Novice hacker Coquettte exposed through OPSEC failure using Proton66 to distribute malware and illicit content via fake antivirus sites.



A maximum severity remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability has been discovered impacting all versions of Apache Parquet up to and including 1.15.0.
The problem stems from the deserialization of untrusted data that could allow attackers with specially crafted Parquet files to gain control of target systems, exfiltrate or modify data, disrupt services, or introduce dangerous payloads such as ransomware.
The vulnerability is tracked under CVE-2025–30065 and has a CVSS v4 score of 10.0. The flaw was fixed with the release of Apache version 1.15.1.

The Hunters International Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) operation is shutting down and rebranding with plans to switch to date theft and extortion-only attacks.
As threat intelligence firm Group-IB revealed this week, the cybercrime group remained active despite announcing on November 17, 2024, that it was shutting down due to declining profitability and increased government scrutiny.
Since then, Hunters International has launched a new extortion-only operation known as “World Leaks” on January 1, 2025.



An Arlington-based venture capital firm has announced it will pour $32 million in funding into cybersecurity startups.
Runtime Ventures, based out of Arlington and Austin, Texas, officially announced the capital commitment today (Wednesday).
It has already made 11 investments from the fund so far, supporting seed-stage cybersecurity companies focused on domains including code analysis, fraud protection, threat detection and browser security.

When your social media account starts spewing out nonsensical or threatening status updates, it’s safe to assume that it has been hacked and must be shut down.
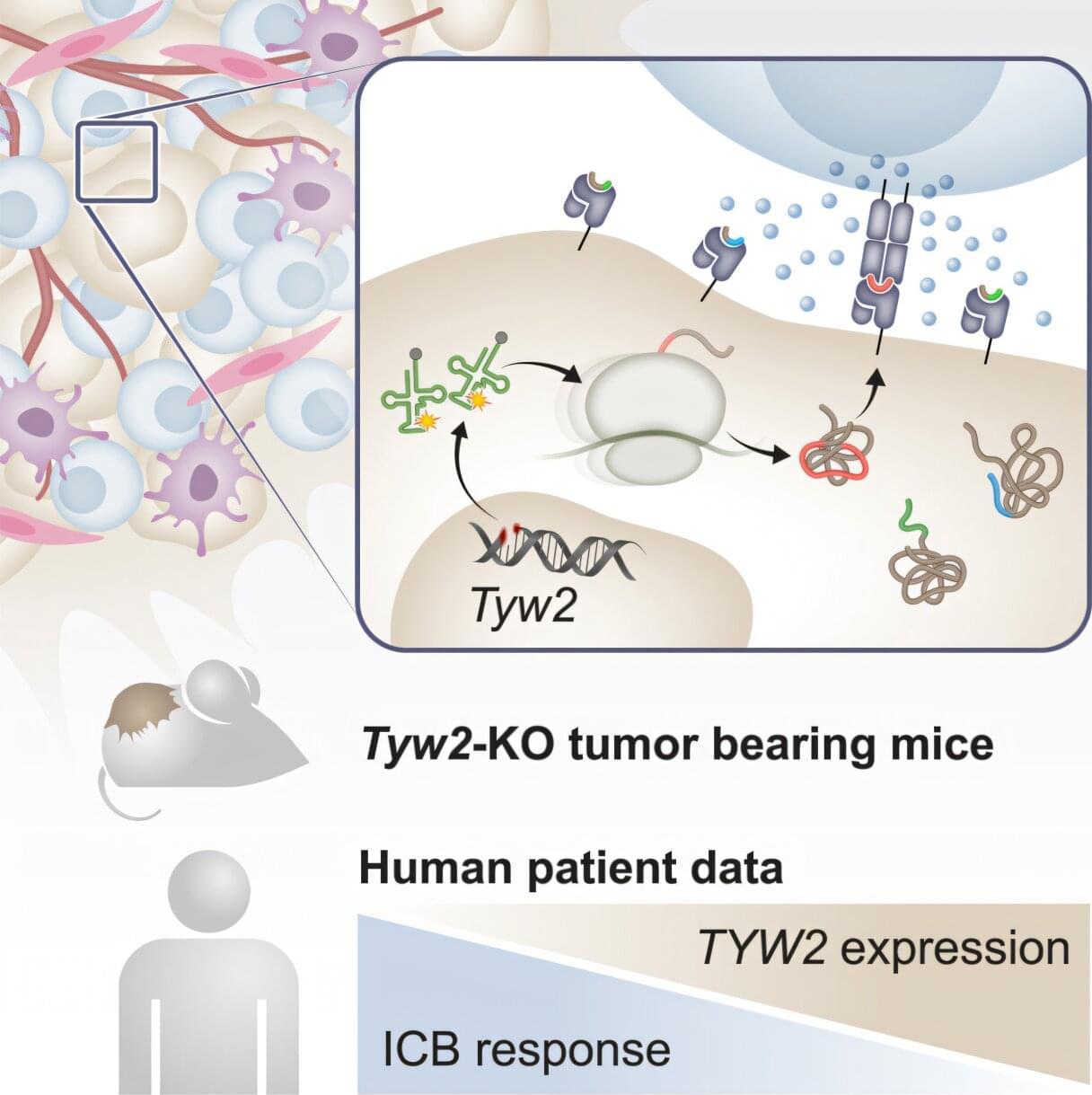
The cells in our body also update their “status” by presenting to their environment small proteins that are constantly being produced inside the cell. Our immune system monitors these statuses and destroys cells that produce unusual proteins. A classic example of this is when a cell is infected by a virus and presents parts of the viral proteins on its surface, which allows the immune system to recognize them and destroy the cell.
In contrast, cancer cells often evade detection by displaying very few suspicious proteins that the immune system can identify and target. A new approach to cancer treatment, developed by researchers from Prof. Yardena Samuels’s lab at the Weizmann Institute of Science, increases the number of the immune system’s targets by disrupting protein production in cancerous cells.
