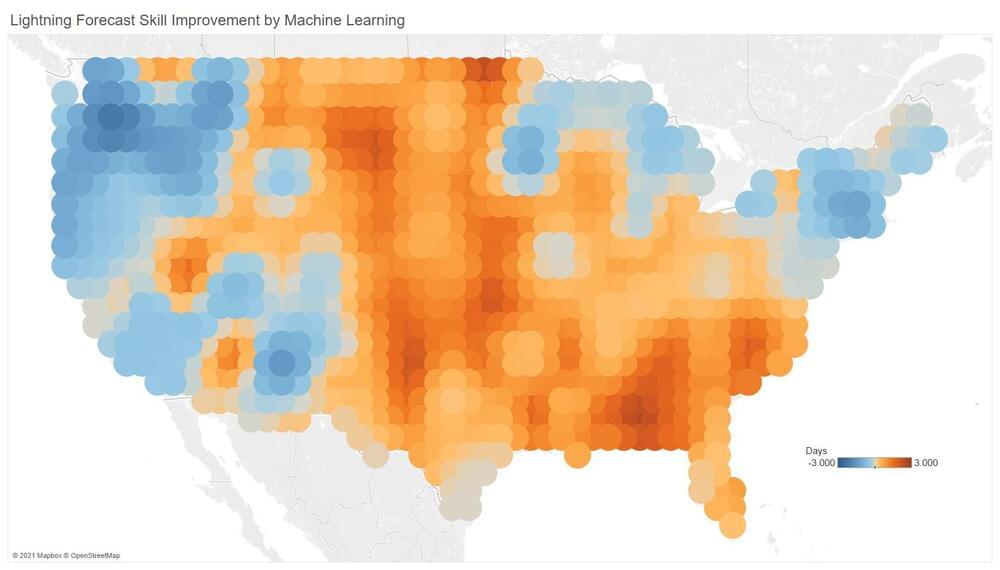
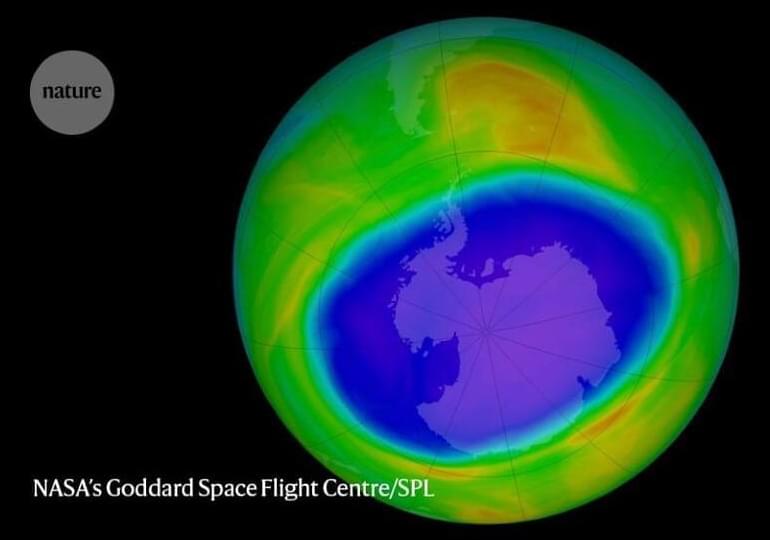
Climate Emergency Basics.
Most people now accept that things are out of balance, and it is only those with warped agendas or a lack of understanding that are left behind.
Use these ten facts as starting points with which to move forward.
Use your vote, where you have one, in politics, the boardroom or a shareholders meeting to push for change in the right direction.
Use your money to buy goods and services from those making the right decisions to make the future cleaner, renewable and sustainable.
Finally, USE YOUR VOICE. Talk to everyone and share these thoughts, and challenge misinformation when you hear it being spread.
We can create a better future.
We waste billions subsidising fossil fuels when we could be scaling renewables and developing alternatives faster.
The more people vote for those with net zero policies and buy from those with net zero aims and ambitions, the sooner the balance will tip and momentum will do the rest.
If you want to see some ideas for how we move forward to solve these issues then watch this video next smile Can we save our planet?
https://youtu.be/qxY0p1MqjJs.
Idea based upon content from the book.
There is no planet B by Mike Berners-Lee.