For makers, 3D printed circuit boards are no longer a mere dream. 3D printers. which can do DIY PCB printing, will become commercially available soon.
The making of DIY circuit boards is a complex task. First, you’ll have to plan the PCB, make a 2D print of the layout, cut a copper plate, transfer the PCB layout to the copper plate, iron the circuit, go through the process of etching, cleaning, disposing… and after some hours of manual labor, you should be ready.
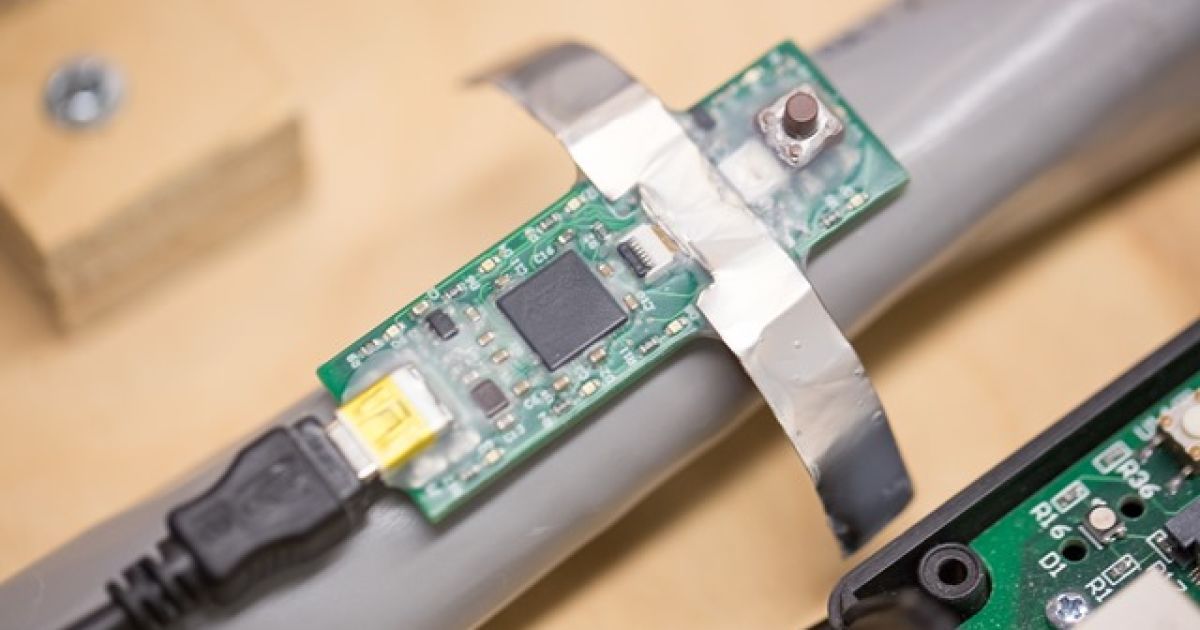
There must be a way to do this more efficiently, right? Wouldn’t a 3D printer be perfect for that job? Fortunately, the first PCB 3D printers will become available soon. Currently, these machines are able to 3D print electronics.