A new proposal suggests using stem cell-derived ‘minibrains’ to create brand-new biocomputers. Such ‘organoid computers’ could be far off, but ethical questions abound.

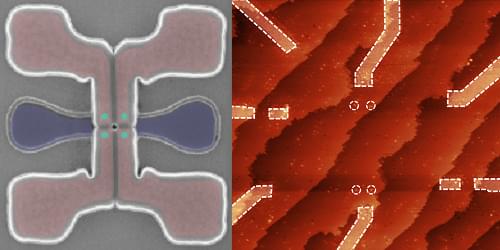
Heat causes errors in the qubits that are the building blocks of a quantum computer, so quantum systems are typically kept inside refrigerators that keep the temperature just above absolute zero (−459 degrees Fahrenheit).
But quantum computers need to communicate with electronics outside the refrigerator, in a room-temperature environment. The metal cables that connect these electronics bring heat into the refrigerator, which has to work even harder and draw extra power to keep the system cold. Plus, more qubits require more cables, so the size of a quantum system is limited by how much heat the fridge can remove.
To overcome this challenge, an interdisciplinary team of MIT researchers has developed a wireless communication system that enables a quantum computer to send and receive data to and from electronics outside the refrigerator using high-speed terahertz waves.

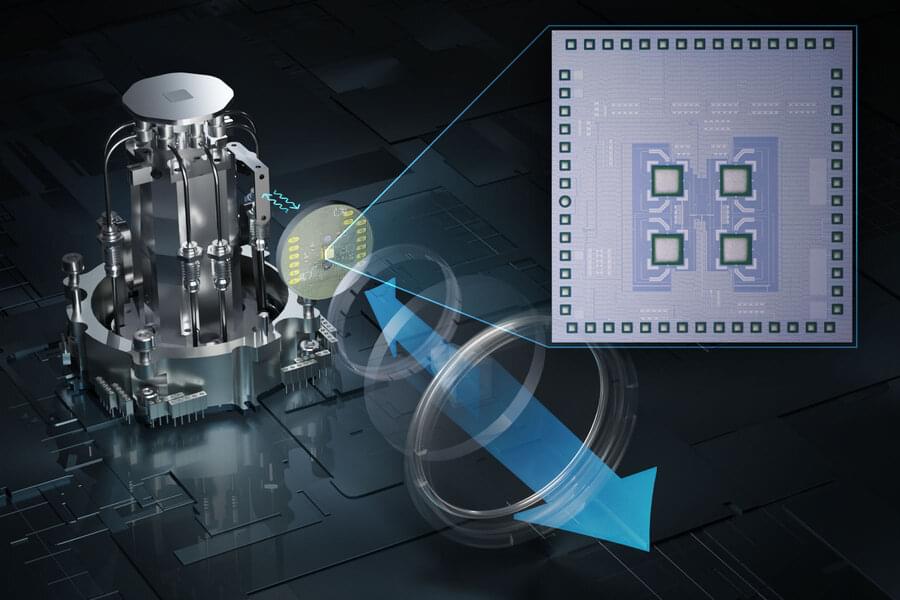
Google scientists said Wednesday they have passed a major milestone in their quest to develop effective quantum computing, with a new study showing they reduced the rate of errors – long an obstacle for the much-hyped technology.
Quantum computing has been touted as a revolutionary advance that uses our growing scientific understanding of the subatomic world to create a machine with powers far beyond those of today’s conventional computers.
However, the technology remains largely theoretical, with many thorny problems still standing in the way – including stubbornly high error rates.
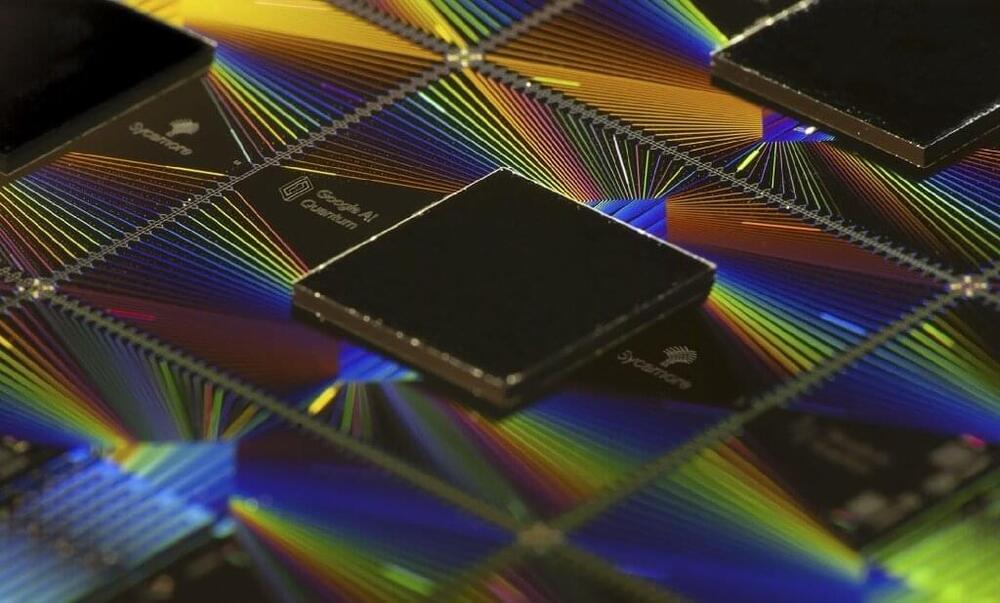

Google scientists said Wednesday they have passed a major milestone in their quest to develop effective quantum computing, with a new study showing they reduced the rate of errors—long an obstacle for the much-hyped technology.
Quantum computing has been touted as a revolutionary advance that uses our growing scientific understanding of the subatomic world to create a machine with powers far beyond those of today’s conventional computers.
However the technology remains largely theoretical, with many thorny problems still standing in the way—including stubbornly high error rates.
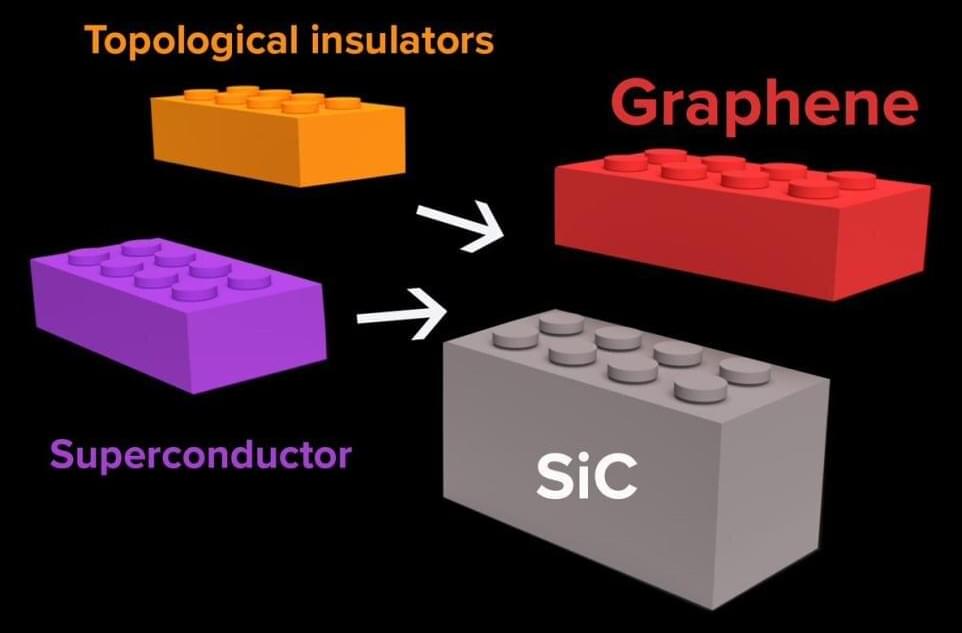
A new form of heterostructure of layered two-dimensional (2D) materials may enable quantum computing to overcome key barriers to its widespread application, according to an international team of researchers.
The researchers were led by a team that is part of the Penn State Center for Nanoscale Science (CNS), one of 19 Materials Research Science and Engineering Centers (MRSEC) in the United States funded by the National Science Foundation. Their work was published Feb. 13 in Nature Materials.
A regular computer consists of billions of transistors, known as bits, and are governed by binary code (“0” = off and “1” = on). A quantum bit, also known as a qubit, is based on quantum mechanics and can be both a “0” and a “1” at the same time. This is known as superposition and can enable quantum computers to be more powerful than the regular, classical computers.
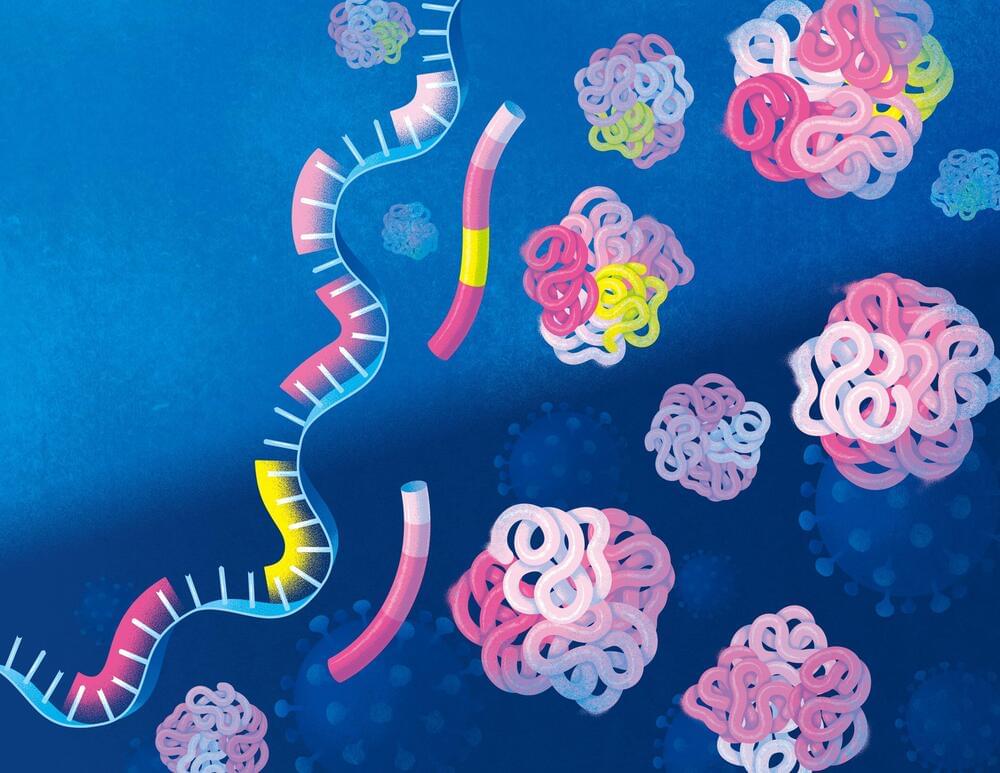
Most existing COVID-19 tests “rely on the same principle, which is that you have accumulated a detectable amount of viral material, for example, in your nose,” says study lead author Frank Zhang, who worked on the project as a Flatiron research fellow at the Flatiron Institute’s Center for Computational Biology (CCB) in New York City. “That poses a challenge when it’s early in the infection time window and you haven’t accumulated a lot of viral material, or you’re asymptomatic.”
The new technique is instead based on how our bodies mount an immune response when invaded by SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. When the assault starts, specific genes turn on. Segments of those genes produce mRNA molecules that guide the building of proteins. The particular blend of those mRNA molecules changes the types of proteins produced, including proteins involved in virus-fighting functions. The new method can confidently identify when the body is mounting an immune response to the COVID-19 virus by measuring the relative abundance of the various mRNA molecules. The new study is the first to use such an approach to diagnose an infectious disease.


It can boost conductivity by a billion percent.
A collaboration of physicists working at different institutes in the U.S. have discovered a new quantum state in an alloy made of magnesium, silicon, and tellurium, a press release said. The finding could result in applications in quantum computing, such as building sensors and communication systems.
Electrons can move around freely inside the structure.
Vchal/istock.
The alloy is a crystalline structure denoted as Mn3Si2Te6 and consists of octagonal cells placed in a honeycomb-like arrangement when viewed from above. Though, when viewed from the side, it consists of stacked sheets.
Apollo’s successful computing software was optimized to deal with unknown problems and to interrupt one task to take on a more important one.