Caption :
New research from MIT suggests that a certain type of computer vision model that is trained to be robust to imperceptible noise added to image data encodes visual representations similarly to the way humans do using peripheral vision.



Circa 2021
Small, affordable, ‘plug-and-play’ quantum computing is one step closer. An Australian startup has won $13 million to make its diamond-based computing cores shine. Now it needs to grow.
ANU research spinoff Quantum Brilliance has found a way to use synthetic diamonds to drive quantum calculations. Now it’s on a five-year quest to produce commercially viable Quantum Accelerators. The goal is a card capable of being plugged into any existing computer system similar to the way graphics cards are now.
“We’re not deluding ourselves,” says CEO Dr Andrew Horsley. “There’s still a lot of work to do. But we’ve now got a five-year pathway to produce a lunchbox-sized device”.
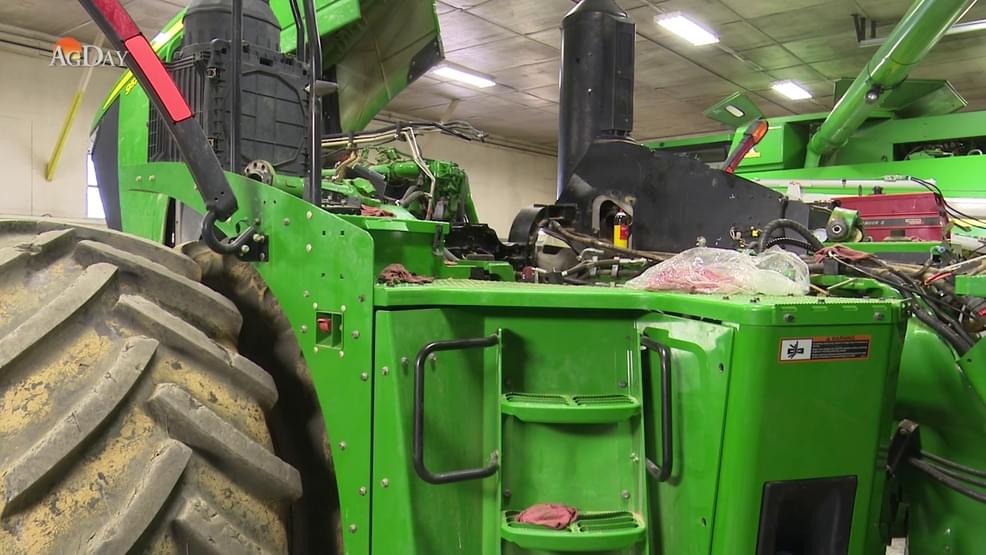

These days, new tractors and combines are more like big computers, and require special tools to repair them. Farmers say they’re having to travel farther and pay more to fix them to make sure their harvest schedules stay on track. Jim Birge grew up farming in central Illinois and is now the Manager of the Sangamon County Farm Bureau in Springfield. He describes how new tractors and combines have gone high-tech, and farmers no longer have access to the tools to fix them.
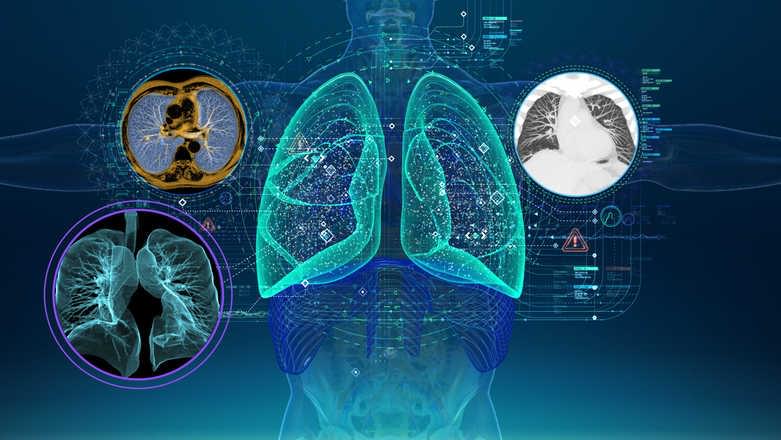
While advancements in healthcare have come in leaps and bounds since the 20th century, there is perhaps none more exciting than what digital twin technology could offer. The healthcare industry has the potential to be revolutionized by this application of new advancements, which will ultimately lead to improved research capabilities and patient outcomes.
Defined as the virtual representation of a physical object or system across its life cycle, a digital twin is a computer program that uses real world data to create simulations that can predict the outcomes of a product or process. A concept initially utilized by NASA in the 1960s, this technology has grown exponentially in the last decade, now further expanding into the world of healthcare.
Beginning in 2014 with The Living Heart Project headed by Dassault Systémes, healthcare research with digital twins has broadened to include organs such as the brain and lungs, as well as projects for virtual parts of the body. With these models, doctors have the potential to discover undeveloped illnesses, experiment with treatments, and improve surgical outcomes. They allow clinicians to test multiple treatments across a vast range of therapies, equipment, and interventions by comparing possible outcomes without taking any risks in terms of patient safety. Ultimately, care can become more precise, targeted, and based on the most accurate data available when digital twins are utilized.

We all know Linux is written in C. What you may not know is that it’s written in a long-outdated C dialect: The 1989 version of the C language standard, C89. This is also known as ANSI X3.159‑1989, or ANSI C. Linus Torvalds has decided that enough is enough and will move Linux’s official C to 2011’s C11 standard.
The Linux kernel’s foundation is the ancient C89 standard of C. Now, Torvalds has decided to upgrade to 2011’s more modern C11 standard.

Often, reprogramming a microcontroller involves placing it in reset, flashing the code, and letting it fire back up. It usually involves shutting the chip down entirely. However, [bor0] has built a virtual machine that runs on the ESP32, allowing for dynamic program updates to happen.
The code is inspired by the CHIP-8, a relatively ancient interpreter that had some gaming applications. [bor0] had already created a VM simulating the CHIP-8, and repurposed it here, taking out the gaming-related drawing instructions and replacing them with those that control IO pins. Registers have also been changed to 16 bits for added flexibility and headroom.
It’s probably not something with immediate ground-breaking applications for most people, but it’s a different way of working with and programming the ESP32, and that’s pretty neat.
A silicon wasteland.
In a sign that the United States government’s export restrictions on semiconductor sales to Russia due to its war against Ukraine have been enacted swiftly, multiple reports have emerged today that both Intel and AMD have suspended chip sales to Russia. In addition, reports have also emerged that TSMC’s decision to participate in the sanctions will thwart Russia’s supply of homegrown chips. We have reached out to Intel, AMD, and Nvidia for comment.
The Russian media outlets also claim that the suspensions have been confirmed by the Association of Russian Developers and Electronics Manufacturers (ARPE). Additionally, Chinese IT companies are said to have been notified by Intel that sales to Russia have been banned.
The extent of the halted sales is currently unclear. The new export restrictions are primarily aimed at chips for military purposes or dual-use chips that could be used for both civilian and military purposes. That means sales of most consumer-focused chips, like AMD’s Ryzen and Intel’s Core chips, likely won’t be impacted. However, it is widely expected that there will be a temporary halt for all semiconductor sales to Russia as companies work to decide which products are impacted. Additionally, the US DoC has added 49 Russian companies to the Entity List, and those companies aren’t eligible to purchase any type of chip.

The late 90s and early 2000s were a breakout time for mobile phones, with cheap GSM handsets ushering in the era in which pretty much everybody had a phone. Back then, a popular way to customize one’s phone was to install a sticker that would flash when the phone rang. These required no batteries or any other connection to the phone, and [Big Clive] has dived in to explain how they worked.
It’s an old-fashioned teardown that requires a bit of cutting to get inside the sticker itself. A typical example had three LEDs in series for a total voltage drop of around 7V, hooked up to two diodes and a PCB trace antenna. A later evolution used raw unpackaged components bonded to the PCB. Future versions went down to a single diode, using the LEDs to serve as the second. The basic theory was that the PCB traces would pick up RF transmitted by the phone when a call was coming in, lighting the LEDs.
In the 2G era, the freuqencies used were on the order of 300 MHz to 1.9GHz. A combination of the change in frequencies used by modern phone technology and the lower transmit powers used by handsets means that the stickers don’t work properly with modern phones according to [Big Clive].