At CES, LG Display is showing off a 65-inch concept TV that can bend at the edges, allowing it to switch from a flat-screen display to a curved one in about five seconds. The company also put a bendable OLED on a foldable tablet/laptop.
Category: electronics – Page 73
The Tech That Will Invade Our Lives in 2020
In 2020 and the coming decade, these trends are likely to gather momentum. They will also be on display next week at CES, an enormous consumer electronics trade show in Las Vegas that typically serves as a window into the year’s hottest tech developments.
From smart homes to ultrafast wireless speeds, here’s what to watch.

AirTV Mini adds Prime Video to the Android TV dongle
AirTV Mini is one of the few dongles using Google’s Android TV platform and now, the product has been updated to support Amazon Prime Video.

Watch SpaceX launch a Boeing-built satellite and attempt to recover its spacecraft fairing live
SpaceX is launching yet another rocket this evening — its 13th this year. This Falcon 9 launch is set for liftoff sometime during a window that’ll last for just over an hour, and that opens at 7:10 PM EST (4:10 PM PST) and extends to 8:38 PM EST (5:38 PM PST). The launch will use a first-stage rocket booster that previously flew in May and July of this year, and it’ll include an attempted landing of that booster, as well as a try at recovering both halves of the fairing used to protect the spacecraft’s cargo as it ascends to space.
The cargo itself is a satellite built by Boeing that hosts two payloads for different clients, including Japanese pay TV broadcast service provider SKY Perfect JSAT, and a high-speed broadband connectivity satellite developed by Kratos called Kacific1. The Falcon 9 spacecraft will be looking to deliver these to orbit around half-an-hour after liftoff.
It’s definitely going to be worth watching the secondary mission elements of this one, as SpaceX has so far succeeded only in recovering one half of a fairing used during a mission with a single barge stationed in the ocean. This will see it try to catch both pieces, using two ships named “Ms. Tree” and “Ms. Chief” that have been retrofitted with a large net assembly specifically for the purpose.

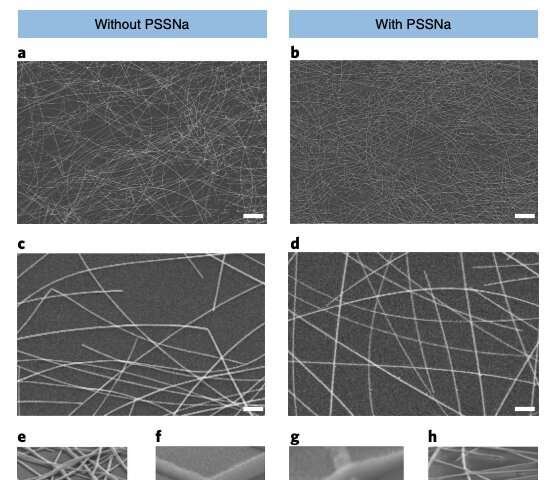
Flexible organic electrodes built using water-processed silver nanowires
Organic electronic devices, which are made of small molecules or polymers (i.e., substances composed primarily or completely of similar units bound together) are known to have several advantageous properties. In fact, organic electronics have relatively low production costs, they are easy to integrate with other systems and they enable good device flexibility.
Despite their advantages, most organic optoelectronics devices do not perform as well as devices built on rigid substrates. This is primarily due to the lack of existing flexible electrodes that can simultaneously provide low resistance, high transparency and smooth surfaces.
With this in mind, researchers at Nankai University in China have recently set out to create new organic electrodes for flexible photovoltaics, devices that can be used to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. The electrodes they developed, presented in a paper published in Nature Electronics, were built using water-processed silver nanowires and a polyelectrolyte.
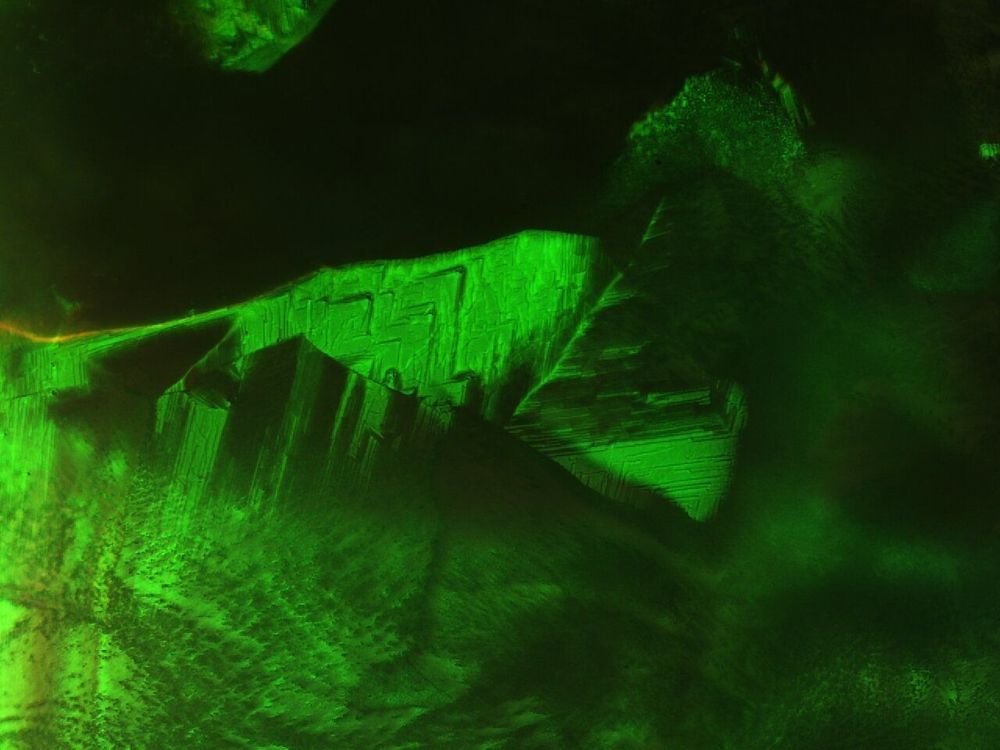
New photonic liquid crystals could lead to next-generation displays
A new technique to change the structure of liquid crystals could lead to the development of fast-responding liquid crystals suitable for next generation displays—3D, augmented and virtual reality—and advanced photonic applications such as mirrorless lasers, bio-sensors and fast/slow light generation, according to an international team of researchers from Penn State, the Air Force Research Laboratory and the National Sun Yat-sen University, Taiwan.
“The liquid crystals we are working with are called blue-phase liquid crystals,” said Iam Choon Khoo, the William E. Leonhard Professor of Electrical Engineering, who is the corresponding author for this article. “The most important thing about this research is the fundamental understanding of what happens when you apply a field, which has led to the development of Repetitively-Applied Field technique. We believe that this method is almost a universal template that can be used for reconfiguring many similar types of liquid crystals and soft matter.”
Blue-phase liquid crystals typically self-assemble into a cubic photonic-crystal structure. The researchers believed that by creating other structures they could develop properties not present in the current form. After nearly two years of experimentation, they realized that by applying an intermittent electrical field and allowing the system to relax between applications and to dissipate accumulated heat, they could slowly coax the crystals into stable and field-free orthorhombic and tetragonal structures.
Spaceflight and Rocket Lab will put a Japanese shooting-star satellite into orbit
Seattle-based Spaceflight says it’s handling the pre-launch logistics for a Japanese satellite that’s designed to spray artificial shooting stars into the sky.
Tokyo-based ALE’s spacecraft is just one of seven satellites due to be sent into orbit from New Zealand as early as Nov. 25, aboard a Rocket Lab Electron launch vehicle.
It’ll be the 10th Electron launch, earning the nickname “Running Out of Fingers.” It’ll also be the first launch to test the guidance and navigation hardware as well as the sensors that Rocket Lab will eventually use to help make the Electron’s first stage recoverable.