The CL1 biological computer, manufactured by the Australian company Cortical Labs, is designed for biomedical research, but also promises to deliver a more fast-paced and energy-efficient computing system

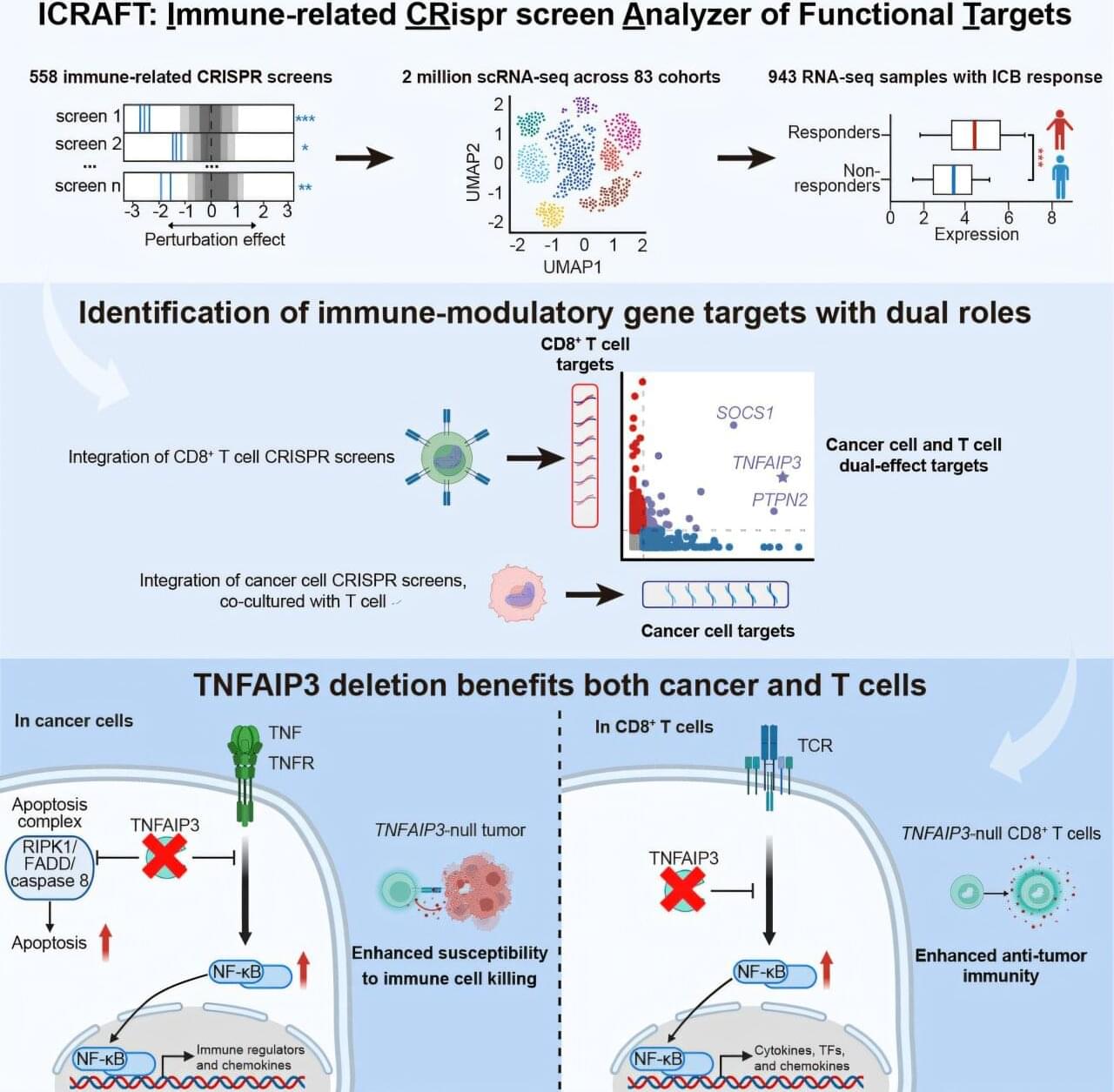
There is an urgent need for precision immunotherapy strategies that simultaneously target both tumor cells and immune cells to enhance treatment efficacy. Identifying genes with dual functions in both cancer and immune cells opens new possibilities for overcoming tumor resistance and improving patient survival.
Professor Zeng Zexian’s team from the Center for Quantitative Biology at the Peking University Academy for Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, in collaboration with the Peking University-Tsinghua University Joint Center for Life Sciences, has developed ICRAFT, an innovative computational platform for identifying cancer immunotherapy targets. Their study has been published in Immunity.
ICRAFT integrates 558 CRISPR screening datasets, 2 million single-cell RNA sequencing datasets, and 943 RNA-Seq datasets from clinical immunotherapy samples.
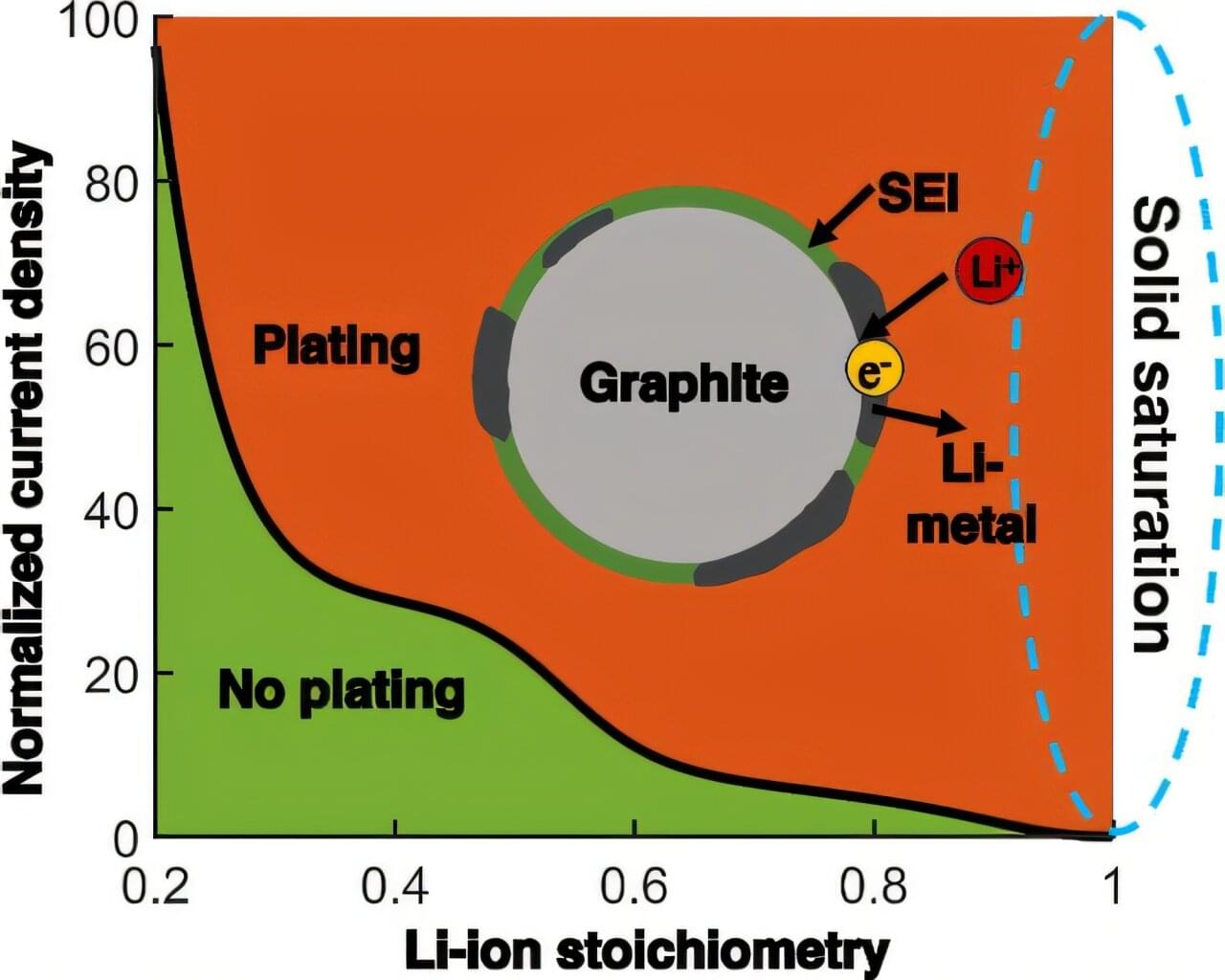
Fast-charging lithium-ion batteries are ubiquitous, powering everything from cellphones and laptops to electric vehicles. They’re also notorious for overheating or catching fire.
Now, with an innovative computational model, a University of Wisconsin–Madison mechanical engineer has gained new understanding of a phenomenon that causes lithium-ion batteries to fail.
Developed by Weiyu Li, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering at UW–Madison, the model explains lithium plating, in which fast charging triggers metallic lithium to build up on the surface of a battery’s anode, causing the battery to degrade faster or catch fire.
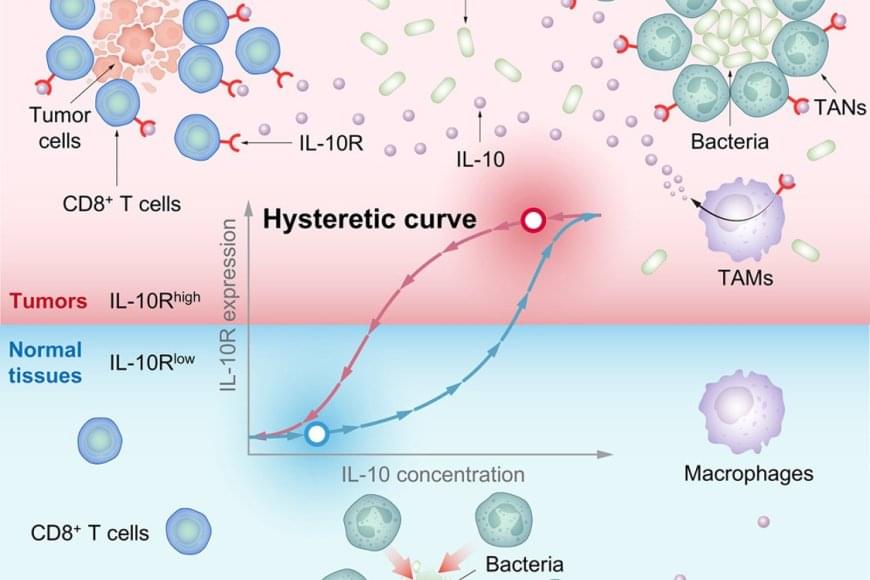
In this study, researchers engineered an attenuated strain, Designer Bacteria 1 (DB1), which efficiently survives and proliferates in tumor tissues while being cleared in normal tissues, achieving a remarkable “tumor-targeting” effect as well as “tumor-clearing” effect.
To understand how DB1 simultaneously achieves these effects, researchers investigated the interactions between the bacteria and tumors. They discovered that DB1’s antitumor efficacy is closely linked to tissue-resident memory (TRM) CD8+ T cells within the tumor, which are reinvigorated and expanded following DB1 therapy. Interleukin-10 (IL-10) plays a crucial role in mediating this effect, with efficacy depending on the high expression of interleukin-10 receptor (IL-10R) on CD8+ TRM cells.
To investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying the high expression of IL-10R on CD8+ TRM cells, researchers conducted a series of computational and quantitative experiments. They found that IL-10 binds to IL-10R on CD8+ TRM cells, activating the STAT3 protein and further promoting IL-10R expression. This established a positive feedback loop, enabling cells to bind more IL-10 and creating a nonlinear hysteretic effect, whereby CD8+ TRM cells “memorize” previous IL-10 stimulation during tumorigenesis. The high expression of IL-10R on CD8+ TRM cells was exploited by a bacteria-induced IL-10 surge, which activated and expanded CD8+ TRM cells to clear tumor cells.
To examine the source of IL-10 within the tumor microenvironment (TME) after bacterial therapy, researchers found that tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) upregulate IL-10 expression following DB1 stimulation via the Toll-like Receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling pathway. Interestingly, IL-10 reduced the migration speed of tumor-associated neutrophils (TANs), aiding DB1 in evading rapid clearance. These processes depended on high IL-10R expression in tumor-associated immune cells, highlighting the critical role of IL-10R hysteresis.
A research team elucidated the mechanism behind bacterial cancer therapy using a genetically engineered bacterial strain. Their findings were published in Cell.
Exploring the use of antitumor bacteria in cancer therapy dates back to the 1860s. Despite this long history, however, clinical application of bacterial-based cancer therapy has faced significant challenges in terms of safety and efficacy.
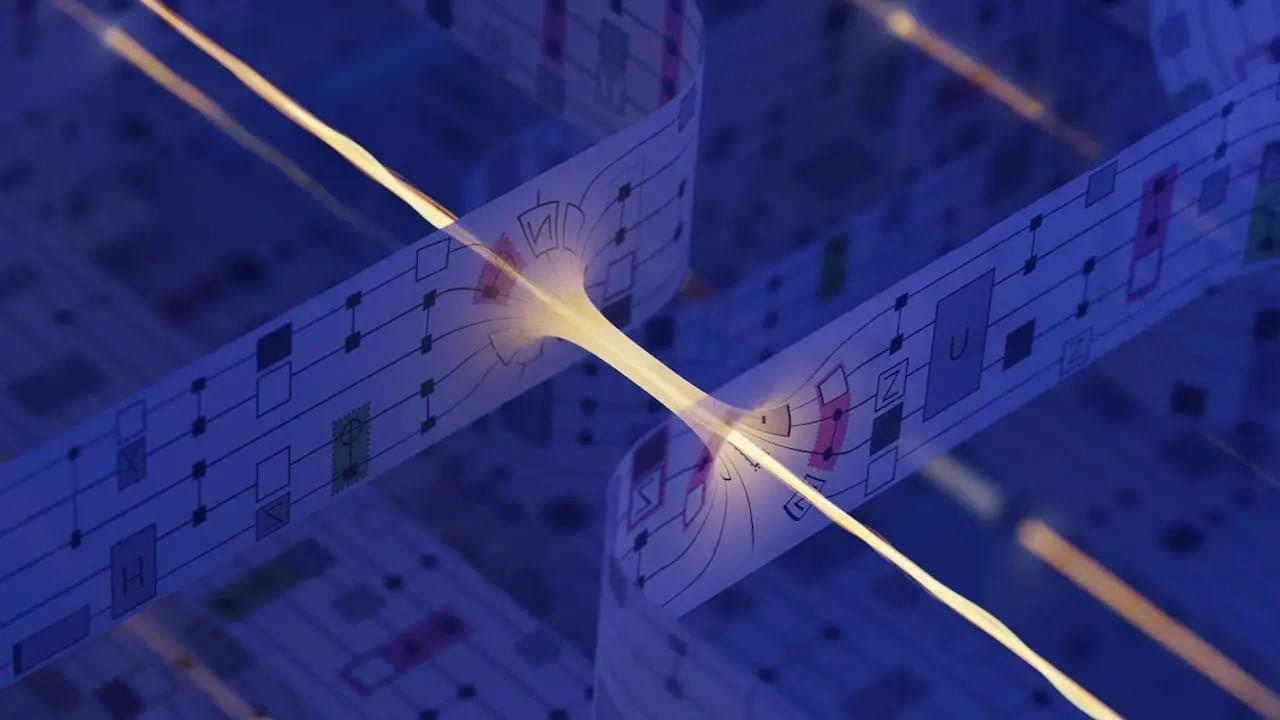

Researchers have announced a groundbreaking experiment that simulated a traversable wormhole using a quantum computer. While no physical rupture in space-time was created, the study offers a significant step toward understanding Einstein-Rosen bridges, theoretical constructs first described by Albert Einstein and Nathan Rosen. Published in the journal Nature, the findings represent a promising avenue for probing quantum gravity experimentally.
A Glimpse of Wormhole Dynamics
The experiment, conducted on Google’s Sycamore quantum processor, involved simulating two minuscule black holes connected by a tunnel-like space-time structure. A quantum message was transmitted between these points, and researchers observed behaviors consistent with wormhole-like dynamics. Study co-author Joseph Lykken, a physicist at Fermilab, remarked, “It looks like a duck, walks like a duck, and quacks like a duck,” indicating the simulation closely mimicked a theoretical wormhole.
Take your personal data back with Incogni! Use my code INTECH at the link below and get 60% off an annual plan: http://incogni.com/intechTimestamps:00:00 — N…

An invention from Twente improves the quality of light particles (photons) to such an extent that building quantum computers based on light becomes cheaper and more practical. The researchers published their research in the journal Physical Review Applied.
Quantum computers are at a tipping point: tech giants and governments are investing billions, but there are two fundamental obstacles: the quantity of qubits and the quality of these qubits. UT researchers have invented a component for a photonic quantum computer that exchanges quantity for quality, and have shown that this exchange yields more computing power.
“Our discovery brings a future with powerful quantum computers a lot closer. That means improved medicines, new materials and safer communications. But also applications that we cannot yet imagine today,” says lead researcher Jelmer Renema. “This technology is an essential part of any future photonic quantum computer.”

Discovering and controlling exotic physical states is key in condensed matter physics and materials science. It has the potential to drive advancements in quantum computing and spintronics.
While studying a ferrimagnet model, scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Brookhaven National Laboratory uncovered a new phase of matter called “half-ice, half-fire.” This state is a twin to the “half-fire, half-ice” phase discovered in 2016.