What if we tapped into billions of years of evolution to harness a greener future?


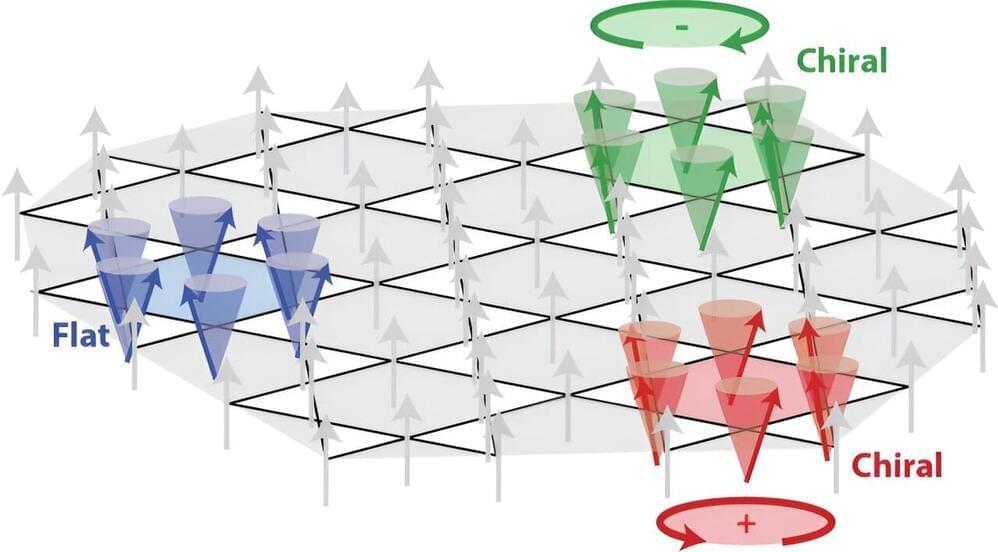
“People are always searching for chiral ground states,” McQueeney said. “The reason we use the concept of quasiparticle here is because it is a way of transmitting energy or information, like an electron is a quasiparticle, and we can send it from point A to point B, carrying some information.
A chiral quasiparticle would have other attributes to it. It would have a handedness, for example, and so you could think about novel ways to, say, transmit information from point A to point B, which didn’t involve moving a charge, but moving some chiral signal.
Discovering this new chiral excitation was especially exciting for McQueeney, You don’t expect it to be there, he said. And we still don’t understand why it’s there. As a matter of fact, we’re setting up other experiments to look for it in other materials.

Hydrogen offers significant potential as both a chemical and energy carrier for decarbonizing society. Unlike traditional fuels, using hydrogen does not produce carbon dioxide. However, most hydrogen currently produced derives from methane, a fossil fuel, through a process called methane reforming, which unfortunately emits a considerable amount of carbon dioxide. Consequently, developing scalable alternatives for producing green hydrogen is essential.
Water electrolysis offers a path to generate green hydrogen which can be powered by renewables and clean electricity. This process needs cathode and anode catalysts to accelerate the otherwise inefficient reactions of water splitting and recombination into hydrogen and oxygen, respectively. From its early discovery in the late 18th century, the water electrolysis has matured into different technologies. One of the most promising implementations of water electrolysis is the proton-exchange-membrane (PEM), which can produce green hydrogen by combining high rates and high energy efficiency.
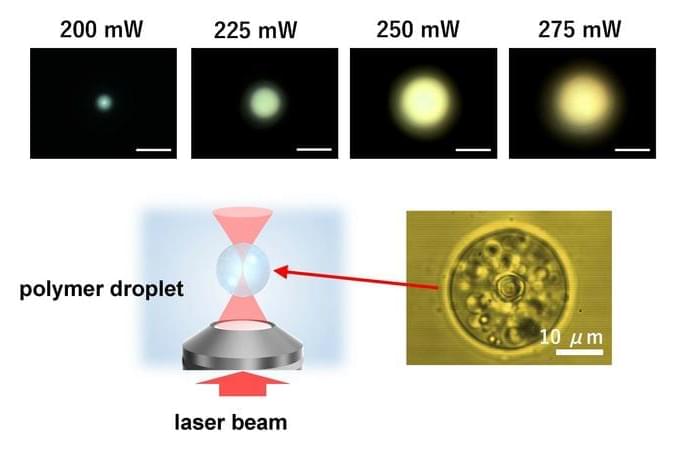
A novel technique with potential applications for fields such as droplet chemistry and photochemistry has been demonstrated by an Osaka Metropolitan University-led research group.
The findings were published in Advanced Optical Materials (“Förster Resonance Energy Transfer Control by Means of an Optical Force”).
Professor Yasuyuki Tsuboi of the Graduate School of Science and the team investigated Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET), a phenomenon seen in photosynthesis and other natural processes where a donor molecule in an excited state transfers energy to an acceptor molecule.

Earth’s H2O is 97 percent seawater, and most of the remaining 3 percent is inaccessible, frozen in glaciers or permafrost. Only a small portion, about half of a percent, exists as freshwater in aquifers and rivers that humans can tap into. A process called, however, allows us to dip into the oceans to satisfy our thirst.
Desal has been around for decades and is used to make both seawater and salty groundwater drinkable. But scientists think that it will become increasingly important in a warmer, drier future. In a recent UN-led review, researchers stated that “‘conventional’ sources of water such as rainfall, snowmelt and river runoff captured in lakes, rivers, and aquifers are no longer sufficient to meet human demands in water-scarce areas.”
During a media roundtable at the 2019 American Geophysical Union conference, Peter Fiske, director of the Water-Energy Resilience Research Institute at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, discussed why we might need to more strongly consider this technology—at times written off for its high costs and energy use—to stabilize water supplies in the future. Here’s what you need to know.

(NewsNation) — Researchers have found a significant source of geothermal energy underneath the U.S.-Mexico border along the Rio Grande, which could lead to promising clean energy development in the rural region.
The findings came after a monthslong study conducted by the Bureau of Economic Geology at the University of Texas at Austin, which discovered that the region of Presidio County in Texas, which shares a border with Mexico, has the conditions necessary for geothermal development.
“There’s a thin, 10-to 15-mile-wide region that runs parallel or along the Rio Grande that has very high heat by at least by most standards, and even in the interior part of the county, which is probably two-thirds of the county,” Ken Wisian, head of the research team, told NewsNation.
Japanese firm TDK aims to improve next-gen solid-state battery design with a new material utilizing multi-layer lamination technology.
Bioenergy Innovation For The U.S. Bioeconomy — Dr. Valerie Sarisky-Reed Ph.D. — Director, Bioenergy Technologies Office, Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy, U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)
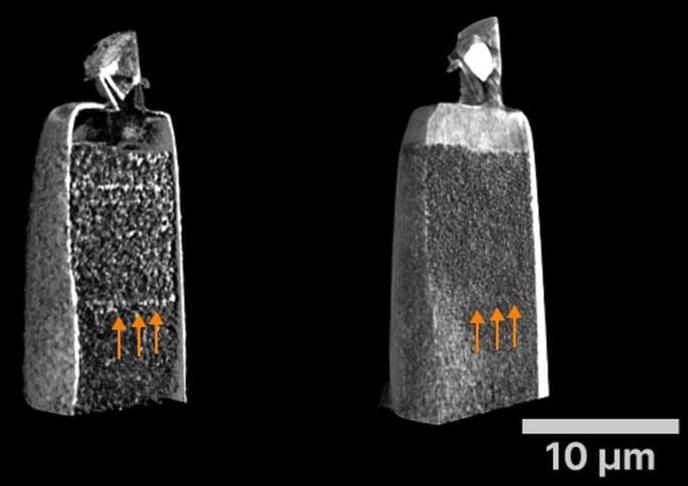
X-ray microscopes are essential for examining components and materials because they can be used to detect changes and details in the material. Until now, however, it has been difficult to detect small cracks or tiny inclusions in the images. By developing a new method, researchers at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon are now able to visualize such changes in the nanometer regime. In particular materials research and quality assurance will profit from this development.
The team reported on their new development in the scientific journal Optica (“Nanoscale dark-field imaging in full-field transmission X-ray microscopy”).
The quality must be right. This also applies to materials science. When metal parts are welded together, you need to know whether the weld seam is any good — or whether small cracks or pores have formed inside, which could lead to failure. High-performance materials, e.g. for electrodes in electric car batteries or fuel cells, should not contain defects to allow the current to flow undisturbed.