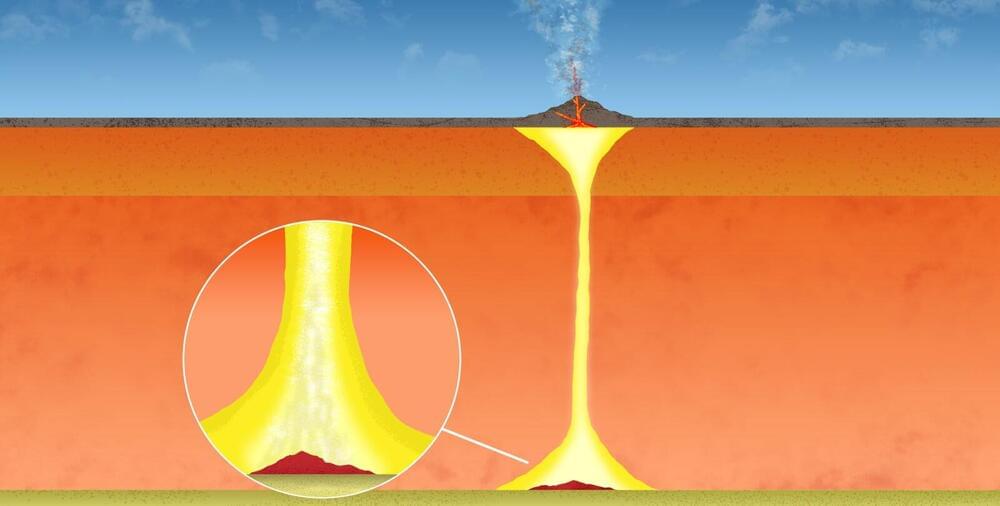
The core–mantle boundary (CMB) is the interface between the Earth’s iron metal core and the thick rocky layer of mantle just above the core. It is a world of extremes—temperatures thousands of degrees Fahrenheit and pressures over a million times the pressure at the surface of the Earth. While it may seem far away from our environment on Earth’s surface, plumes of material from the CMB can ascend upwards through the planet over tens of millions of years, influencing the chemistry, geologic structure, and plate tectonics of the surface world where we live.
Though scientists cannot travel to the center of the Earth to study the CMB, they can get clues about what lies beneath the planet’s surface by measuring earthquakes. Seismic waves travel at different speeds depending on the material they are traveling through, allowing researchers to infer what lies deep below the surface using seismic signatures. This is analogous to how ultrasound uses waves of sound to image inside of the human body.
Recent research shows that the base of Earth’s mantle is actually complex and heterogeneous—in particular, there are mountain-like regions where seismic waves mysteriously slow down. These blobs, named ultralow velocity zones (ULVZs) and first discovered by Caltech’s Don Helmberger, are dozens of kilometers thick and lie around 3,000 kilometers beneath our feet.