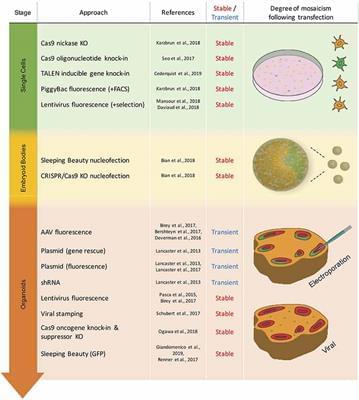
In the past 10 years, gene-editing and organoid culture have completely changed the process of biology. Congenital nervous system malformations are difficult to study due to their polygenic pathogenicity, the complexity of cellular and neural regions of the brain, and the dysregulation of specific neurodevelopmental processes in humans. Therefore, the combined application of CRISPR-Cas9 in organoid models may provide a technical platform for studying organ development and congenital diseases. Here, we first summarize the occurrence of congenital neurological malformations and discuss the different modeling methods of congenital nervous system malformations. After that, it focuses on using organoid to model congenital nervous system malformations. Then we summarized the application of CRISPR-Cas9 in the organoid platform to study the pathogenesis and treatment strategies of congenital nervous system malformations and finally looked forward to the future.
Keywords: organoid, CRISPR-Cas9, congenital nervous system malformation, central nervous system, 3D