Recent findings from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument suggest the possibility of new physics that extends beyond the current standard model of cosmology. Using the lab’s new Aurora exascale computing system, the research team conducted high-resolution simulations of the universe’s evoluti
Category: computing – Page 127
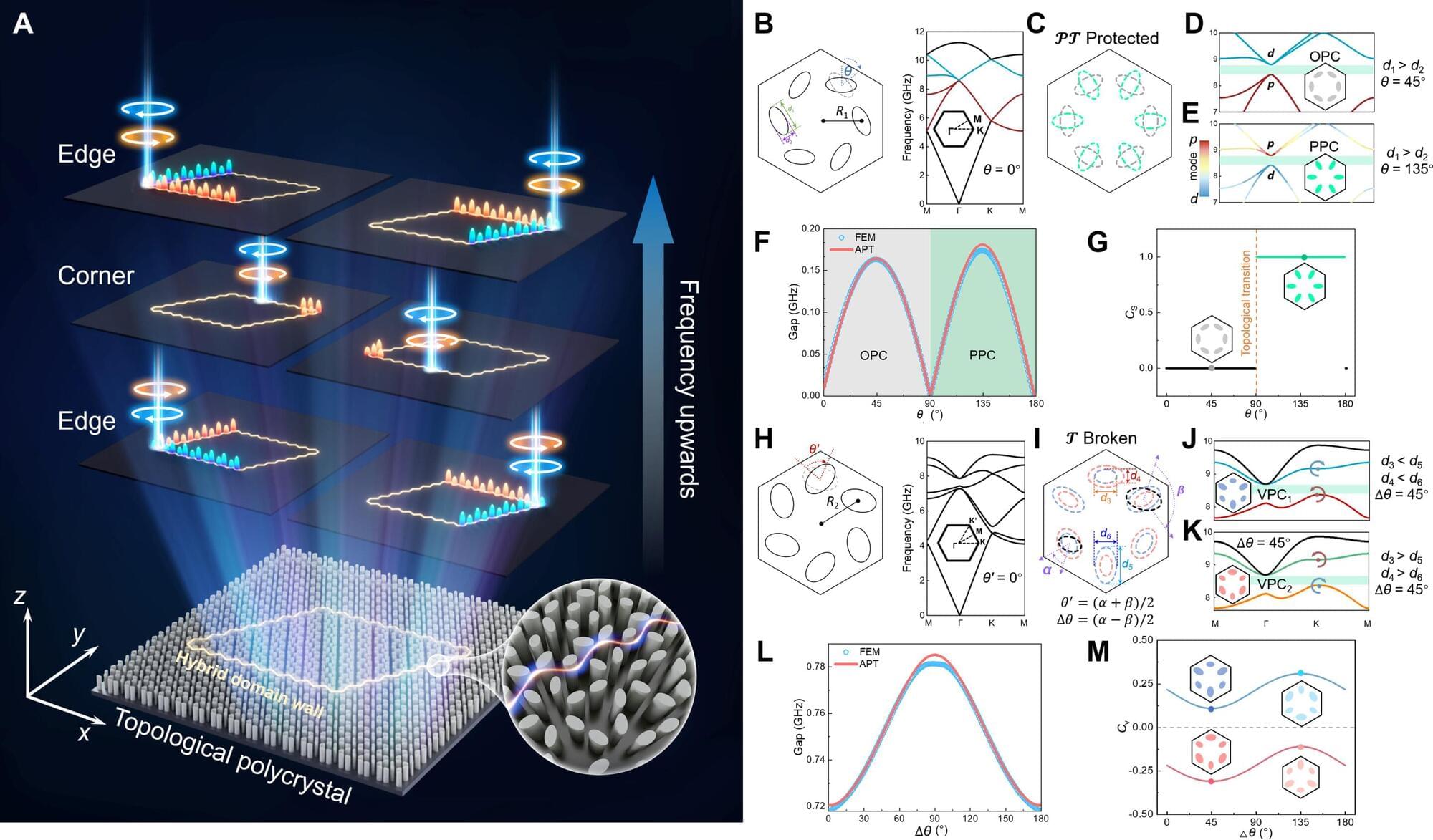
Topological polycrystal: A new approach to configurable, multiband topological photonic circuitry
Molding the flow of light—whether confined to localized regions or propagating in free space—remains crucial for modern integrated photonics. The advancement of the multi-channel, programmable optical waveguide and coupler arrays has enabled us to develop photonic integrated circuits (PICs) as a viable alternative to electronic ones, overcoming limitations in processing speed, bandwidth, and efficiency across the optical-to-microwave spectrum.
However, as on-chip complexity grows, we face significant challenges regarding long-term stability and fabrication-induced defects, making operational reliability critical for practical applications.
The increasing demand for high-capacity information processing drives our need for more complex PICs with additional channels. In this context, topological photonics offers promising solutions due to its inherent robustness against defects.


Turning Non-Magnetic Materials Magnetic with Atomically Thin Films
The rules about magnetic order may need to be rewritten. Researchers have discovered that chromium selenide (Cr₂Se₃) — traditionally non-magnetic in bulk form — transforms into a magnetic material when reduced to atomically thin layers. This finding contradicts previous theoretical predictions, and opens new possibilities for spintronics applications. This could lead to faster, smaller, and more efficient electronic components for smartphones, data storage, and other essential technologies.
An international research team from Tohoku University, Université de Lorraine (Synchrotron SOLEIL), the National Synchrotron Radiation Research Center (NSRRC), High Energy Accelerator Research Organization, and National Institutes for Quantum Science and Technology successfully grew two-dimensional Cr₂Se₃ thin films on graphene using molecular beam epitaxy. By systematically reducing the thickness from three layers to one layer and analyzing them with high-brightness synchrotron X-rays, the team made a surprising discovery. This finding challenges conventional theoretical predictions that two-dimensional materials cannot maintain magnetic order.
“When we first observed the ferromagnetic behavior in these ultra-thin films, we were genuinely shocked,” explains Professor Takafumi Sato (WPI-AIMR, Tohoku University), the lead researcher. “Conventional theory told us this shouldn’t happen. What’s even more fascinating is that the thinner we made the films, the stronger the magnetic properties became—completely contrary to what we expected.”


Aerospace Perspectives Series: Shaping the Future of Aviation with GPU-Powered CFD for Faster, Cleaner Aircraft Design
Flexcompute’s Flow360, the most trusted GPU-native CFD solution for advanced aviation, accelerates the aerospace design process by optimizing evaluations, enhancing aerodatabase development, and reducing time-to-market while ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. In collaboration with OEMs, companies like JetZero are using Flow360 to push the boundaries of efficiency and sustainability, advancing revolutionary designs such as blended-wing-body (BWB) aircraft, hydrogen-powered, and advanced propulsion models. This strategic partnership is crucial to transforming air travel and achieving global sustainability goals, accelerating the next era of aviation innovation.
In this webinar, hear from Qiqi Wang on the latest advancements in high-fidelity CFD, joined by John Vassberg, Chief Design Officer at JetZero, as they explore the cutting-edge technologies driving the future of aviation. They will discuss how GPU-powered CFD is enabling faster, more sustainable aircraft design and how strategic collaboration is key to realizing the industry’s ambitious goals.

Improved modeling of the Pockels effect may help advance optoelectronic technology
The use of light signals to connect electronic components is a key element of today’s data communication technologies, because of the speed and efficiency that only optical devices can guarantee. Photonic integrated circuits, which use photons instead of electrons to encode and transmit information, are found in many computing technologies. Most are currently based on silicon—a good solution because it is already used for electronic circuits, but with a limited bandwidth.
An excellent alternative is tetragonal barium titanate (BTO), a ferroelectric perovskite that can be grown on top of silicon and has much better optoelectronic properties. But since this material is quite new in the field of applied optoelectronics, a better comprehension of its quantum properties is needed in order to further optimize it.
A new study by MARVEL scientists published in Physical Review B presents a new computational framework to simulate the optoelectronic behavior of this material, and potentially of other promising ones.

Can quantum computers handle energy’s hardest problems?
Every week quantum computing hits a new milestone: more qubits, fewer errors, better readout of results. But will these breakthroughs help solve the advanced computational problems facing energy, like how to model energy storage catalysts or ensure power grid reliability? That is what scientists at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) want to know.
Working with local quantum companies, an NREL team is developing benchmarks for quantum computers on the problems that are important to energy science. The pursuit of benchmarks will allow NREL and industry to prioritize practical utility for the next generation of quantum software and hardware.
The first nonverbal patient to receive Elon Musk’s Neuralink shares a video he edited and narrated using his brain chip
The first nonverbal Neuralink patient to receive the chip implant is offering a glimpse into how he uses the technology — editing and narrating a YouTube video using signals from his brain.
Brad Smith is the third person in the world to get a brain chip implant with Elon Musk’s Neuralink, and the first person with ALS to do so.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that primarily affects motor neurons — the nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord responsible for controlling voluntary muscle movement. Over time, patients lose voluntary control of muscle movements, affecting their ability to speak, eat, move, and breathe independently.
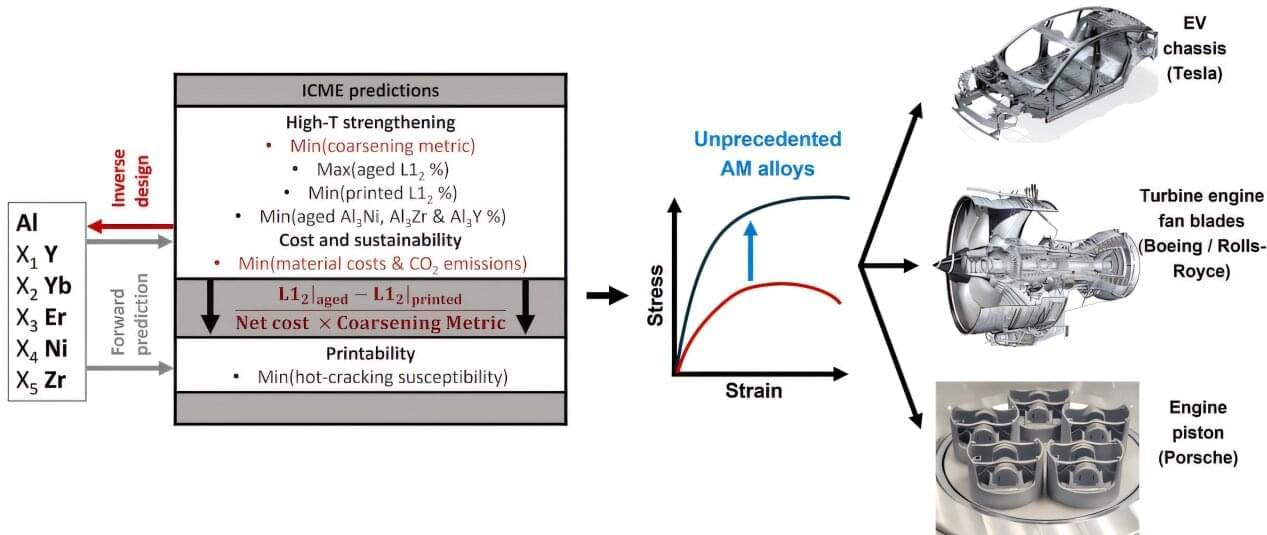
A printable aluminum alloy system can balance strength and cost in the automotive industry
Aluminum alloys are widely used in transportation applications because of their high strength-to-weight ratio, as well as their affordability. However, challenges arise when using them in extremely high-strength and high-temperature applications, particularly in components such as pistons of combustion engines, fan blades of jet engines, and vacuum pumps.
At elevated temperatures, few aluminum alloys can block dislocation movements effectively, which controls the strength. Moreover, few of the designs have considered costs and sustainability metrics in the design, which are essential for high-demand industries. Titanium alloys, such as Ti-64, that are often used in fan blades, are not only heavier and not machinable, but also nearly twice as expensive.
Additive manufacturing (AM) is rapidly evolving and providing new pathways for designing innovative alloys. A recent study by Carnegie Mellon University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) researchers has utilized computational simulations and optimization techniques to identify a new aluminum alloy system that balances strength and cost.