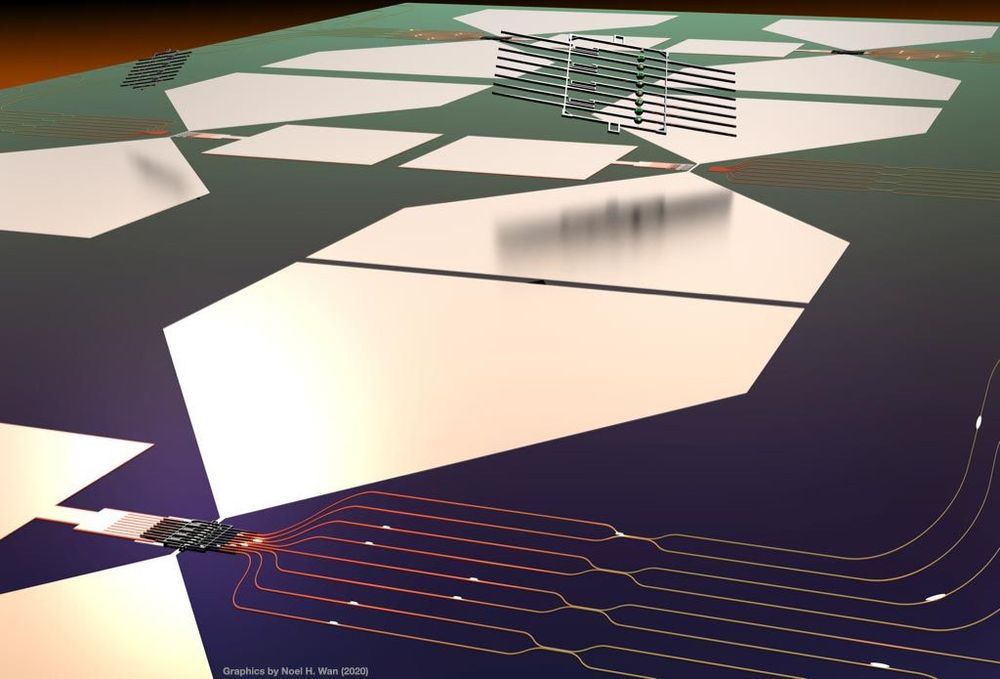
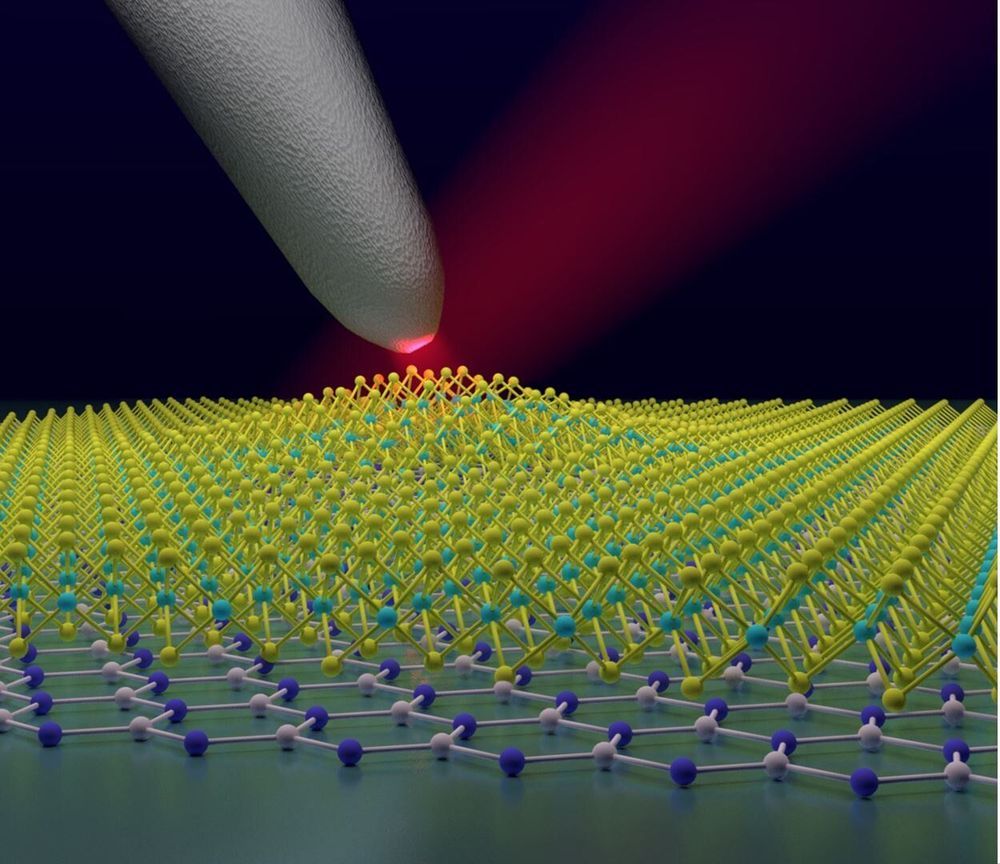
July 13, 2020—Researchers at Columbia Engineering and Montana State University report today that they have found that placing sufficient strain in a 2-D material—tungsten diselenide (WSe2)—creates localized states that can yield single-photon emitters. Using sophisticated optical microscopy techniques developed at Columbia over the past three years, the team was able to directly image these states for the first time, revealing that even at room temperature they are highly tunable and act as quantum dots, tightly confined pieces of semiconductors that emit light.
“Our discovery is very exciting, because it means we can now position a single-photon emitter wherever we want, and tune its properties, such as the color of the emitted photon, simply by bending or straining the material at a specific location,” says James Schuck, associate professor of mechanical engineering, who co-led the study published today by Nature Nanotechnology. “Knowing just where and how to tune the single-photon emitter is essential to creating quantum optical circuitry for use in quantum computers, or even in so-called ‘quantum’ simulators that mimic physical phenomena far too complex to model with today’s computers.”
Developing quantum technologies such as quantum computers and quantum sensors is a rapidly developing field of research as researchers figure out how to use the unique properties of quantum physics to create devices that can be much more efficient, faster, and more sensitive than existing technologies. For instance, quantum information—think encrypted messages—would be much more secure.