Myeloid cells are a population of cells classified to denote a specific lineage. “Myeloid” specifically refers to granulocytes and monocytes generated from the bone marrow. Many cells under this term share common progenitors from which they derive including, macrophages, neutrophils, basophils, and eosinophils. In the context of cancer, many of these cells become ‘pro-tumorigenic’. More specifically, they suppress the immune system to allow the tumor to proliferate and progress. Each myeloid cell type is associated with antitumor immune suppression. Myeloid cells suppress antitumor immune activity by blocking T cell activation, aid in angiogenesis (blood vessel formation) to increase metastasis, and producing cytokines or proteins that activate suppressive activity in other cells. Unfortunately, myeloid cells make up a major percentage within the tumor microenvironment, so targeting these cells is crucial. Many researchers are currently working on different ways to target these cell populations.
A recent article in Nature by Dr. Miriam Merad and her team demonstrated how protein signaling drives pro-tumor myeloid cell generation. Merad is a physician scientist, Director of the Precision Immunology Institute at Mount Sinai School of Medicine in New York, and Director of the Mount Sinai Human Immune Monitoring Center (HIMC). While her work focuses on targeting myeloid cells (particularly macrophages) to lower their suppressive phenotype and improve cancer treatment, her current publication identifies specific drivers of immunosuppressive myeloid states, previously undefined.
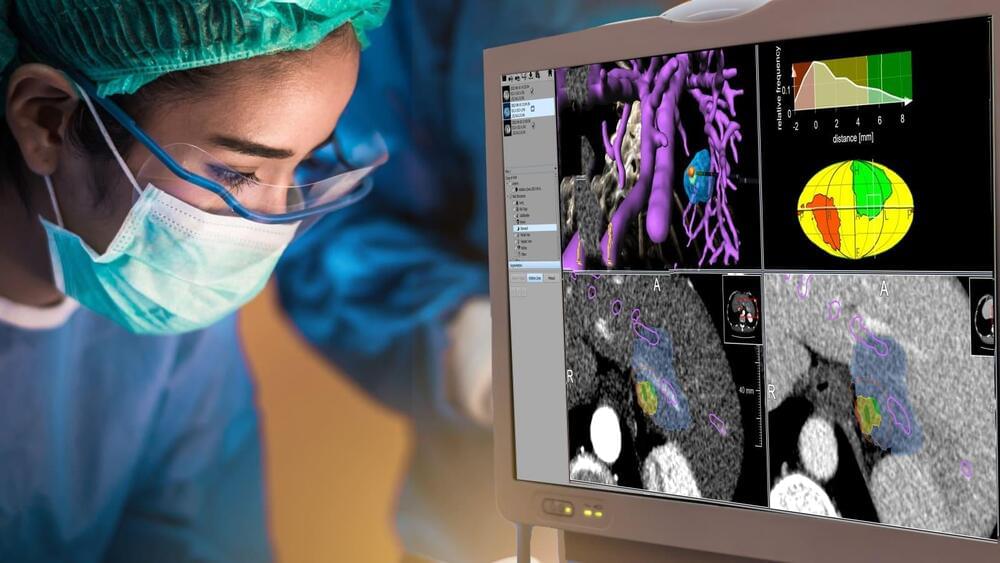
Merad and her team used advanced single cell sequencing to analyze non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) lesions from both humans and mice. Single cell sequencing is commonly used to identified up-and downregulated genes in a variety of cell types. By sequencing the tumor lesions the team discovered that interleukin 4 (IL-4) was a predictive driver of macrophages that infiltrated the tumor. Researchers used various genetically modified mouse models to conclude that the IL-4 receptor is necessary for tumor progression. Interestingly, they concluded that deletion of the IL-4 receptor in the progenitor phase reduced tumor growth compared to IL-4 deletion in mature macrophages which had little effect.