Hackers use trojanized game installers to spread the StaryDobry XMRig miner, hijacking gaming PCs with 8+ core CPUs.



Rubidium could be the next key player in oxide-ion conductors. Researchers at the Institute of Science Tokyo have discovered a rare rubidium (Rb)-containing oxide-ion conductor, Rb5BiMo4O16, with exceptionally high conductivity.
Identified through computational screening and experiments, its superior performance stems from low activation energy and structural features like large free volume and tetrahedral motion. Its stability under various conditions offers a promising direction for solid oxide fuel cells and clean energy technologies.
Oxide-ion conductors enable oxide ions (O2-) to be transported in solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs), which can run on diverse fuels beyond hydrogen, including natural gas, and biogas, and even certain liquid hydrocarbons. This flexibility makes them particularly valuable during the transition to a hydrogen economy.
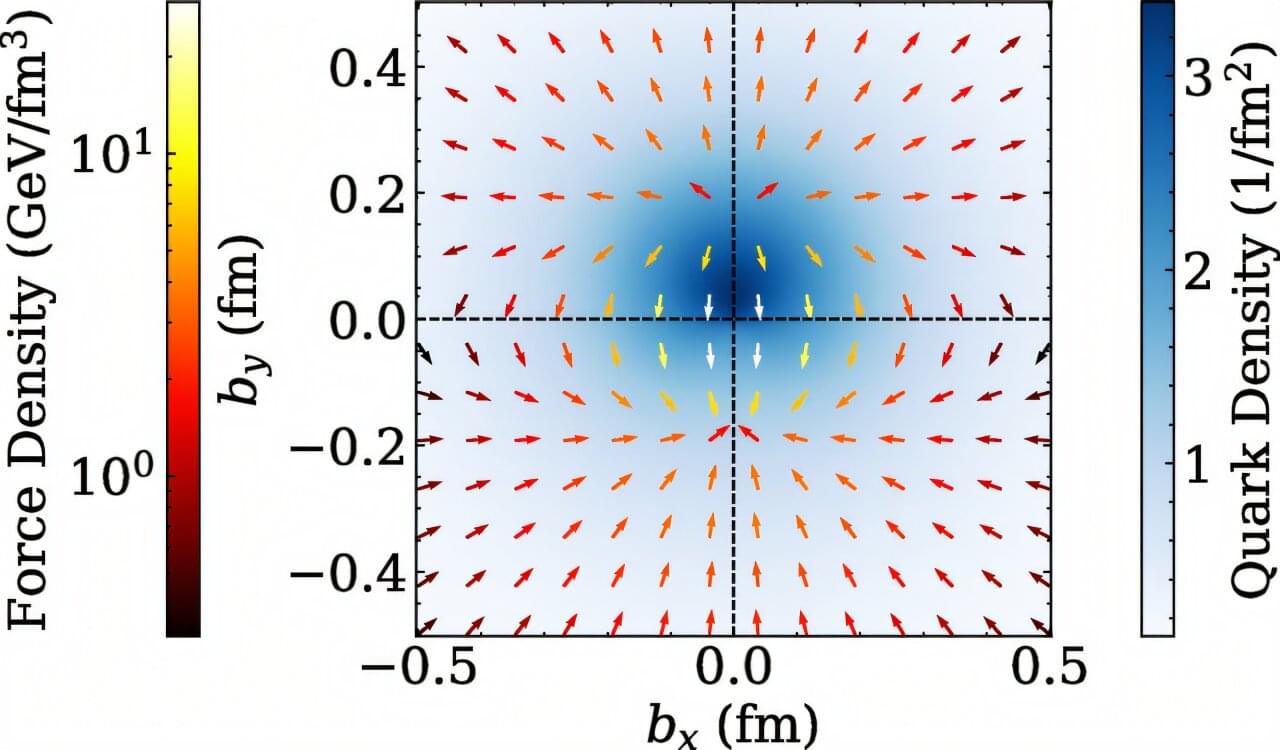
Scientists have now mapped the forces acting inside a proton, showing in unprecedented detail how quarks—the tiny particles within—respond when hit by high-energy photons.
The international team includes experts from the University of Adelaide who are exploring the structure of sub-atomic matter to try and provide further insight into the forces that underpin the natural world.
“We have used a powerful computational technique called lattice quantum chromodynamics to map the forces acting inside a proton,” said Associate Professor Ross Young, Associate Head of Learning and Teaching, School of Physics, Chemistry and Earth Sciences, who is part of the team.

‘Quantum Supremacy’ author Dr. Michio Kaku discusses the future of quantum computing on ‘Making Money.’ #foxbusiness #makingmoney.
Watch more Fox Business Video: https://video.foxbusiness.com.
Watch Fox Business Network Live: http://www.foxnewsgo.com/
FOX Business Network (FBN) is a financial news channel delivering real-time information across all platforms that impact both Main Street and Wall Street. Headquartered in New York — the business capital of the world — FBN launched in October 2007 and is one of the leading business networks on television. In 2025 it opened the year posting double-digit advantages across business day, market hours and total day viewers in January. Additionally, the network continued to lead business news programming, with each business day program placing among the top 15 shows, while FBN delivered its highest-rated month since April 2023 with market hours.
Follow Fox Business on Facebook: / foxbusiness.
Follow Fox Business on Twitter: / foxbusiness.
Follow Fox Business on Instagram: / foxbusiness.
Quantum computing will never be the same again. Join host Konstantinos Karagiannis for a special onsite interview at Microsoft Azure Quantum labs, where he was invited to see the launch of Majorana 1, the world’s first quantum processor powered by topological qubits. On the day this episode is posted, Nature will release a paper validating how Microsoft was able to create a topoconductor, or new material stack of indium arsenide and aluminum, built literally one atom at a time, to bring quantum particles called Majoranas into usable form. The resulting topological qubits have a unique shape called a tetron and can be accurately measured with lower errors than other modalities. Starting with a 4×2 grid of qubits, this same tiny device will hold 1 million qubits in a few years because of its unique system of wiring and measurement. This interview with Chetan Nayak from Microsoft happened a few feet away from a working Majorana 1 system.
For more information on Microsoft Azure Quantum, visit https://quantum.microsoft.com/.
Read the technical blog here: https://aka.ms/MSQuantumAQBlog.
For photos from the Microsoft labs and other links, visit @konstanthacker on X and Instagram.
Visit Protiviti at www.protiviti.com/US-en/technology-consulting/quantum-computing-services to learn more about how Protiviti is helping organizations get post-quantum ready.
Follow host Konstantinos Karagiannis on all socials: @KonstantHacker and follow Protiviti Technology on LinkedIn and Twitter: @ProtivitiTech.
Visit Microsoft Azure Quantum here to learn about quantum computing for free https://quantum.microsoft.com/?ocid=2… https://quantum.microsoft.com/en-us/e… Topological quantum computing is a brand new form of quantum computing being developed by Microsoft as they enter the race to build the world’s first useful quantum computer. In this video I visited Microsoft’s quantum labs to see how they are making their topological quantum computers and learn how topology helps their quantum devices avoid noise by harnessing the power of Majorana quasiparticles which are made from an exotic form of superconductivity where the electrons behave like there is a Majorana particle there which has the special properties of topology.
Get My Posters Here.
For North America visit my DFTBA Store: https://store.dftba.com/collections/d… the rest of the world go to my RedBubble Store: https://www.redbubble.com/people/Domi… I have also made posters available for personal or educational use which you can find here: https://www.flickr.com/photos/9586967… Some Awesome People And many thanks to my $10 supporters and above on Patreon, you are awesome! Join the gang and help support me produce free and high quality science content: / domainofscience Tut Arom Anja Jason Evans machinator rimor Mirik Gogri Eric Epstein Sebastian Theodore Chu My Science Books I also write science books for kids called Professor Astro Cat. You can see them all here: https://flyingeyebooks.com/book/profe… http://profastrocat.com Follow me around the internet http://dominicwalliman.com
/ dominicwalliman
/ dominicwalliman Credits Writer, art, animation and edited by Dominic Walliman I use Adobe Illustrator and After Effects for the graphics (for the many people who ask smile References “InAs-Al hybrid devices passing the topological gap protocol” https://journals.aps.org/prb/abstract… “A cryogenic CMOS chip for generating control signals for multiple qubits” https://www.nature.com/articles/s4192… Topological qubit noise levels — “Assessing requirements to scale to practical quantum advantage” chrome-extension://efaidnbmnnnibpcajpcglclefindmkaj/ https://arxiv.org/pdf/2211.07629 Chapters 00:00 Topological Quantum Computing 02:01 Topology Explained 04:47 Resilience to Noise 05:51 Anatomy of a Quantum Computer 07:05 Chip Fabrication and Lab Tour 09:41 How to Build a Quantum Computer 11:21 Topological Quantum Computing Lego Explainer 15:40 Microsoft’s Results 17:50 Majorana Particle Explained 21:31 Sponsor Message 23:03 Thanks Patrons!
For the rest of the world go to my RedBubble Store: https://www.redbubble.com/people/Domi…
I have also made posters available for personal or educational use which you can find here: https://www.flickr.com/photos/9586967…
Some Awesome People.
And many thanks to my $10 supporters and above on Patreon, you are awesome!
Join the gang and help support me produce free and high quality science content:
/ domainofscience.
Tut Arom.
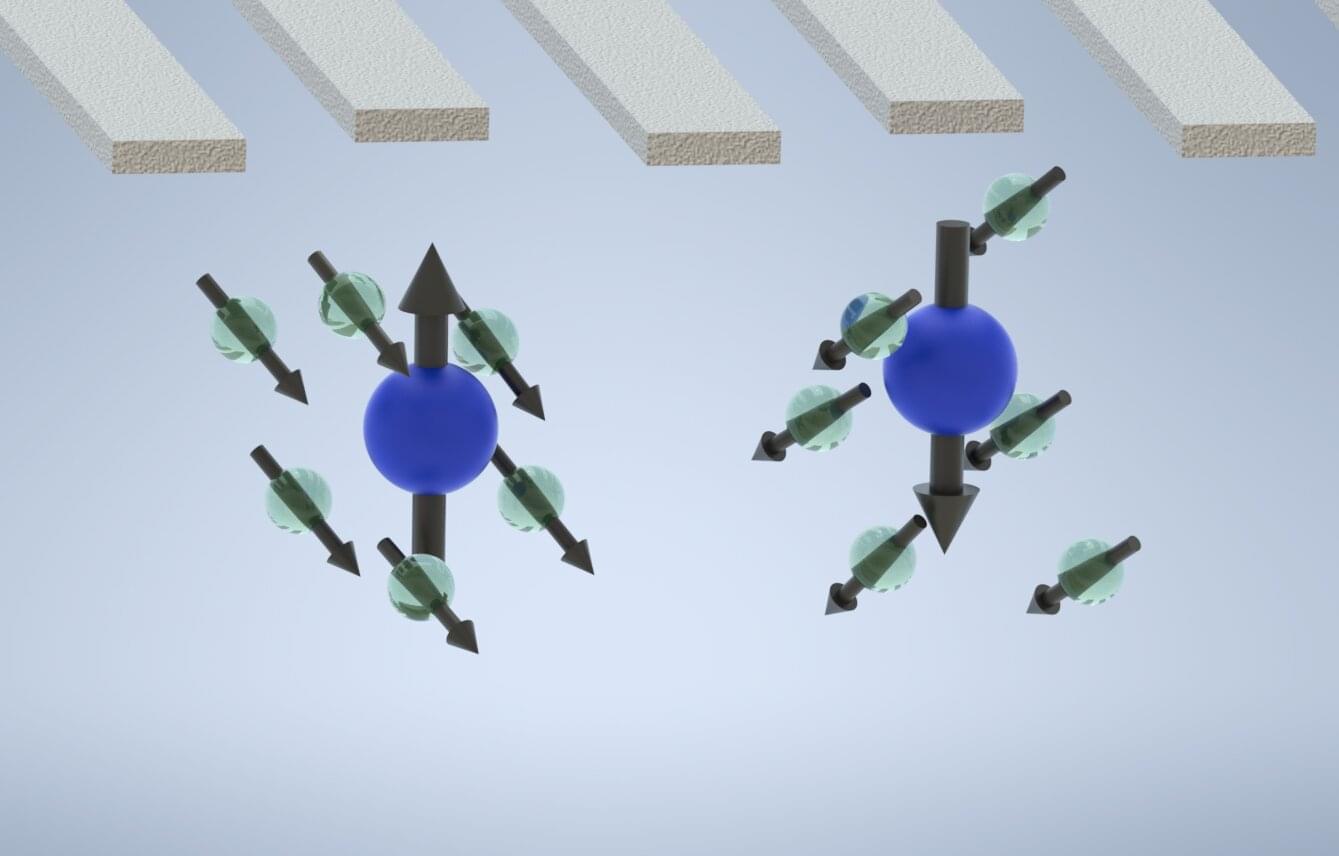
Quantum computers, which operate leveraging quantum mechanics phenomena, could eventually tackle some optimization and computational problems faster and more efficiently than their classical counterparts. Instead of bits, the fundamental units of information in classical computers, quantum computers rely on qubits (quantum bits), which can be in multiple states at once.
Silicon-based quantum dots, semiconductor-based structures that trap individual electrons, have been widely used as qubits, as the spin state of the electrons they confine can be leveraged to encode information. Despite their promise, many quantum computers developed so far are susceptible to decoherence, which entails the disruption of qubit states due to their interaction with the surrounding environment.
Researchers at the University of Rochester recently set out to experimentally realize a so-called nuclear-spin dark state, a condition that has been theorized to improve the performance of quantum computers, suppressing undesirable interactions and thus reducing decoherence. Their paper, published in Nature Physics, demonstrates the potential of this state for reducing decoherence in quantum systems and thus potentially improving control over quantum information processing.

Northwestern University researchers have identified structural features in engineered cell receptors that correlate with variations in receptor function.
Computational protein structure prediction tools were used to analyze a library of synthetic receptors, revealing that specific structural attributes such as ectodomain (ECD) distance and transmembrane domain (TMD) interactions are associated with receptor performance.
Engineered cell therapies rely on synthetic receptors to transduce external signals into intracellular responses. The precise relationship between receptor structure and function remains poorly understood. Advances in protein structure prediction tools, such as AlphaFold and ColabFold, have enabled the modeling of complex proteins, including single-pass transmembrane receptors.
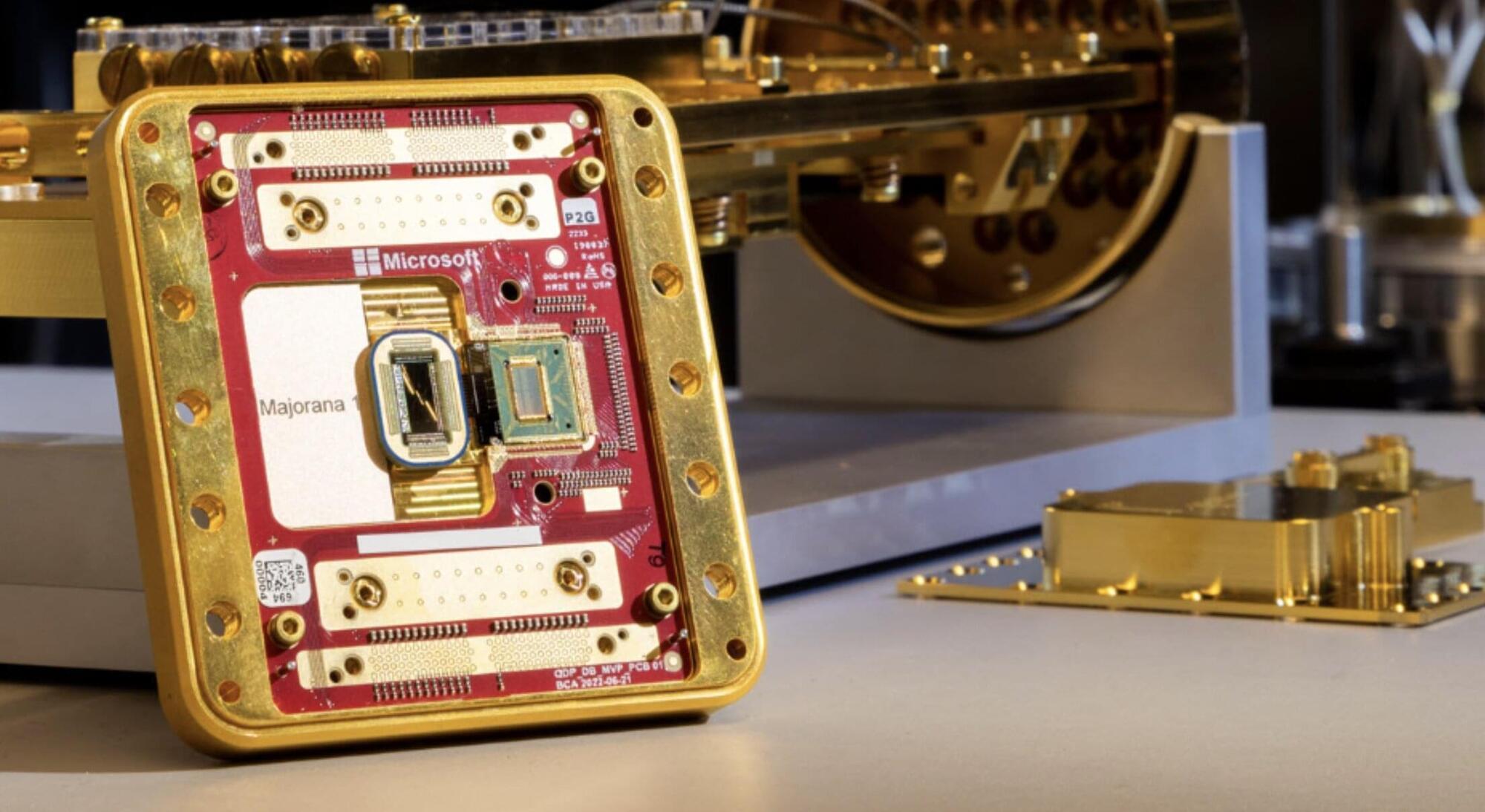
In a leap forward for quantum computing, a Microsoft team led by UC Santa Barbara physicists on Wednesday unveiled an eight-qubit topological quantum processor, the first of its kind. The chip, built as a proof-of-concept for the scientists’ design, opens the door to the development of the long-awaited topological quantum computer.
“We’ve got a bunch of stuff that we’ve been keeping under wraps that we’re dropping all at once now,” said Microsoft Station Q Director Chetan Nayak, a professor of physics at UCSB and a Technical Fellow for Quantum Hardware at Microsoft. The chip was revealed at Station Q’s annual conference in Santa Barbara, and accompanies a paper published in the journal Nature, authored by Station Q, their Microsoft teammates and a host of collaborators that presents the research team’s measurements of these new qubits.
“We have created a new state of matter called a topological superconductor,” Nayak explained. This phase of matter hosts exotic boundaries called Majorana zero modes (MZM) that are useful for quantum computing, he explained. Results of rigorous simulation and testing of their heterostructure devices are consistent with the observation of such states. “It shows that we can do it, do it fast and do it accurately,” he said.