Virginia Tech researchers are exploring quantum applications to improve communications systems, bring new methods for securing data, make devices more energy efficient, and make computers smaller.



From TVs, to solar cells, to cutting-edge cancer treatments, quantum dots are beginning to exhibit their unique potential in many fields, but manufacturing them at scale would raise some issues concerning the environment. Scientists at Japan’s Hiroshima University have demonstrated a greener path forward in this area, by using discarded rice husks to produce the world’s first silicon quantum dot LED light.
“Since typical quantum dots often involve toxic material, such as cadmium, lead, or other heavy metals, environmental concerns have been frequently deliberated when using nanomaterials,” said Ken-ichi Saitow, lead study author and a professor of chemistry at Hiroshima University. “Our proposed process and fabrication method for quantum dots minimizes these concerns.”
The type of quantum dots pursued by Saitow and his team are silicon quantum dots, which eschew heavy metals and offer some other benefits, too. Their stability and higher operating temperatures makes them one of the leading candidates for use in quantum computing, while their non-toxic nature also makes them suitable for use in medical applications.
Engineering is often inspired by nature—the hooks in velcro or dermal denticles in sharkskin swimsuits. Then there’s DARPA’s SyNAPSE, a collaboration of researchers at IBM, XX, and XX universities. Not content with current computer architecture, SyNAPSE takes its cues from the human brain.
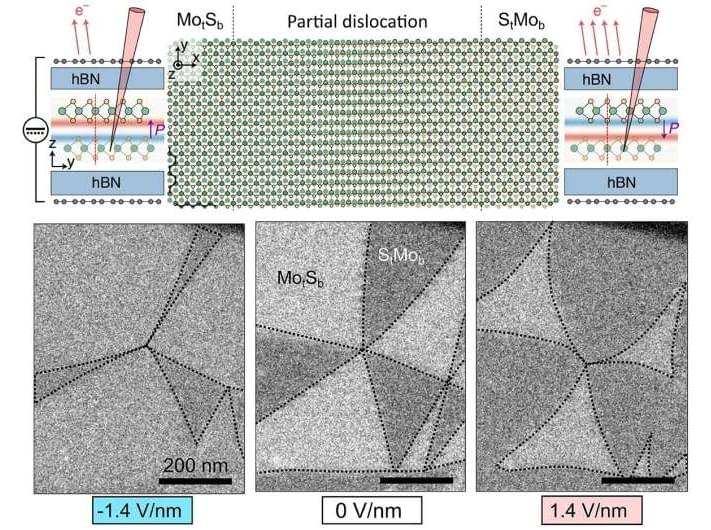
A team of researchers at The University of Manchester’s National Graphene Institute (NGI) and the National Physical Laboratory (NPL) has demonstrated that slightly twisted 2D transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) display room-temperature ferroelectricity.
This characteristic, combined with TMDs’ outstanding optical properties, can be used to build multi-functional optoelectronic devices such as transistors and LEDs with built-in memory functions on nanometre length scale.
Ferroelectrics are materials with two or more electrically polarisable states that can be reversibly switched with the application of an external electric field. This material property is ideal for applications such as non-volatile memory, microwave devices, sensors and transistors. Until recently, out-of-plane switchable ferroelectricity at room temperature had been achieved only in films thicker than 3 nanometres.
There’s a key aspect of quantum computing you may not have thought about before. Called ‘quantum non-demolition measurements’, they refer to observing certain quantum states without destroying them in the process.
If we want to put together a functioning quantum computer, not having it break down every second while calculations are made would obviously be helpful. Now, scientists have described a new technique for recording quantum non-demolition measurements that shows a lot of promise.
In this case, the research involved mechanical quantum systems – objects that are relatively large in quantum computing terms, but exceedingly tiny for us. They use mechanical motion (such as vibration) to handle the necessary quantum magic, and they can be combined with other quantum systems too.
Cutting-edge computer technology designed to mimic the human brain is being used by hackers to create lifelike videos of celebrities and politicians. But now, bad actors are using this readily available tech to target everyday social media users in cryptocurrency scams.
Networks (connectivity) and dynamics are two key pillars of network neuroscience – an emerging field dedicated to understanding structure and function of neural systems across scales, from neurons to circuits to the whole brain. In this presentation I will review current themes and future directions, including structure/function relationships, use of computational models to map information flow and communication dynamics, and a novel edge-centric approach to map functional connectivity at fine temporal scales. I will argue that network neuroscience represents a promising theoretical framework for understanding the complex structure and functioning of nervous systems.
This video is part of the SNAC seminar series organized by Mac Shine, Joe Lizier, and Ben Fulcher (The University of Sydney).
Simulating complex scientific models on the computer or processing large volumes of data such as editing video material takes considerable computing power and time. Researchers from the Chair of Laser Physics at Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU) and a team from the University of Rochester in New York have demonstrated how the speed of fundamental computing operations could be increased in the future to up to a million times faster using laser pulses. Their findings were published on May 11, 2022, in the journal Nature.
The computing speed of today’s computer and smartphone processors is given by field-effect transistors. In the competition to produce faster devices, the size of these transistors is constantly decreased to fit as many together as possible onto chips. Modern computers already operate at the breathtaking speed of several gigahertz, which translates to several billion computing operations per second. The latest transistors measure only 5 nanometers (0.000005 millimeters) in size, the equivalent of not much more than a few atoms. There are limits to how far chip manufacturers can go and at a certain point, it won’t be possible to make transistors any smaller.
Physicists are working hard to control electronics with light waves. The oscillation of a light wave takes approximately one femtosecond, which is one-millionth of one billionth of a second. Controlling electrical signals with light could make the computers of the future over a million times faster, which is the aim of petahertz signal processing or light wave electronics.
A “forever battery” is much smaller and more energy-dense than lithium-ion. They’ll change the world and unlock a trillion-dollar revolution.
In this week’s episode, Aaron and I discuss what could be the “holy grail” of energy: the solid-state — or forever battery. Obviously, lithium-ion cells are the status quo of today. And they power pretty much everything, like your smartphone, laptop and electric vehicle.
However, since they comprise liquids and can only be compressed so much, they aren’t the most energy-dense. And we see this limitation all around us. It’s why that EV in your parking space can’t drive long ranges or recharge very fast. And it’s why that smartphone in your pocket will run out of juice by the end of the day.
The truth about the EV Revolution that’s got everyone hyped is that it won’t boom until we make better batteries. Enter solid-state battery technology — much smaller, more effective and energy-dense than its liquid-state counterparts. This “forever battery,” as insiders have dubbed it, will fundamentally alter the way things work in society. And it’ll unlock a potentially multi-trillion-dollar revolution in the process.
