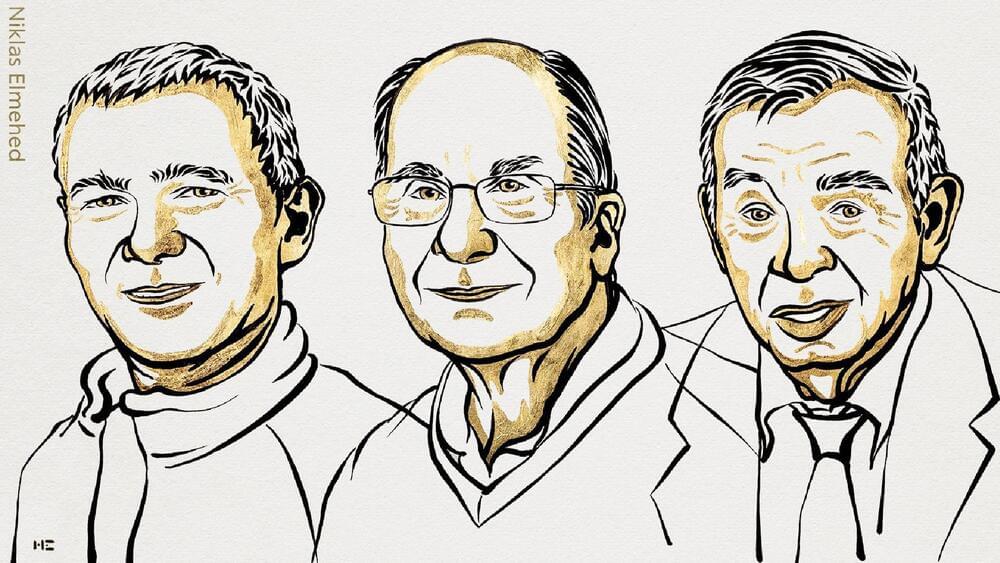
The 2023 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to three scientists who discovered and developed quantum dots, which are very small particles that can change color depending on their size. Quantum dots are tiny particles of a special kind of material called a semiconductor. They are so small that they behave differently from normal materials. They can absorb and emit light of different colors depending on their size and shape.
You can think of quantum dots as artificial atoms that can be made in a lab! They have some of the same properties as atoms, such as having discrete energy levels (meaning they can only exist in certain distinct energy states, and they cannot have energy values between these specific levels) and being able to form molecules with other quantum dots. But they also have some unique features that make them useful for many applications, such as displays, solar cells, sensors, and medicine, which I shall discuss later in this story!
To grasp the workings of quantum dots, a bit of quantum mechanics knowledge comes in handy. Quantum mechanics teaches us that these tiny entities can possess only specific amounts of energy, and they transition between these energy levels by absorbing or emitting light. The energy of this light is determined by the difference in energy levels. In typical materials like metals or plastics, energy levels are closely packed, forming continuous bands where electrons can move freely, resulting in less specific light absorption or emission. However, in semiconductors like silicon or cadmium selenide, there’s a gap between these bands known as the “band gap.” Electrons can only jump from one band to another by interacting with light having an energy level that precisely matches the band gap, making semiconductors valuable for creating devices like transistors and LEDs.