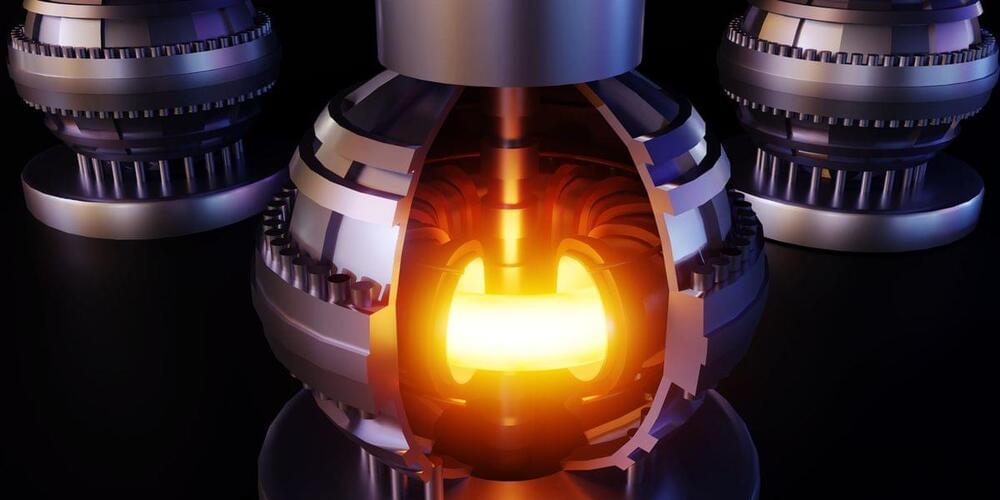
Researchers at the University of Rochester’s Laboratory for Laser Energetics (LLE) have led experiments showcasing an efficient “spark plug” for direct-drive approaches to inertial confinement fusion (ICF). In a pair of studies featured in Nature Physics, the team shares their findings and details the potential for scaling up these methods, aiming for successful fusion in a future facility.
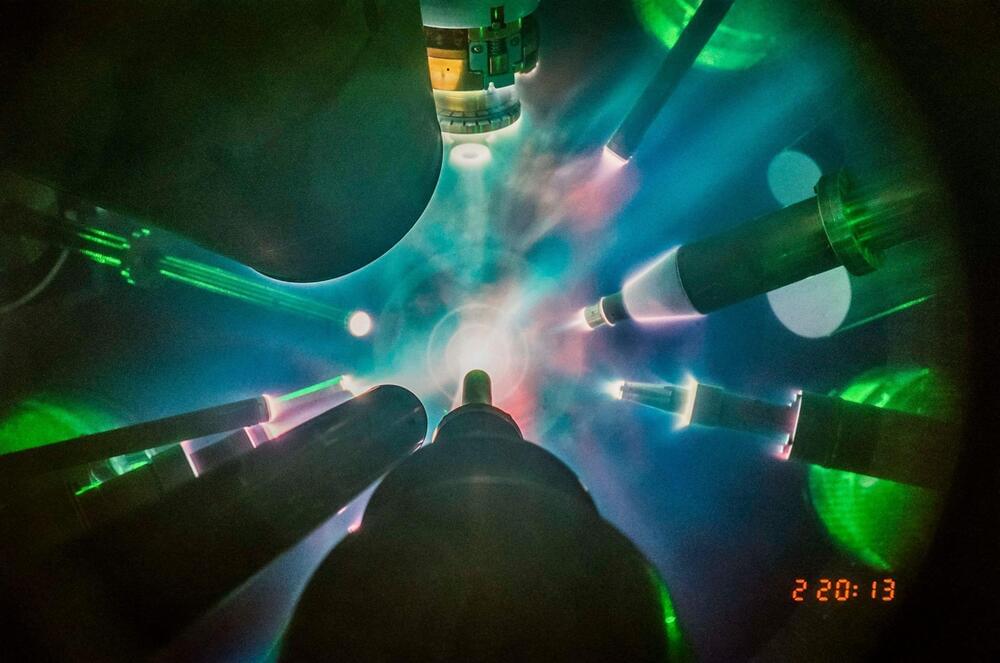
LLE is the largest university-based U.S. Department of Energy program and hosts the OMEGA laser system, which is the largest academic laser in the world but still almost one hundredth the energy of the National Ignition Facility (NIF) at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in California. With OMEGA, Rochester scientists completed several successful attempts to fire 28 kilojoules of laser energy at small capsules filled with deuterium and tritium fuel, causing the capsules to implode and produce a plasma hot enough to initiate fusion reactions between the fuel nuclei. The experiments caused fusion reactions that produced more energy than the amount of energy in the central hot plasma.
The OMEGA experiments use direct laser illumination of the capsule and differ from the indirect drive approach used on the NIF. When using the indirect drive approach, the laser light is converted into X-rays that in turn drive the capsule implosion. The NIF used indirect drive to irradiate a capsule with X-rays using about 2,000 kilojoules of laser energy. This led to a 2022 breakthrough at NIF in achieving fusion ignition —a fusion reaction that creates a net gain of energy from the target.