How can cannabidiol (CBD) be used to treat epilepsy? This is what a recent study published in Neuropsychopharmacology hopes to address as a team of researc | Cannabis Sciences



Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of liver cancer and is associated with poor clinical prognosis and high mortality, despite the advances related to therapeutic options for HCC. Therefore, exploring alternative therapeutic options and their associated mechanisms is relevant and urgently needed. Natural products may be an important source of novel anti-cancer compounds. Coffee consumption is associated with protective effects against liver diseases, but the molecular mechanisms underlying these benefits remain poorly understood. Objectives: In this study, we evaluated the in vitro effects of green (GC) and roasted coffee (RC) extracts, alongside chlorogenic acid (CGA), on the proliferation of HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells.

Researchers at Trinity Translational Medicine Institute (TTMI) and the Irish Mycobacterial Reference Laboratory at St James’s Hospital have uncovered how the bacterium Mycobacterium avium—a leading cause of difficult-to-treat chronic lung infections—changes and adapts inside patients over many years of illness.
Their findings, published in the journal Genome Medicine, could help doctors understand why M. avium infections come back and why antibiotics sometimes fail.
The team undertook this research to understand how M. avium manages to survive for years in people’s lungs, even during long courses of antibiotics. This bacterium causes a type of chronic lung infection that’s becoming more common around the world.

A new study by investigators from Mass General Brigham has used next-generation imaging technology to discover that when the brain is falling asleep, it shows a coordinated shift in activity.
The researchers found that during NREM (non-rapid eye movement) sleep, parts of the brain that handle movement and sensory input stay active and keep using energy, while areas involved in thinking, memory and daydreaming quiet down and use less energy. Their results are published in Nature Communications.
“This research helps explain how the brain stays responsive to the outside world even as awareness fades during sleep,” said corresponding author Jingyuan Chen, Ph.D., an assistant investigator at the Athinoula A. Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging at Massachusetts General Hospital.
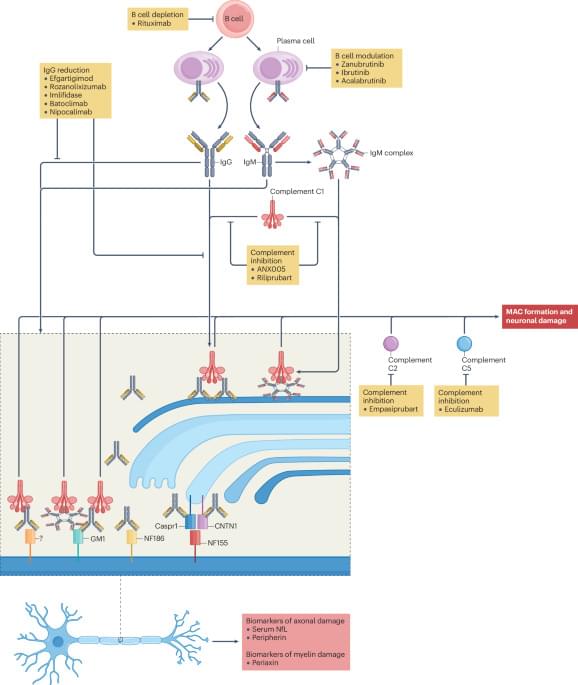
Management of autoimmune neuropathies has remained unchanged for much of the past 30 years, but recent advances are changing the rate of progress. In this Review, the authors summarize the latest developments, including discoveries in disease mechanisms, new diagnostic guidelines, identification of new biomarkers and the status of promising clinical trials.
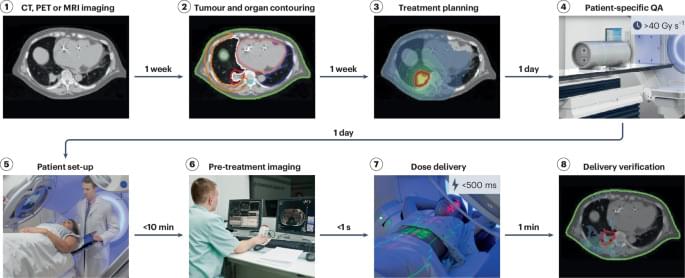
FLASH radiotherapy delivers a cancer treatment dose in less than a second, reducing side effects while maintaining tumour control. This Review explores technological advances, safety considerations and future directions needed to bring this promising ultra-fast radiotherapy approach into clinical practice.
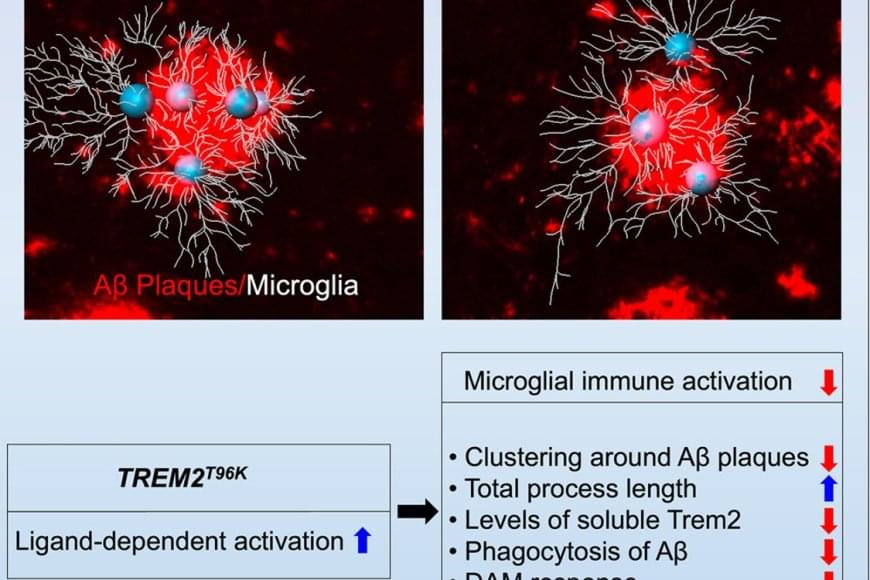
The team wanted to understand how immune cells of the brain, called microglia, contribute to Alzheimer’s disease (AD) pathology. It’s known that subtle changes, or mutations, in genes expressed in microglia are associated with an increased risk for developing late-onset AD.
The study focused on one such mutation in the microglial gene TREM2, an essential switch that activates microglia to clean up toxic amyloid plaques (abnormal protein deposits) that build up between nerve cells in the brain. This mutation, called T96K, is a “gain-of-function” mutation in TREM2, meaning it increases TREM2 activation and allows the gene to remain super active.
They explored how this mutation impacts microglial function to increase risk for AD. The authors generated a mutant mouse model carrying the mutation, which was bred with a mouse model of AD to have brain changes consistent with AD. They found that in female AD mice exclusively, the mutation strongly reduced the capability of microglia to respond to toxic amyloid plaques, making these cells less protective against brain aging.
