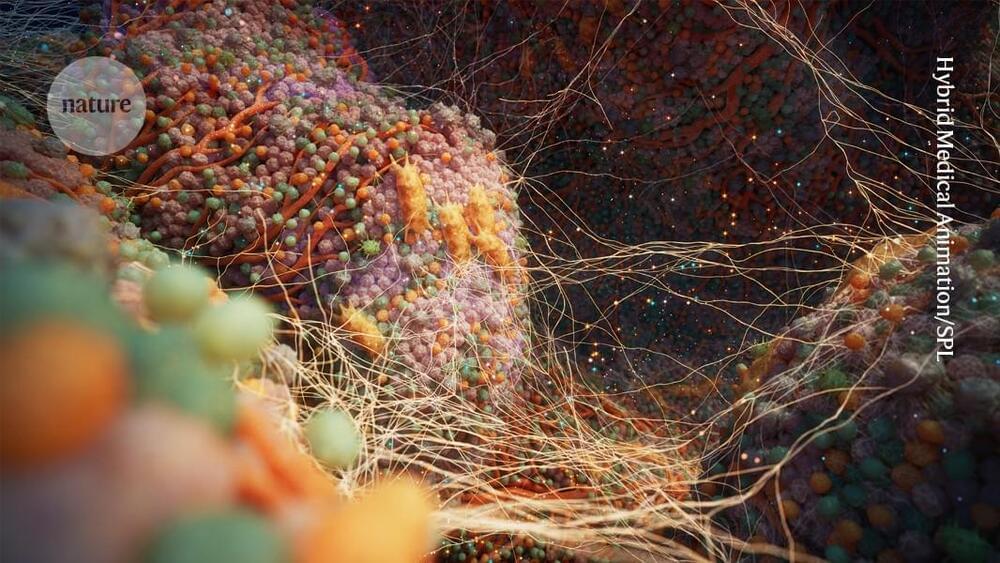
Lupus, doctors like to say, affects no two patients the same. The disease causes the immune system to go rogue in a way that can strike virtually any organ in the body, but when and where is maddeningly elusive. One patient might have lesions on the face, likened to wolf bites by the 13th-century physician who gave lupus its name. Another patient might have kidney failure. Another, fluid around the lungs. What doctors can say to every patient, though, is that they will have lupus for the rest of their life. The origins of autoimmune diseases like it are often mysterious, and an immune system that sees the body it inhabits as an enemy will never completely relax. Lupus cannot be cured. No autoimmune disease can be cured.
Two years ago, however, a study came out of Germany that rocked all of these assumptions. Five patients with uncontrolled lupus went into complete remission after undergoing a repurposed cancer treatment called CAR-T-cell therapy, which largely wiped out their rogue immune cells. The first treated patient has had no symptoms for almost four years now. ‘We never dared to think about the cure for our disease,’ says Anca Askanase, a rheumatologist at Columbia University’s medical center who specializes in lupus. But these stunning results—remission in every patient—have fueled a new wave of optimism. More than 40 people with lupus worldwide have now undergone CAR-T-cell therapy, and most have gone into drug-free remission. It is too early to declare any of these patients cured for life, but that now seems within the realm of possibility.
From The Atlantic.