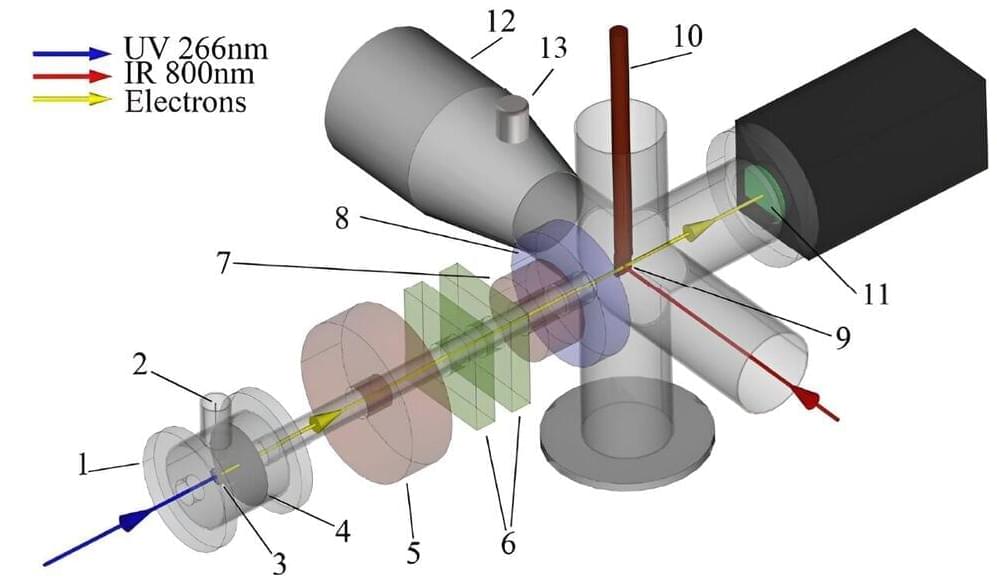
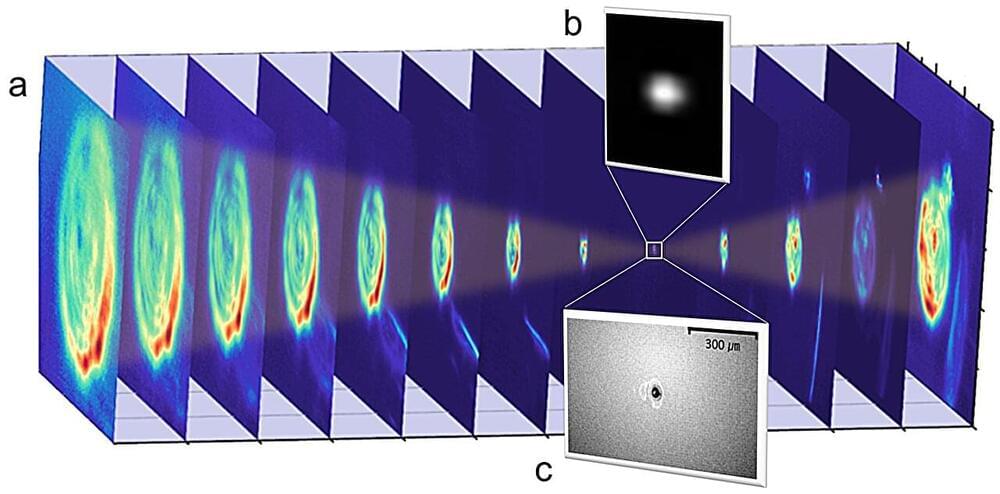
Lying between the microwave and infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, the terahertz (1 THz = 10¹² Hz) gap is being rapidly closed by development of new terahertz sources and detectors, with promising applications in spectroscopy, imaging, sensing, and communication.
These applications greatly benefit from terahertz sources delivering high-energy or high-average-power radiation. On the other hand, high-intensity or strong-field terahertz sources are essential to observe or exploit novel nonlinear terahertz-matter interactions, where the electric and/or magnetic field strengths play a key role.
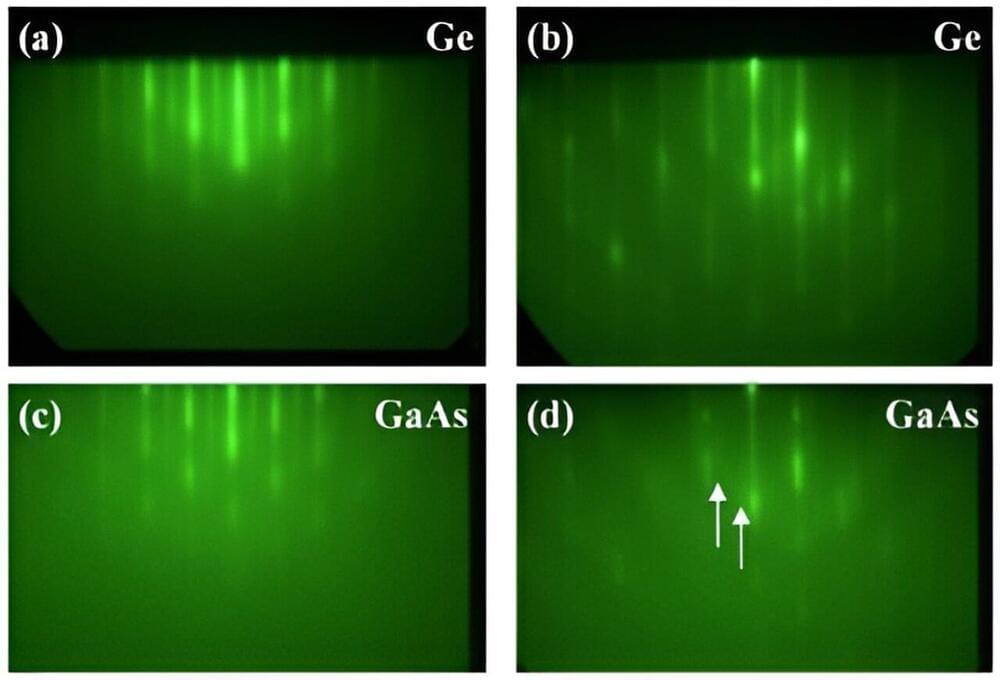
The team of scientists, led by Dr. Chul Kang from Advanced Photonics Research Institute, Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST), Korea, and Professor Ki-Yong Kim from Institute for Research in Electronics and Applied Physics, University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland, U.S., has created the world’s strongest terahertz fields of 260 megavolts per centimeter (MV/cm) or equivalent peak intensity of 9 × 10¹³ watts per square centimeter (W/cm²).