It is estimated that 95% of the planet’s population has access to broadband internet, via cable or a mobile network. However, there are still some places and situations in which staying connected can be very difficult. Quick responses are necessary in emergency situations, such as after an earthquake or during a conflict. So too are reliable telecommunications networks that are not susceptible to outages and damage to infrastructure, networks can be used to share data that is vital for people’s well-being.
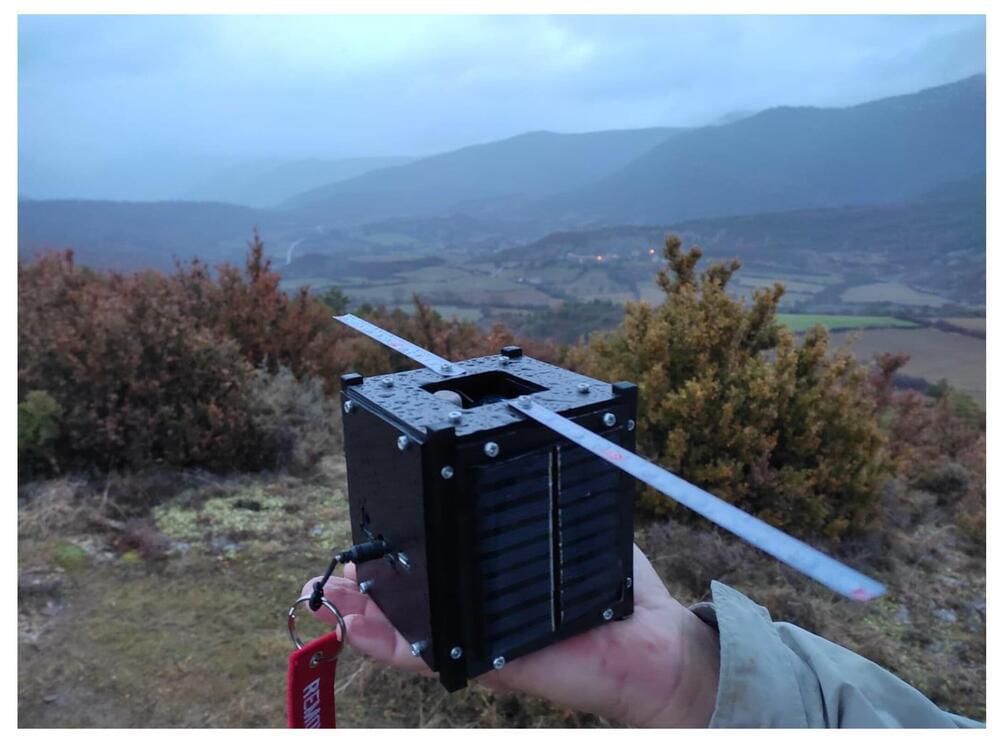
A recent article, published in the journal Aerospace, proposes the use of nanosatellites to provide comprehensive and stable coverage in areas that are hard to reach using long-range communications. It is based on the bachelor’s and master’s degree final projects of Universitat Oberta de Catalunya (UOC) graduate David N. Barraca Ibort.
The paper is co-authored by Raúl Parada, a researcher at the Telecommunications Technological Center of Catalonia (CTTC/CERCA) and a course instructor with the UOC’s Faculty of Computer Science, Multimedia and Telecommunications; Carlos Monzo, a researcher and member of the same faculty; and Víctor Monzón, a researcher at the Interdisciplinary Center for Security Reliability and Trust at the University of Luxembourg.