heating and cooling energy in urban buildings but also resolving the persistent issue of ‘light pollution’ in urban living.
Professor Hong Chul Moon’s research team at KAIST’s Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering have developed a ‘smart window technology’ that allows users to control the light and heat entering through windows according to their intent, and effectively neutralize glare from external sources.
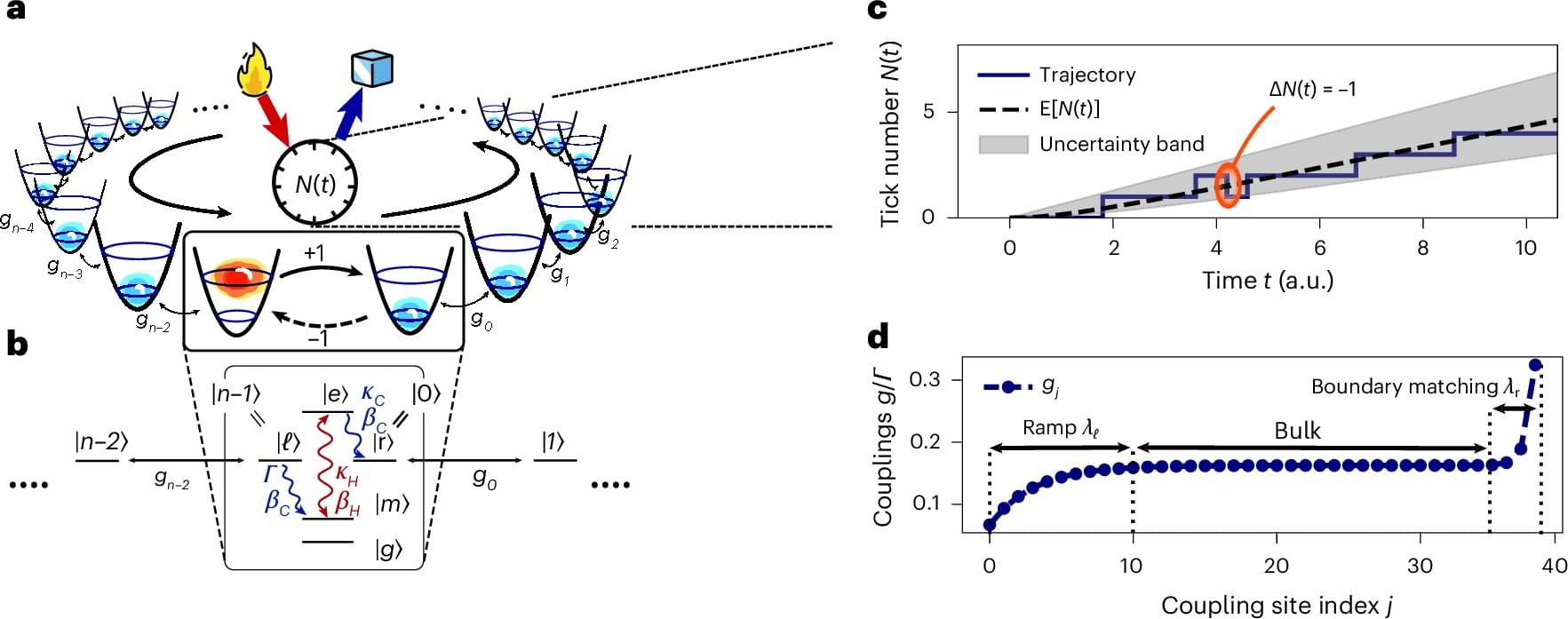
Over the past decades, physicists have been trying to develop increasingly sophisticated and precise clocks to reliably measure the duration of physical processes that unfold over very short periods of time, helping to validate various theoretical predictions. These include so-called quantum clocks, timekeeping systems that leverage the principles of quantum mechanics to measure time with extremely high precision.
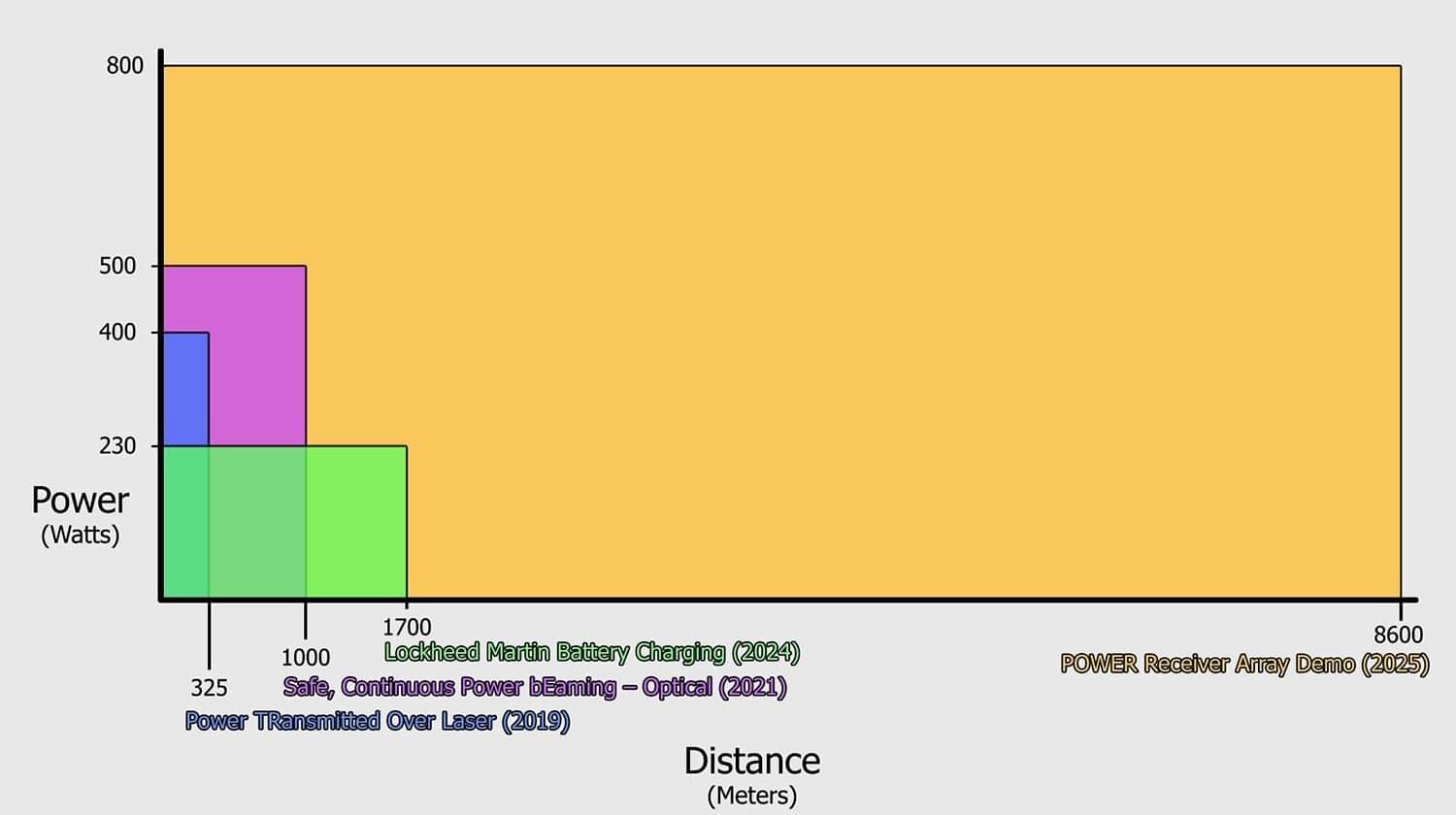
Previously, the greatest reported distance records for an appreciable amount of optical power (1 microwatt) were 230 watts of average power at 1.7 kilometers for 25 seconds and a lesser (but undisclosed) amount of power at 3.7 kilometers.
“It is beyond a doubt that we absolutely obliterated all previously reported optical power beaming demonstrations for power and distance,” said POWER Program Manager Paul Jaffe after the results were confirmed. The DARPA-led team brought together industry and government, including the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory and the High Energy Laser Systems Test Facility (HELSTF) at the U.S. Army’s White Sands Missile Range.
Energy is a fundamental requirement for military operations, and traditional means of getting energy to the edge (battlefields, disaster zones, etc.) are often incredibly slow, risky, and resource intensive. These tests, referred to as PRAD (POWER Receiver Array Demo), mark an important step towards the POWER program’s long-term goal of being able to instantly beam power from a location where it can be easily generated to wherever it’s needed, opening a novel design space for platform capabilities unbounded by fuel limitations.
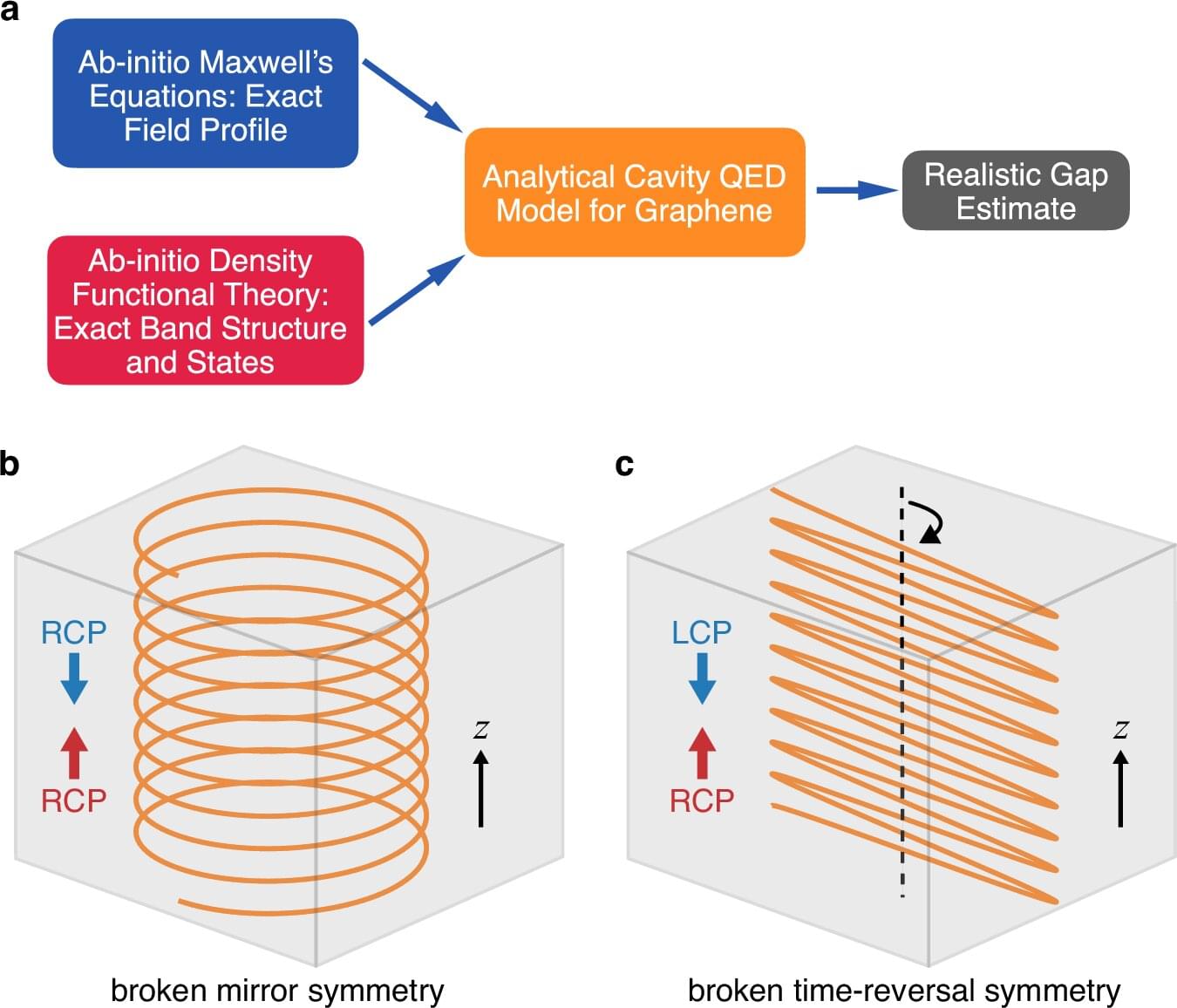
Vacuum is often thought of as empty, but in fact it is teeming with fleeting energy fluctuations—virtual photons popping in and out of existence that can interact with matter, giving rise to new, potentially useful properties.
Researchers use optical cavities, structures made of mirrors facing one another, to confine these fluctuations, harnessing their effects to engineer new forms of matter.
Conventional optical cavities boost fluctuations, or vacuum fields, for both right-and left-handed circularly polarized light. Rice University researchers and collaborators have developed a new cavity design that selectively enhances the quantum vacuum fluctuations of circularly polarized light in a single direction, achieving chirality—a feat that typically requires the use of a strong magnetic field.
Scientists have achieved a major breakthrough by creating the world’s first next-generation betavoltaic cell. This advanced power source was made by directly connecting a radioactive isotope electrode to a perovskite absorber layer, a cutting-edge material known for its efficiency.
To boost performance, the team embedded carbon-14-based quantum dots into the electrode and improved the structure of the perovskite layer. These innovations led to a highly stable power output and impressive energy conversion efficiency.
The findings were published in the journal Chemical Communications and led by Professor Su-Il In of the Department of Energy Science & Engineering at DGIST (President Kunwoo Lee).