
Category: energy – Page 258


Exclusive: IBM achieves quantum computing breakthrough
IBM has created a quantum processor able to process information so complex the work can’t be done or simulated on a traditional computer, CEO Arvind Krishna told “Axios on HBO” ahead of a planned announcement.
Why it matters: Quantum computing could help address problems that are too challenging for even today’s most powerful supercomputers, such as figuring out how to make better batteries or sequester carbon emissions.
Driving the news: IBM says its new Eagle processor can handle 127 qubits, a measure of quantum computing power. In topping 100 qubits, IBM says it has reached a milestone that allows quantum to surpass the power of a traditional computer.
Construction’s Graphene Revolution Has (Finally) Begun
From super-strength concrete to fortified infrastructure, this is what the ‘wonder material for the 21st century’ is now bringing to construction. For more by Tomorrow’s Build subscribe now — https://bit.ly/3vOOJ98
Executive Producer and Narrator — Fred Mills.
Producer — Adam Savage.
Video Editing and Graphics — Thomas Canton.
Special thanks to Dr Lisa Scullion and University of Manchester. Additional footage and images courtesy of University of Manchester, Absolute Photography, Gerdau Graphene, Graphene Flagship, HS2 Ltd, ICON Technology, Kansas State University, NASA/Pat Rawlings, Nanotech Energy and Skanska.
Follow us on Twitter — https://twitter.com/TomorrowsBuild/
Like us on Facebook — https://www.facebook.com/TomorrowsBuild/
Follow us on LinkedIn — https://www.linkedin.com/company/TomorrowsBuild/
Follow us on Instagram — https://www.instagram.com/TomorrowsBuild/
#construction #architecture #science.
Tomorrow’s Build is owned and operated by The B1M Limited. We welcome you sharing our content to inspire others, but please be nice and play by our rules: http://www.theb1m.com/guidelines-for-sharing.
What If Humanity Was A Type IV Civilization? | Unveiled
What would humanity be like if it was Level 4 on the Kardashev Scale? In this video, Unveiled takes a dramatic trip into the future to discover how the human race would change and evolve if it ever hoped to be a Type IV Civilization. We’re talking a whole universe’s worth of power and energy here, so hold on to your hats!
This is Unveiled, giving you incredible answers to extraordinary questions!
Find more amazing videos for your curiosity here:
What If Humanity Was a Type II Civilization? — https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y6Aj_bnZ3Gs.
What If Humanity Was a Type V Civilization? — https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DGB7hPX0wc0
Are you constantly curious? Then subscribe for more from Unveiled ► https://wmojo.com/unveiled-subscribe.
#Civilization #KardashevScale #WhatIf

Reaction Engines assembles partners for its ammonia aviation project
The UK’s Reaction Engines has announced a joint venture to create compact, lightweight ammonia reactors it says can be used to decarbonize difficult sectors like shipping and off-grid energy generation – and surprisingly, also aviation.
We’ve written before about ammonia’s potential in the clean transport sector; check out our ammonia clean fuel primer piece from September. Compared against hydrogen, ammonia’s much easier and cheaper to store and transport, and although it only carries about 20 percent as much energy as hydrogen by weight, it carries about 70 percent more energy than liquid H2 by volume.
The weight issue generally rules ammonia out of aviation discussions; at less than half the specific energy of jet fuel it looks less attractive than hydrogen. But hydrogen’s volume issues must also be taken into account. Today’s airliners are built for jet fuel so retro-fitting large-volume long-range hydrogen tanks can mean you lose seats. And anyone who’s flown economy can attest, airlines really like fitting in as many seats as they can.
Space startup wants to sling satellites into orbit with a huge centrifuge
In a nutshell: In the 21st century, there’s a new space race, primarily between Tesla (SpaceX) and Amazon (Blue Origin). Both are concentrating on traditional methods of launching satellites into space—namely, big rockets. However, a small space startup called SpinLaunch is developing a cheaper and environmentally cleaner way of launching satellites.
SpinLaunch is using a gigantic centrifuge to shoot stuff into space. By “stuff,” we mean things that can withstand the G-force created by being spun at 5,000 miles per hour (over 10,000 Gs), which is a category of stuff that does not yet include satellites. However, it did launch a missile-like projectile tens of thousands of feet into the air last month, using only 20 percent of the accelerator’s power.
The design is relatively simple. A carbon fiber tether holds the projectile inside a span vacuum chamber as it spins up to speed. Once the centrifuge has reached the desired velocity, the launch vehicle is released out a tube taller than the Statue of Liberty (50.4 meters). It is not unlike launching your friends off the merry-go-round when you were a kid. A more mature and controlled application of the principle would be the hammer throw event in the Olympics.
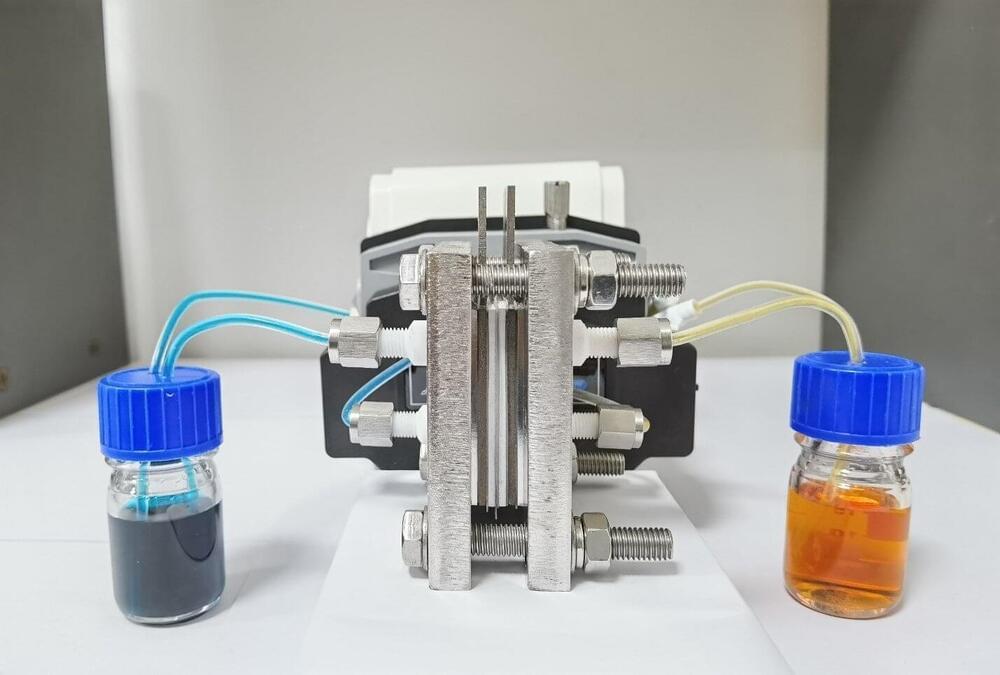

Newly developed compound may enable sustainable, cost-effective, large-scale energy storage
To produce a cost-effective redox flow battery, researchers based at the South China University of Technology have synthesized a molecular compound that serves as a low-cost electrolyte, enabling a stable flow battery that retains 99.98% capacity per cycle. They published their approach on August 14 in the Energy Material Advances.
Comprising two tanks of opposing liquid electrolytes, the battery pumps the positive and negative liquids along a membrane separator sandwiched between electrodes, facilitating ion exchanges to produce energy. Significant work has been dedicated to developing the negative electrolyte liquid, while the positive electrolyte liquid has received less attention, according to corresponding author Zhenxing Liang, professor in the Key Laboratory of Fuel Cell Technology of Guangdong Province, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, South China University of Technology.
“Aqueous redox flow batteries can realize the stable electrical output for using unsteady solar and wind energy, and they have been recognized as a promising large-scale energy storage technology,” Liang said. “Electroactive organic merit of element abundance, low cost and flexible molecular control over the electrochemical features for both positive and negative electrolytes are regarded as key to developing next-generation redox flow batteries.”

Battery-Powered Chainsaws Are Proving to Be a Better Choice Than Those Powered by Gas Engines
The revolution will be electrified.
For decades, gas-engine power equipment was the only choice for yardwork, followed by corded power tools at a distant second. Anything powered by a battery was either ineffective or an expensive novelty. The few successful versions of battery-powered outdoor equipment were limited to low-power applications, like grass shears. Of course, for every rule there’s an exception: We reported on the highly effective GE Elec-Trak battery-powered tractor and Black & Decker’s somewhat effective battery mowers in our April 1970 issue.
In many respects, gas-engine equipment still rules the outdoors in terms of power and cost effectiveness–at least for people with serious work to do. But a revolution in outdoor power is occurring. For many people doing yardwork, cordless power tools are now the default choice. This has stood the status quo on its head.
🛠 Want to fine-tune your yard care and maintenance? Come learn how with us.
The new SUPER WEAPONS with which CHINA hopes to BEAT USA (At least in Asia) — VisualPolitik EN
Play Conflict of Nations for FREE on PC or Mobile: 💥 https://con.onelink.me/kZW6/VisualPolitik.
Receive an Amazing New Player Pack, only available for the next 30 days! Thanks to Conflict of Nations for sponsoring this video!
Asia-Pacific has become the most important region in the world. A region in which the United States and China are fighting a battle for political and military dominance. As we told you in a past video, the distance separating these two powers is still worlds apart, yet China is committed to becoming a regional mega-power.
To achieve this, the People’s Liberation Army is developing a whole new series of weapons with which they aspire to gain control of Asia Pacific. In this video we give you some clues about the weapons programs with which China wants to pursue its goal.
Recommended video: Why won’t China Surpass the United States? https://youtu.be/ZqowS-hlZ3M
Join the VisualPolitik community and support us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/VisualPolitik
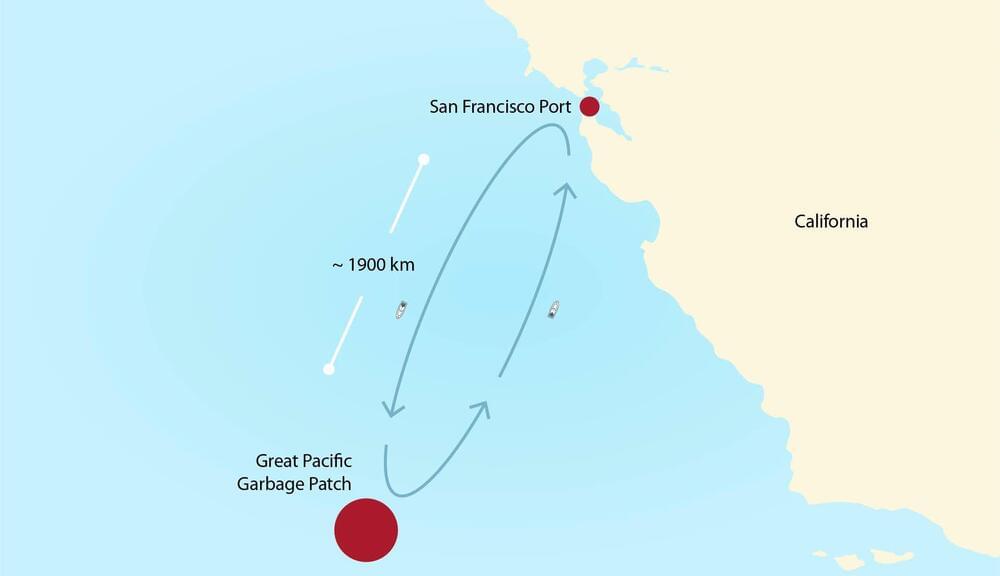
Using ocean plastic waste to power ocean cleanup ships
A team of researchers from Worcester Polytechnic Institute, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution and Harvard University believes that the plastic amassing in floating islands in the oceans could be used to power the ships that are sent to clean them up. In their paper published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the group describes how ocean plastics could be converted to ship fuel.
Prior research has shown that millions of tons of plastics enter the ocean each year—some of it is ground into fragments and disperses, and some of it winds up in colossal garbage patches floating in remote parts of the ocean. Because of the danger that such plastics present to ocean life, some environmentalists have begun cleanup operations. Such operations typically involve sending a ship to a garbage patch, collecting as much as the ship will hold and then bringing it back to port for processing. In this new effort, the researchers suggest it would be far more efficient and greener to turn the plastic into fuel for both a processing machine and for uninterrupted operation of the ships.
The researchers note that the plastic in a garbage dump could be converted to a type of oil via hydrothermal liquefaction (HTL). In this process, the plastic is heated to 300–550 degrees Celsius at pressures 250 to 300 times that of sea-level conditions. The researchers have calculated that a ship carrying an HTL converter would be capable of producing enough oil to run the HTL converter and the ship’s engine. Under their scenario, plastic collection booms would be permanently stationed at multiple sites around a large garbage patch, able to load the plastic it collects onto ships.