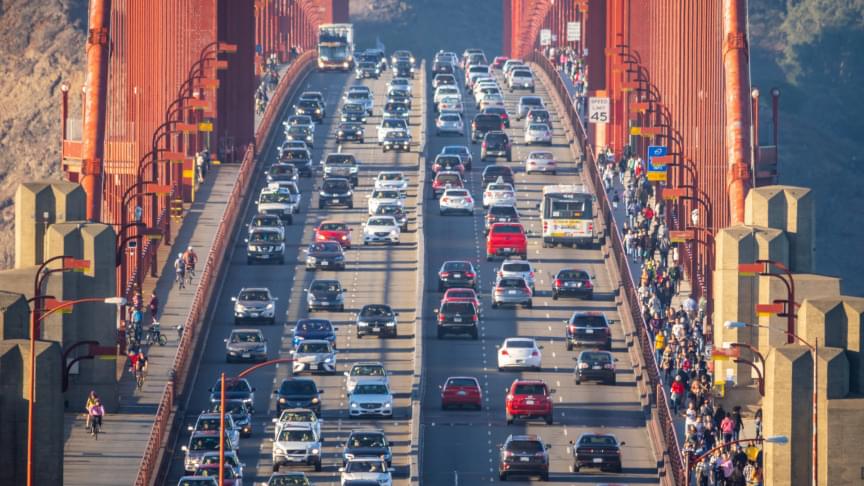
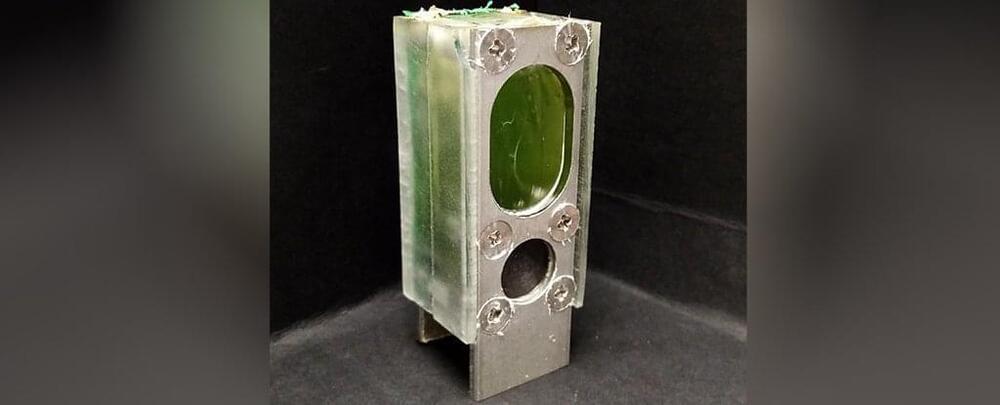
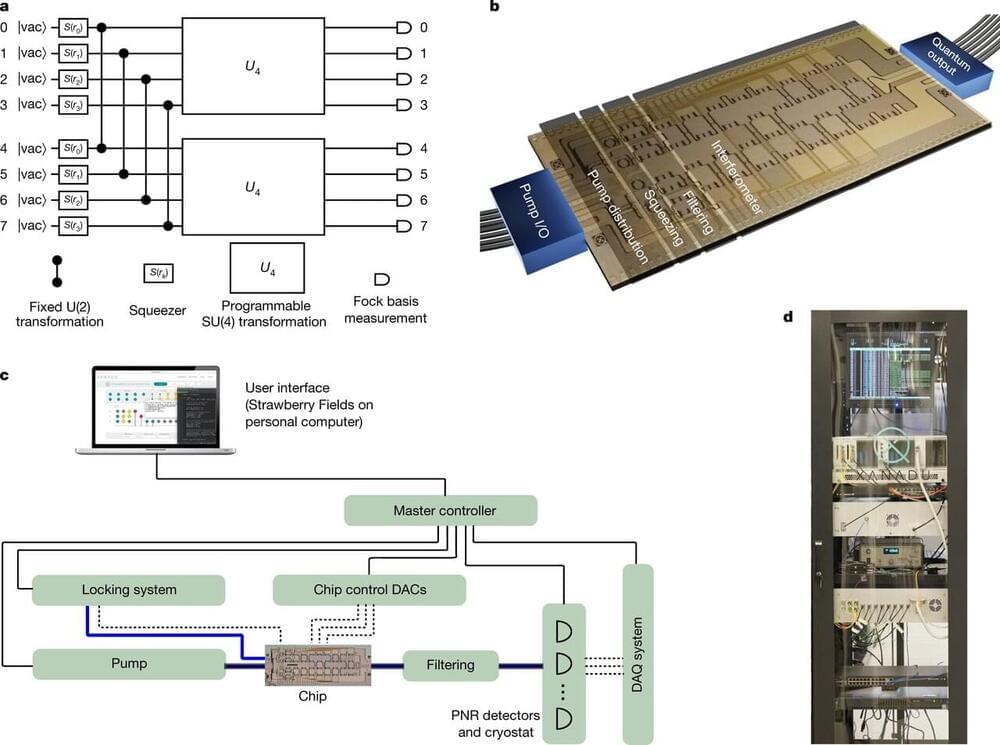
A team of researchers and engineers at Canadian company Xanadu Quantum Technologies Inc., working with the National Institute of Standards and Technology in the U.S., has developed a programmable, scalable photonic quantum chip that can execute multiple algorithms. In their paper published in the journal Nature, the group describes how they made their chip, its characteristics and how it can be used. Ulrik Andersen with the Technical University of Denmark has published a News & Views piece in the same journal issue outlining current research on quantum computers and the work by the team in Canada.
Scientists around the world are working to build a truly useful quantum computer that can perform calculations that would take traditional computers millions of years to carry out. To date, most such efforts have been focused on two main architectures—those based on superconducting electrical circuits and those based on trapped-ion technology. Both have their advantages and disadvantages, and both must operate in a supercooled environment, making them difficult to scale up. Receiving less attention is work using a photonics-based approach to building a quantum computer. Such an approach has been seen as less feasible because of the problems inherent in generating quantum states and also of transforming such states on demand. One big advantage photonics-based systems would have over the other two architectures is that they would not have to be chilled—they could work at room temperature.
In this new effort, the group at Xanadu has overcome some of the problems associated with photonics-based systems and created a working programmable photonic quantum chip that can execute multiple algorithms and can also be scaled up. They have named it the X8 photonic quantum processing unit. During operation, the chip is connected to what the team at Xanadu describe as a “squeezed light” source—infrared laser pulses working with microscopic resonators. This is because the new system performs continuous variable quantum computing rather than using single-photon generators.