A NIMS research team has developed the world’s first n-channel diamond MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor). The developed n-channel diamond MOSFET provides a key step toward CMOS (complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor: one of the most popular technologies in the computer chip) integrated circuits for harsh-environment-applications as well as the development of diamond power electronics.
This research was published in Advanced Science (“High-temperature and high-electron mobility metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors based on n-type diamond”).
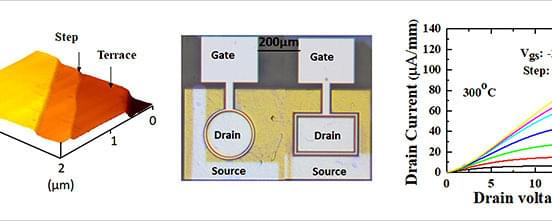
World’s First N-Channel Diamond Field-Effect Transistor: (Left) Atomic force microscope image of diamond epilayer surface morphology. (Middle) Optical microscope image of the diamond MOSFET. (Right) Performance of the MOSFET measured at 300 °C. The drain current increased when the gate voltage (Vg) was increased from −20 V (indicated by a black line) to 10 V (indicated by a yellow line). (Image: NIMS)