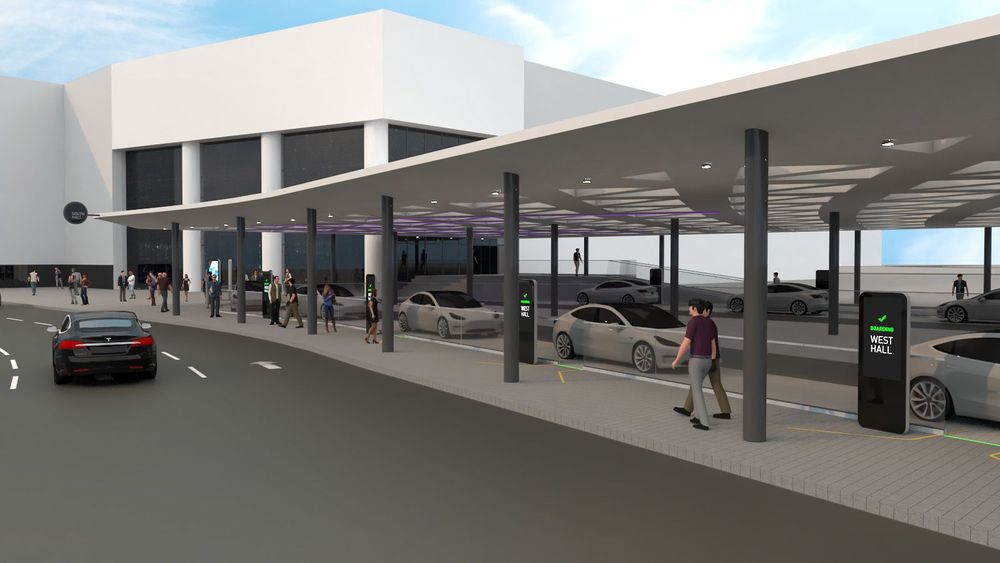
The ambitious rocket, designed to send the first humans to Mars and establish a city, is taking shape.

Former astronaut Jeffrey Hoffman: For the long-term survival of our species, we have to become a multi-planet being.
With our rising planet’s population competing for space and resources, some people are convinced we need to look beyond Earth to help ensure humanity’s survival. As Elon Musk, the entrepreneur behind space tourism company SpaceX told Aeon’s Ross Andersen: “I think there is a strong argument for making life multi-planetary in order to safeguard the existence of humanity in the event that something catastrophic were to happen.”
Last month’s NASA and SpaceX successful launch of astronauts from US soil for the first time in almost a decade, has reignited discussion about space travel to Mars and beyond. Musk has been pushing Mars colonisation as extinction insurance for more than a decade now and he told Andersen that he would need a million people to form a sustainable, genetically diverse civilisation. Andersen reports:
‘Even at a million, you’re really assuming an incredible amount of productivity per person, because you would need to recreate the entire industrial base on Mars,’ he said. ‘You would need to mine and refine all of these different materials, in a much more difficult environment than Earth. There would be no trees growing. There would be no oxygen or nitrogen that are just there. No oil.’
I asked Musk how quickly a Mars colony could grow to a million people. ‘Excluding organic growth, if you could take 100 people at a time, you would need 10,000 trips to get to a million people,’ he said. ‘But you would also need a lot of cargo to support those people. In fact, your cargo to person ratio is going to be quite high. It would probably be 10 cargo trips for every human trip, so more like 100,000 trips. And we’re talking 100,000 trips of a giant spaceship.’

Elon Musk has sent a somewhat cryptic email to Tesla employees about going “all out” for the end of the quarter to have a “good outcome.”
On Monday afternoon, Musk sent a short email to all Tesla employees.
In the email obtained by Electrek, the CEO addressed the importance of the last week of the quarter:
My hero my guy.


Like many things about Elon Musk, Tesla’s approach to achieving autonomous driving is polarizing. Bucking the map-based trend set by industry veterans such as Waymo, Tesla opted to dedicate its resources in pursuing a vision-based approach to achieve full self-driving instead. This involves a lot of hard, tedious work on Tesla’s part, but today, there are indications that the company’s controversial strategy is finally paying off.
In a recent talk, Tesla AI Director Andrej Karpathy discussed the key differences between the map-based approach of Waymo and Tesla’s camera-based strategy. According to Karpathy, Waymo’s use of pre-mapped data and LiDAR make scaling difficult, since vehicles’ autonomous capabilities are practically tied to a geofenced area. Tesla’s vision-based approach, which uses cameras and artificial intelligence, is not. This means that Autopilot and FSD improvements can be rolled out to the fleet, and they would function anywhere.
This rather ambitious plan for Tesla’s full self-driving system has caught a lot of skepticism in the past, with critics pointing out that map-based FSD is the way to go. Tesla, in response, dug its heels in and doubled down on its vision-based initiative. This, in a way, resulted in Autopilot improvements and the rollout of FSD features taking a lot of time, particularly since training the neural networks, which recognize objects and driving behavior on the road, requires massive amounts of real-world data.

Elon Musk’s SpaceX has applied to offer high-speed internet to Canadians living in remote areas by beaming it to them via satellites.
The Globe and Mail newspaper first reported that space exploration company SpaceX applied with Canada’s telecom regulator, the Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC), for what’s known as a Basic International Telecommunications Services, or BITS, licence.

The rule of awkward silence is simple: When faced with a challenging question, instead of answering, you pause and think deeply about how you want to answer.
But make no mistake, this is no short pause. You might go five, 10, or even 15 seconds before offering a response. Which, if you’re not used to doing it, will feel very awkward—at first.
Garrett Reisman, an engineer and former astronaut who left NASA to join SpaceX, described how Musk uses this technique in a recent interview.
SpaceX software team members who helped “develop and deploy software that flew” the Crew Dragon capsule used to launch NASA astronauts into orbit in May, held a Reddit “Ask Me Anything” session on June 6. They answered questions about how to land a job at Elon Musk’s rocket company.
