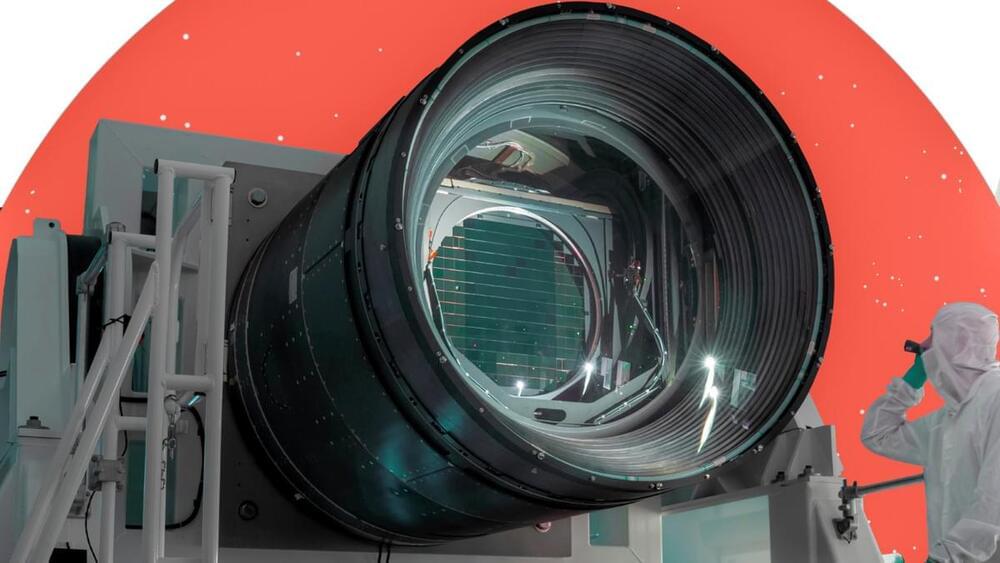
Resolve specializes in detecting “soft” X-rays, a form of light with energies 5,000 times greater than visible light. This allows it to pierce through the veil and observe the universe’s most violent and energetic phenomena: supermassive black holes, sprawling galaxy clusters, and the fiery aftermath of supernovae.
However, these 36 pixels are far from ordinary. They function as a “microcalorimeter spectrometer,” explains Brian Williams, NASA’s XRISM project scientist. Each pixel acts like a miniature thermometer, meticulously measuring the temperature change caused by an incoming X-ray. This seemingly simple act reveals a wealth of information.