MIT spin-off Quaise says it’s going to use hijacked fusion technology to drill the deepest holes in history, unlocking clean, virtually limitless, supercritical geothermal energy that can re-power fossil-fuelled power plants all over the world.
Category: energy – Page 239



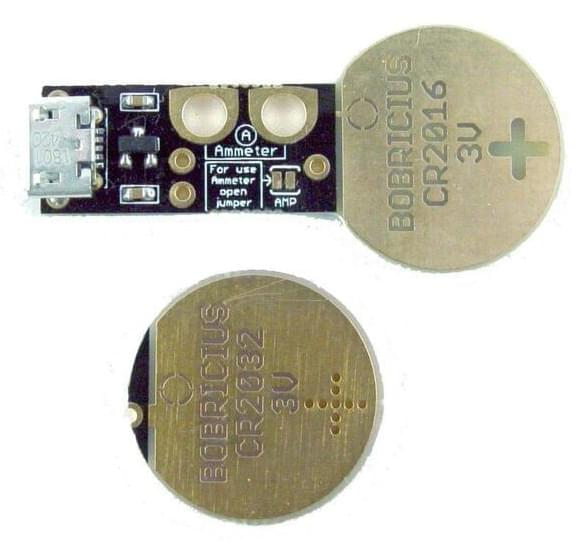
Coin Cell Eliminator Does More Than Save Batteries
Coin cells are useful things that allow us to run small electronic devices off a tiny power source. However, they don’t have a lot of capacity, and they can run out pretty quickly if you’re hitting them hard when developing a project. Thankfully, [bobricius] has just the tool to help.
The device is simple – it’s a PCB sized just so to fit into a slot for a CR2016 or CR2032 coin cell. The standard board fits a CR2016 slot thanks to the thickness of the PCB, and a shim PCB can be used to allow the device to be used in a CR2032-sized slot instead.
It’s powered via a Micro USB connector, and has a small regulator on board to step down the 5 V supply to the requisite 3 V expected from a typical coin cell. [bobricius] also gave the device a neat additional feature – a pair of pads for easy attachment of multimeter current probes. Simply open the jumper on the board, hook up a pair of leads, and it’s easy to measure the current being drawn from the ersatz coin cell.
NanoWire Tech Could Usher In a New Age of Supercomputing
Building a better supercomputer is something many tech companies, research outfits, and government agencies have been trying to do over the decades. There’s one physical constraint they’ve been unable to avoid, though: conducting electricity for supercomputing is expensive.
Not in an economic sense—although, yes, in an economic sense, too—but in terms of energy. The more electricity you conduct, the more resistance you create (electricians and physics majors, forgive me), which means more wasted energy in the form of heat and vibration. And you can’t let things get too hot, so you have to expend more energy to cool down your circuits.

Two More Energy Companies Go Under As Crisis Worsens
Whoop Energy and XCel Power have ceased trading – affecting around 550 customers.
Consumers from both energy firms will be designated a new supplier by market regulator Ofgem – through its supplier of last resort process.
Whoop Energy (Whoop) provides gas and electricity to 262 customers, including 50 households (domestic consumers).

Large content platforms want to contribute to the cost of European digital infrastructure
New applications in energy, defense and telecommunications could receive a boost after a team from The University of Texas at Austin created a new type of “nanocrystal gel”—a gel composed of tiny nanocrystals each 10,000 times smaller than the width of a human hair that are linked together into an organized network.
