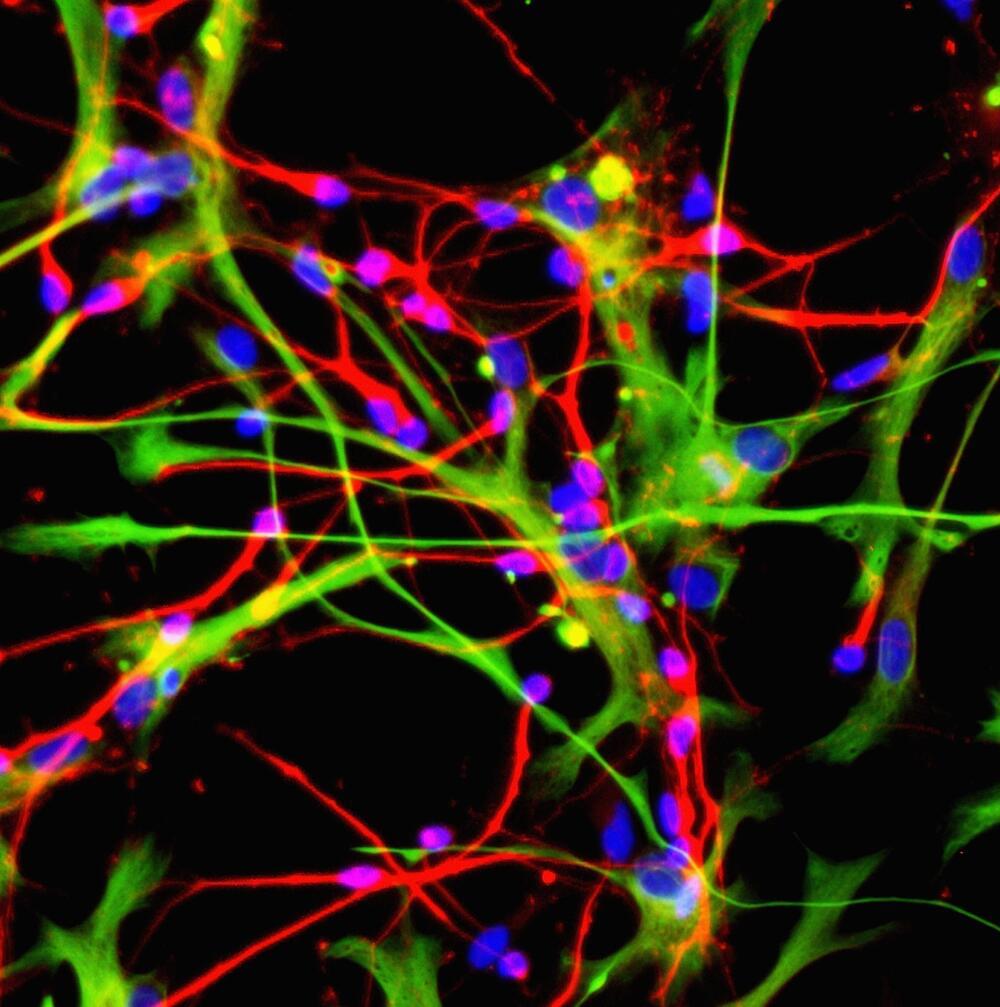
For now, cyborgs exist only in fiction, but the concept is becoming more plausible as science progresses. And now, researchers are reporting in ACS’ Nano Letters that they have developed a proof-of-concept technique to “tattoo” living cells and tissues with flexible arrays of gold nanodots and nanowires. With further refinement, this method could eventually be used to integrate smart devices with living tissue for biomedical applications, such as bionics and biosensing.
Advances in electronics have enabled manufacturers to make integrated circuits and sensors with nanoscale resolution. More recently, laser printing and other techniques have made it possible to assemble flexible devices that can mold to curved surfaces. But these processes often use harsh chemicals, high temperatures or pressure extremes that are incompatible with living cells. Other methods are too slow or have poor spatial resolution. To avoid these drawbacks, David Gracias, Luo Gu and colleagues wanted to develop a nontoxic, high-resolution, lithographic method to attach nanomaterials to living tissue and cells.
The team used nanoimprint lithography to print a pattern of nanoscale gold lines or dots on a polymer-coated silicon wafer. The polymer was then dissolved to free the gold nanoarray so it could be transferred to a thin piece of glass. Next, the gold was functionalized with cysteamine and covered with a hydrogel layer, which, when peeled away, removed the array from the glass. The patterned side of this flexible array/hydrogel layer was coated with gelatin and attached to individual live fibroblast cells. In the final step, the hydrogel was degraded to expose the gold pattern on the surface of the cells. The researchers used similar techniques to apply gold nanoarrays to sheets of fibroblasts or to rat brains. Experiments showed that the arrays were biocompatible and could guide cell orientation and migration.