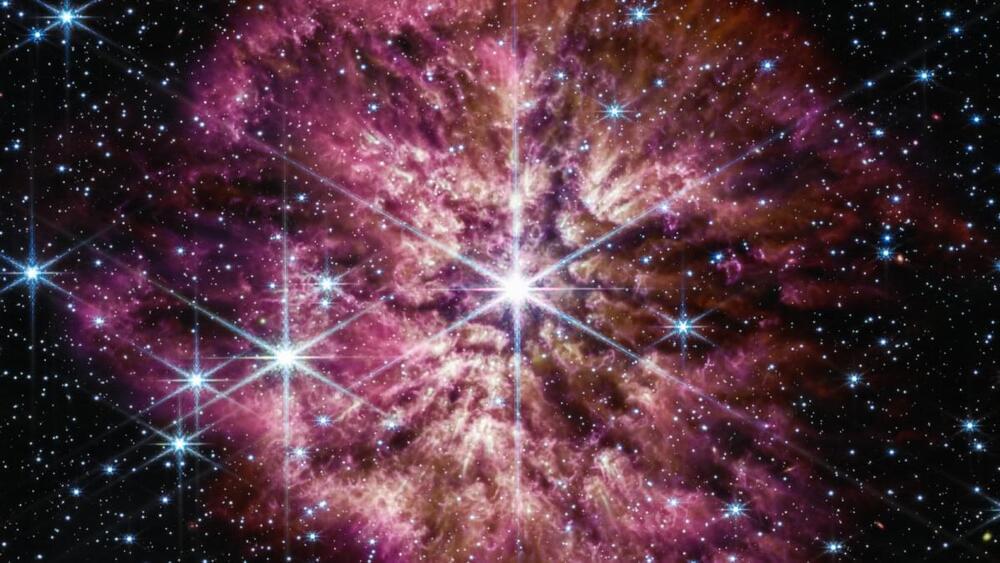
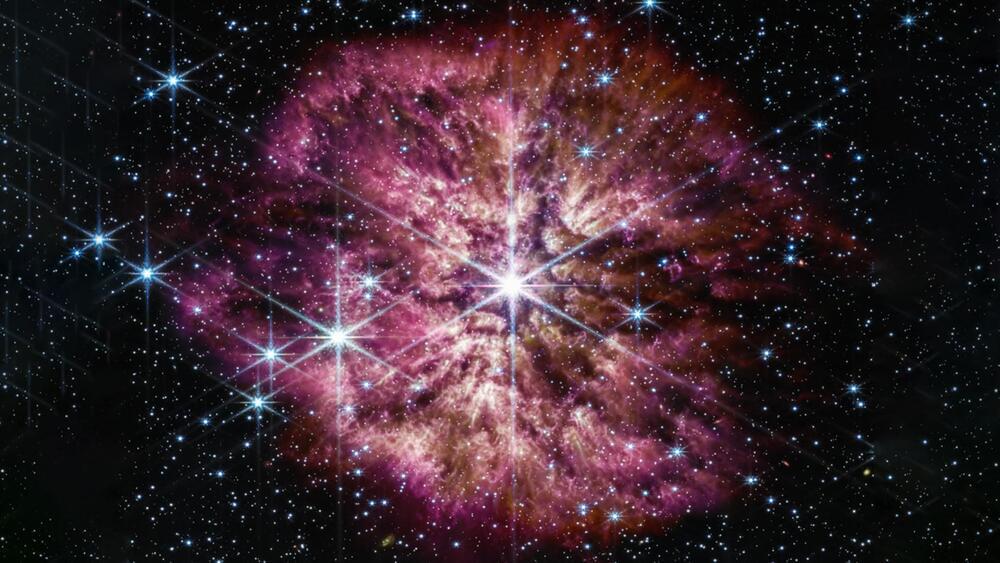
Called a Wolf-Rayet, these stars expel most of their outer layers into their surroundings before exploding as supernovae.
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has released a phenomenal image of a supernova waiting to happen. Called a Wolf-Rayet, these stars are among the most massive, luminous, and “briefly detectable” stars known. They’re at an advanced stage of stellar evolution and expel most of their outer layers into their surroundings before exploding as supernovae.
Webb had a rare sighting of a Wolf-Rayet star in June 2022. In the latest image, the telescope shows the star, WR 124, in unprecedented detail, thanks to its infrared instruments.
NASA, ESA, CSA, stsci, webb ERO production team.
Not all stars go through a brief Wolf-Rayet phase before evolving into a supernova, which is why astronomers think Webb has captured a rare phase. This particular star is 30 times the mass of the Sun and has shed 10 Suns’ worth of material – so far. According to a release, as the ejected gas moves away from the star and cools, cosmic dust forms and glows in the infrared light detectable by Webb.