The coders of tomorrow may be bug-checking the multiverse.


Not long ago, your parents might’ve noticed a kid staring at a smartphone in their front yard. There wasn’t anything there. The kid was just…hanging out. What they didn’t know? Said kid was gazing through a digital window and seeing a mythical beast in their well-manicured roses.
This youngster was playing an augmented reality smartphone sensation called Pokémon Go that swept the online masses before fading back. But don’t confuse ephemerality for significance. Pokémon Go’s simple yet viral appeal suggests AR is going to be huge.
“The reason I’m inspired by this? I don’t think Pokemon Go is the pinnacle of AR. It’s kind of like the Solitaire for Windows 3. It’s a killer app at a certain time, a big milestone,” John Werner said at Singularity University’s Exponential Manufacturing Summit in Boston.
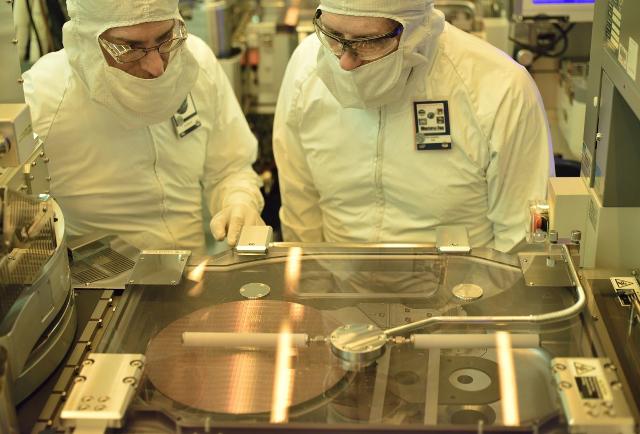
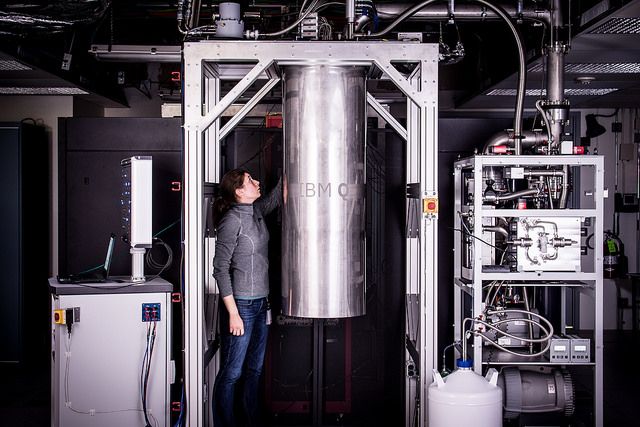


IBM announced today it has successfully built and tested its most powerful universal quantum computing processors. The first new prototype processor will be the core for the first IBM Q early-access commercial systems. The first upgraded processor will be available for use by developers, researchers, and programmers to explore quantum computing using a real quantum processor at no cost via the IBM Cloud. The second is a new prototype of a commercial processor, which will be the core for the first IBM Q early-access commercial systems.
Launched in March 2017, IBM Q is an industry-first initiative to build commercially available universal quantum computing systems for business and science applications. IBM Q systems and services will be delivered via the IBM Cloud platform. IBM first opened public access to its quantum processors one year ago, to serve as an enablement tool for scientific research, a resource for university classrooms, and a catalyst of enthusiasm for the field. To date users have run more than 300,000 quantum experiments on the IBM Cloud.
With the introduction of two new processors today for IBM Q, the company is building the foundation for solving practical problems in business and science that are intractable even with today’s most powerful classical computing systems. The two new IBM-developed processors include:

TAMPA, Fla., May 16, 2017 /PRNewswire/ — Their demanding missions often require soldiers to carry heavy equipment packs long distances over rough terrain, or up and down stairs and underground infrastructure in urban environments. Exhaustion and injury are frequently a consequence of these challenging operational scenarios. A new exoskeleton from Lockheed Martin (NYSE: LMT) offers a solution.
Using licensed DermoskeletonTM bionic augmentation technology, the FORTIS Knee Stress Release Device (K-SRD)TM is a computer-controlled exoskeleton that counteracts overstress on the lower back and legs and increases mobility and load-carrying capability. It boosts leg capacity for physically demanding tasks that require repetitive or continuous kneeling or squatting, or lifting, dragging, carrying or climbing with heavy loads.
What does a prototype computer with 160 terabytes of memory have to do with missions to Mars? The way Kirk Bresniker sees it, a giant leap in computing is required for the giant leap to the Red Planet.
“That’s actually what we need to wrap around that crew,” Bresniker, chief architect at Hewlett Packard Labs, told GeekWire.
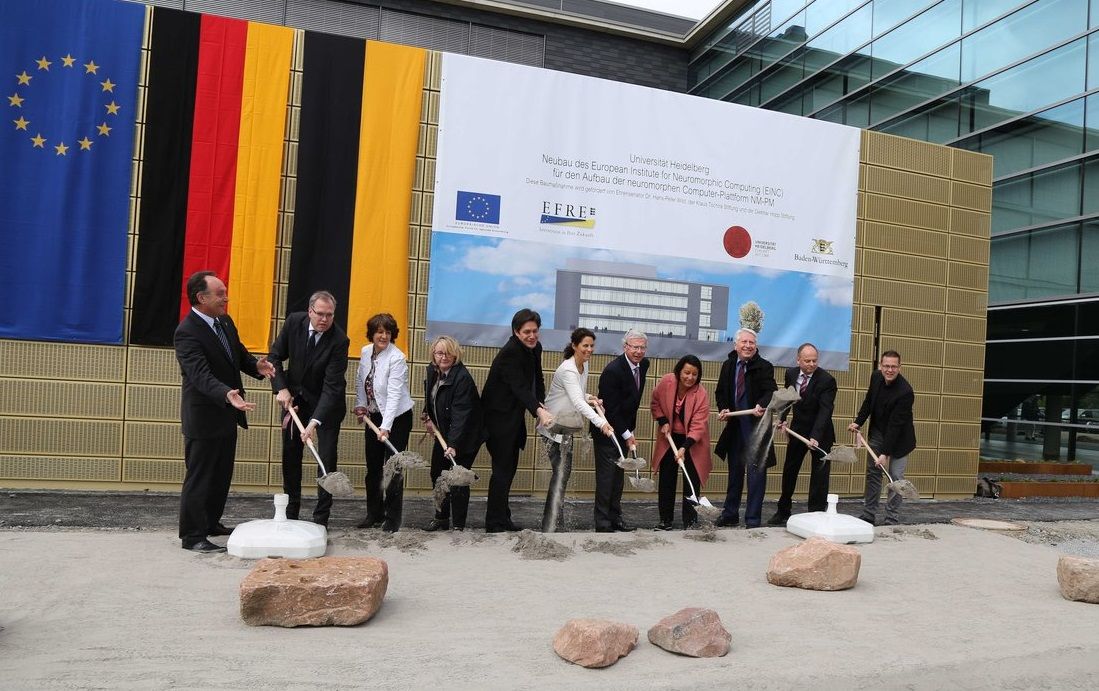

On 5th of May, the cornerstone for the construction of a neuromorphic computing facility in Europe was laid at the University of Heidelberg in Germany. With the financial support of the European Union and German public and private institutions, the new building will house leading European researchers working on neuromorphic computing within the Human Brain Project, a FET Flagship of the European Commission.
With this new facility the research team from Heidelberg University, led by Prof. Dr. Karlheinz Meier, will benefit from an optimal environment to continue working on the neuromorphic computing platform, which they are developing together with other research groups within the Human Brain Project.


Quantum computers finally seem to be coming of age with promises of “quantum supremacy” by the end of the year. But there’s a problem—very few people know how to work them.
The bold claim of achieving “quantum supremacy” came on the back of Google unveiling a new quantum chip design. The hyperbolic phrase essentially means building a quantum device that can perform a calculation impossible for any conventional computer.
In theory, quantum computers can crush conventional ones at important tasks like factoring large numbers. That’s because unlike normal computers, whose bits can either be represented as 0 or 1, a quantum bit—or “qubit”—can be simultaneously 0 and 1 thanks to a phenomenon known as superposition.