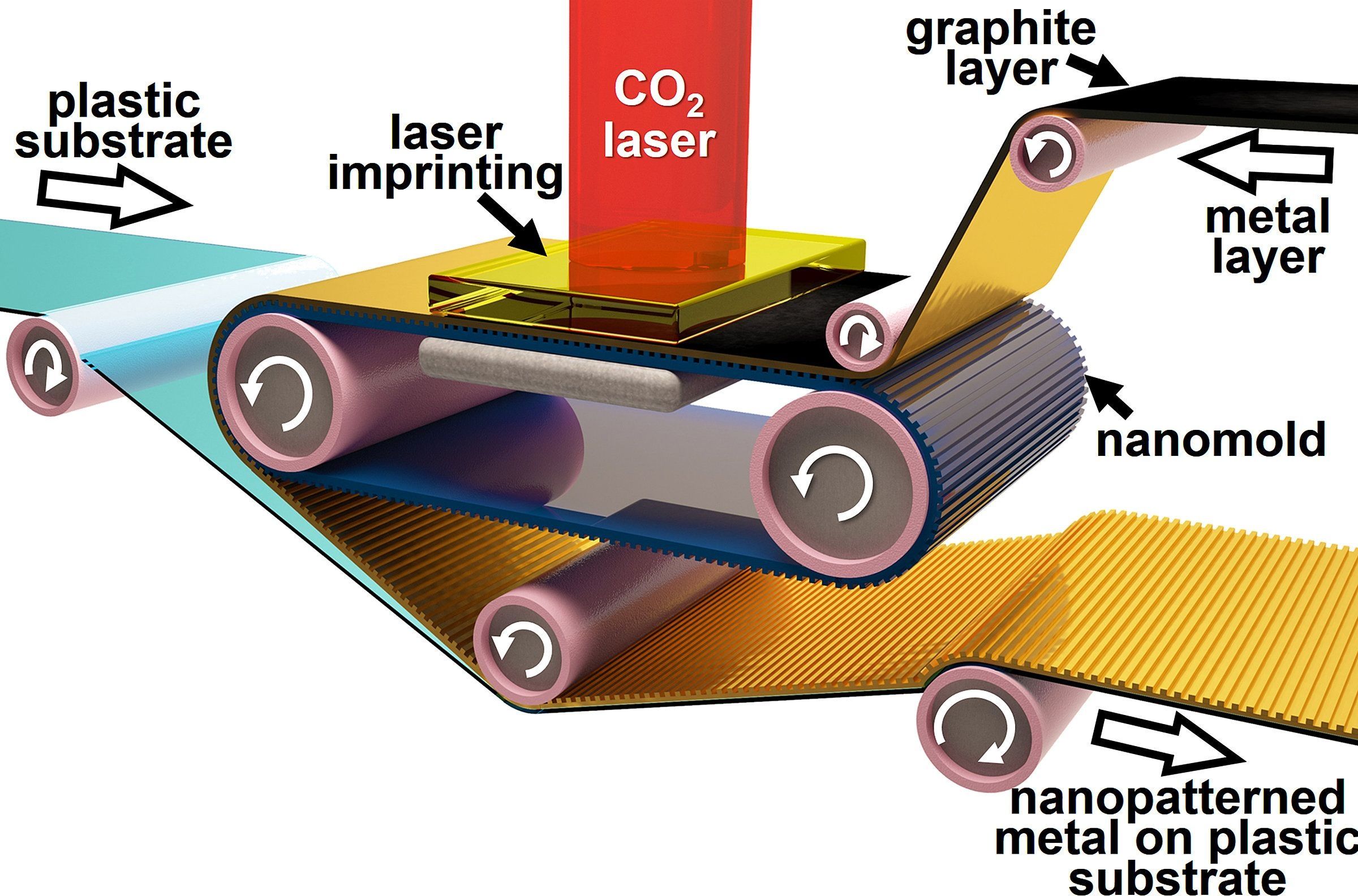
A new manufacturing technique uses a process similar to newspaper printing to form smoother and more flexible metals for making ultrafast electronic devices.
The low-cost process, developed by Purdue University researchers, combines tools already used in industry for manufacturing metals on a large scale, but uses the speed and precision of roll-to-roll newspaper printing to remove a couple of fabrication barriers in making electronics faster than they are today.
Cellphones, laptops, tablets, and many other electronics rely on their internal metallic circuits to process information at high speed. Current metal fabrication techniques tend to make these circuits by getting a thin rain of liquid metal drops to pass through a stencil mask in the shape of a circuit, kind of like spraying graffiti on walls.