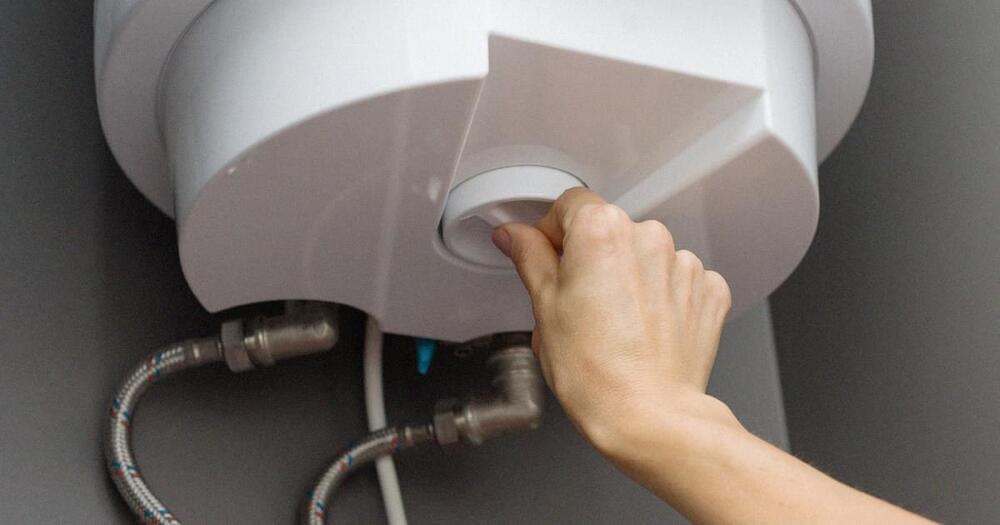
“Electric water heaters offer a cheap way to store large amounts of energy, in the form of hot water. A heater with a 300-litre tank can store about as much energy as a second-generation Tesla Powerwall – at a fraction of the cost.”
Australia’s energy transition is well under way. Some 3 million households have rooftop solar and sales of medium-sized electric cars are surging. But as we work towards fully electric households powered by renewable energy, have we overlooked a key enabling technology, the humble electric water heater?
About half of Australian households use electric water heaters, while the rest use gas. So what’s so great about electric water heaters?