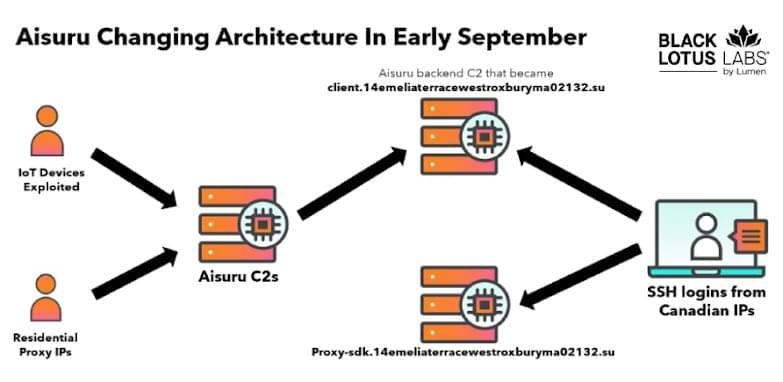
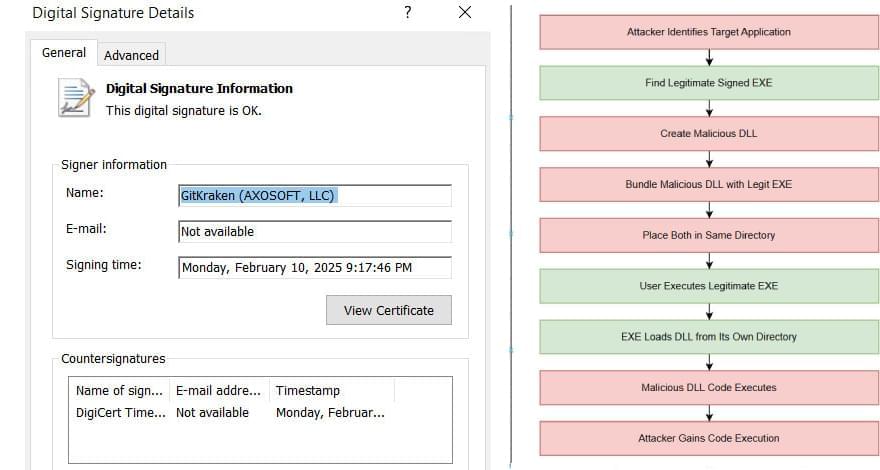
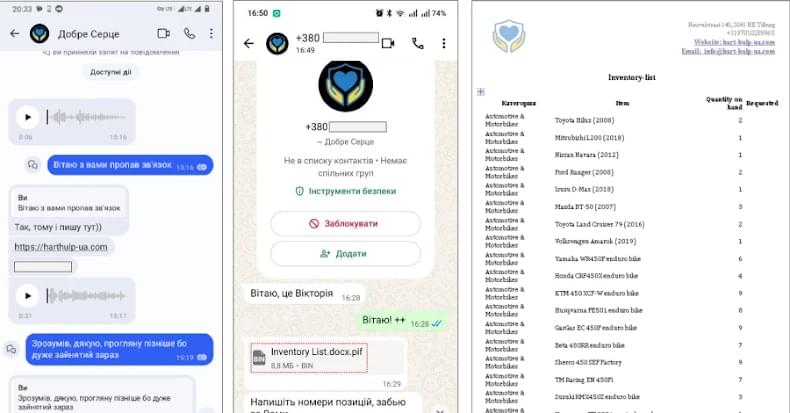
Security experts have disclosed details of a new campaign that has targeted U.S. government and policy entities using politically themed lures to deliver a backdoor known as LOTUSLITE.
The targeted malware campaign leverages decoys related to the recent geopolitical developments between the U.S. and Venezuela to distribute a ZIP archive (“US now deciding what’s next for Venezuela.zip”) containing a malicious DLL that’s launched using DLL side-loading techniques. It’s not known if the campaign managed to successfully compromise any of the targets.
The activity has been attributed with moderate confidence to a Chinese state-sponsored group known as Mustang Panda (aka Earth Pret, HoneyMyte, and Twill Typhoon), citing tactical and infrastructure patterns. It’s worth noting that the threat actor is known for extensively relying on DLL side-loading to launch its backdoors, including TONESHELL.