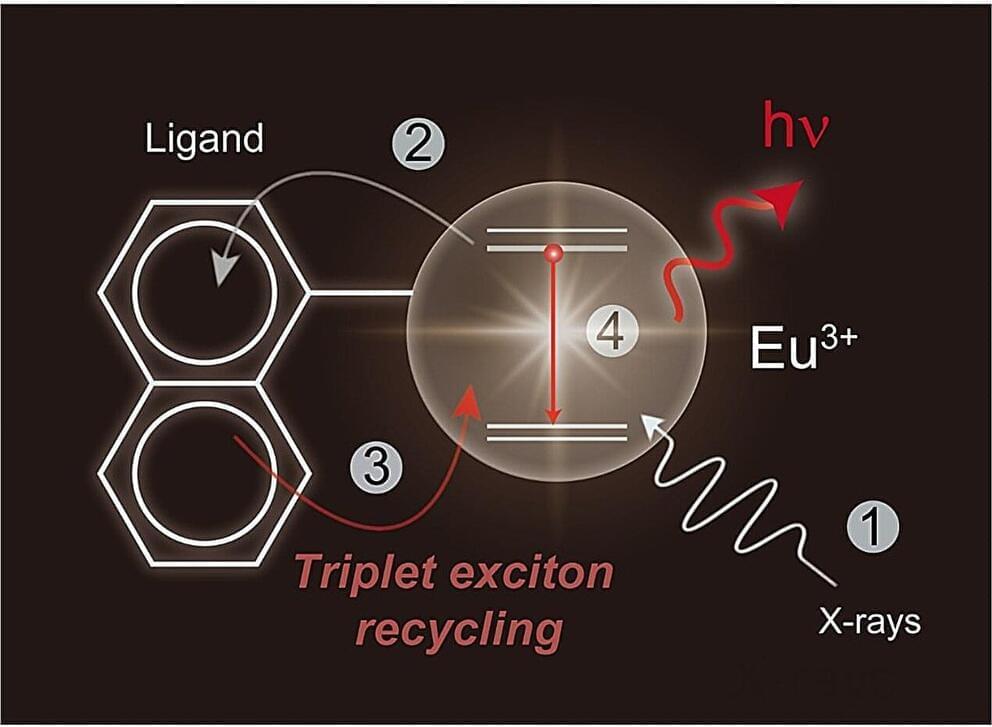
The evidence presented by Boldrini et al2 was considered resilient and convincing because the authors ensured that the samples were taken from healthy individuals using more biological parameters, such as angiogenesis and change in volume of DG, for a suitable comparison. They also employed unbiased stereology, which is the gold standard for counting number of neurons.2
The contrary results presented by the Sorrels study and Boldrini study highlight the existing ambiguity regarding the concept of neurogenesis in adult humans. Both studies employed reasonably similar immunohistological methods and included many of the same neurogenesis markers, yet contrasting results were observed. The study by Boldrini et al examined samples from humans aged 14 to 79 years, finding more than a thousand cells in each part of the DG, which was in stark contrast to what was observed by Sorrells et al, who found very few cells in the neurogenic niche of subjects in the same age range. Even if we consider that some discrepancies in numbers might arise due to the difference in counting methods (or subjective reasons), such marked and obvious disparity is perplexing. Sorrels et al justified their findings, noting the limitation that relying solely on the presence of markers might cause glial lineage cells to be identified as neuronal lineage cells. However, the authors stated that they used additional methods for confirmation, including transmission electron microscopy (TEM)-immunogold and in-situ hybridization. The relative paucity of any type of progenitor or immature cells, including glia in the neurogenic niche of DG in their study, remains unexplained.
Kempermann et al7 expressed skepticism regarding the negative findings of Sorrells et al, naming the postmortem interval, the lack of known status regarding neuropsychiatric disease or chronic ailment, and using patients with epilepsy as key factors of concern.7 Kempermann et al argued that, in severe epilepsy, destruction of the neurogenic niche is an explicit possibility, and that, in some cases, epilepsy could be the reason for the lack of neurogenesis.7 Additionally, Kempermann et al also criticized the use of 10% formalin in some of the samples due its potential to mask the expression of proteins.7 However, Sorrells et al clearly mentioned that they performed appropriate antigen retrieval for the selected sections.1 Kempermann et al7 suggested that dependence on the protein markers to denote neurogenesis could be an erroneous approach and that some of the markers, such as DCX, are known for fast degradation. Additionally, the presence of DCX-negative immature neurons and high inter-individual variation in expression of DCX in humans, which was also reflected in the data presented by Boldrini et al, are not unusual.7 The use of fluorescence markers also was presented as a caveat by Kempermann et al7 because it is prone to fade away and might give rise to false negative impression.