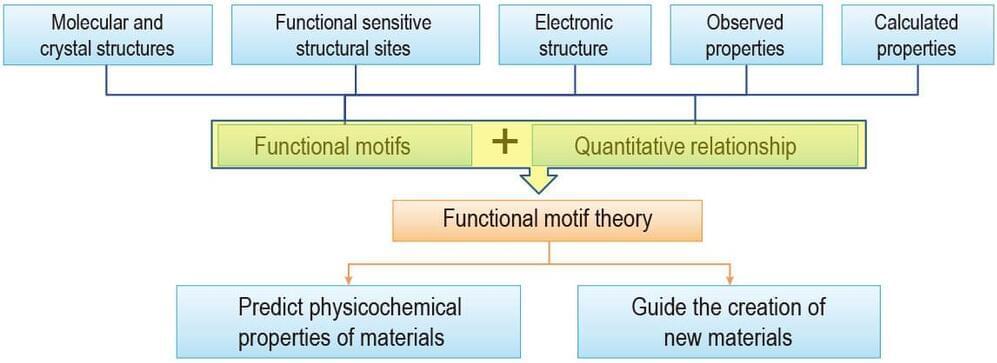
On account of the improvement the Internet of things (IoTs) and smart devices, our lives have been noticeably facilitated in the past few years. Machines and devices are becoming more ingenious with the help of artificial intelligence and various sensors1,2. So, integrated circuits are necessary to provide convenient and effectual communication3 Since the first report on TENG by Wang’s group in 20124, triboelectric systems have been recognized as a proper choice to harvest and convert the energy from the environment5,6. Photodetectors, as one of the most significant types of sensors that can precisely convert incident light into electrical signals have attracted increasing attention in recent years. Various applications including photo-sensors, spectral analysis7,8, environment monitoring9, communication devices10, imaging11, take advantage of narrow band or broad band photodetectors from ultraviolet to terahertz wavelenght. Literature reviews show that the heterojunction/heterostructure based on 2D/3D materials have been widely used in PD applications. In fact, to attain high performance of PDs based heterojunction, the built-in electrical field is needed to suppress the photogenerated recombination and stimulating collection12. Although, Si based PDs offer reliably high performance results, their complexity and expensive manufacturing process have limited their expansion and adoptability for industrial purposes13,14,15. Hence, most available PDs are designed based on external power supplies such as electrochemical batteries for signal production and processing, their design not only increases the sensor’s dimension and weight, but also creates limitations for sensor maintenances16 which is not proper in the IoTs. In 2014, ZH Lin et al. and Zheng et al. represented an investigation on the self-powered PD based on TENG system3,17, and since then, self-driven PDs have been extensively investigated2,5,9,18,19,20. These devices can find potential applications in health monitoring systems such as heart checking21 and health protection from some detrimental radiation such as high levels of UV radiance22.
But in the other hand, even though TENGs could be promise for using in wearable electronics, they still inevitably have limitations in power generation, sensing range, sensitivity, and also the sensing domain for the intrinsic limitations of electrification23,24,25. Moreover, due to high voltage, low current, and alternating current output of the TENGs, they cannot be used in order to supply power to electronic devices effectively without using power management circuits (PMCs) based on the LC modules. There are several reports that describe the importance of the impedance matching of the TENG and PMC units for better energy storage efficiency of the pulsed-TENG26,27. Without using the PMC unit, there are some challenges as a result of synching the TENG, as the power supply, and the consumption element such as the PD device. These challenges include the process of matching the resistance of the device and the impedance of the TENG to achieve effective performance of the self-powered system6,28.
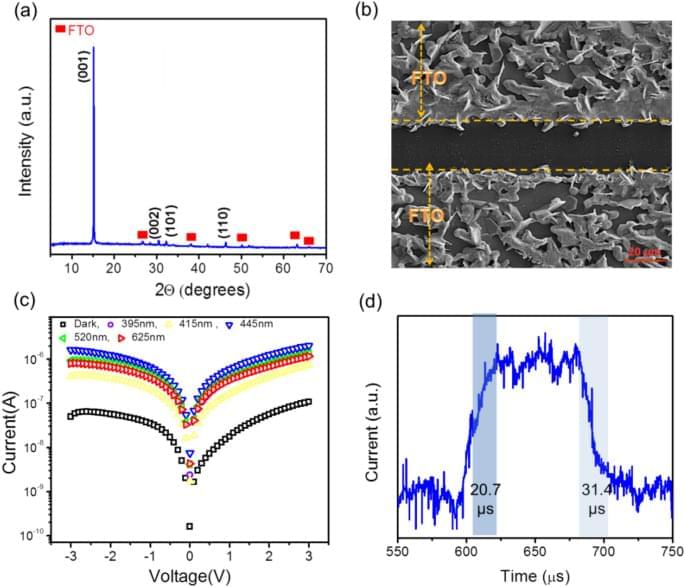
In this study an efficient battery-free photodetector based on bulk heterojunction SnS2 nanosheets and perovskite materials has been designed and powered employing three different TENGs (GO paper/ Kapton, FTO/Kapton and hand/ FTO). In the first step for circuit designing to have better performance of the photodetector in coupling with TENG, the effect load resistance amount in the circuit on the impedance matching the TENG and the inner resistance of the photodetector, has been investigated through output current amplitude. The investigation, shows that to achieve the high amount of the photocurrent, the load resistance should be positioned in both critical zone of the out-put voltage of the TENG and the resistance range of high power density production of the TENG. In the second step, for investigation the effect of the dark resistance of the photodetector on out-put current of the self-powered photodetector, a device with very lower initial resistance (All-oxide Cu2O/ZnO photodetector) has been used with and without different load resistance in the circuit; in this regard, it is concluding that the initial resistance is too important to have proper design impedance matching circuit.