The astounding numbers of the human body:
Your body consists of 37 trillion cells divided into 200 different types.
100 billion cells make up the skin, which is the largest organ in your body. 100 billion neurons in the brain allow you to process as many as 60,000 thoughts per day.
You also have 127 million retinal cells that allow you to see the world in as many as 10 million different colors. You have 30 trillion red blood cells, 42 billion blood vessels, and 6 liters (1.6 gallons) of blood in your body. Your blood makes up approximately 10% of your body weight. Your nose has 1,000 olfactory receptors that allow you to distinguish 50,000 different smells.
Your lungs allow you to breathe 23,040 breaths per day, while your heart beats around 115,200 heartbeats per day or 42 million heartbeats per year. You have 640 muscles, 360 joints, 206 bones and 100,000 hair follicles. You produce around 23,000 liters (6,075 gallons) of saliva in your lifetime, which is enough to fill two swimming pools.
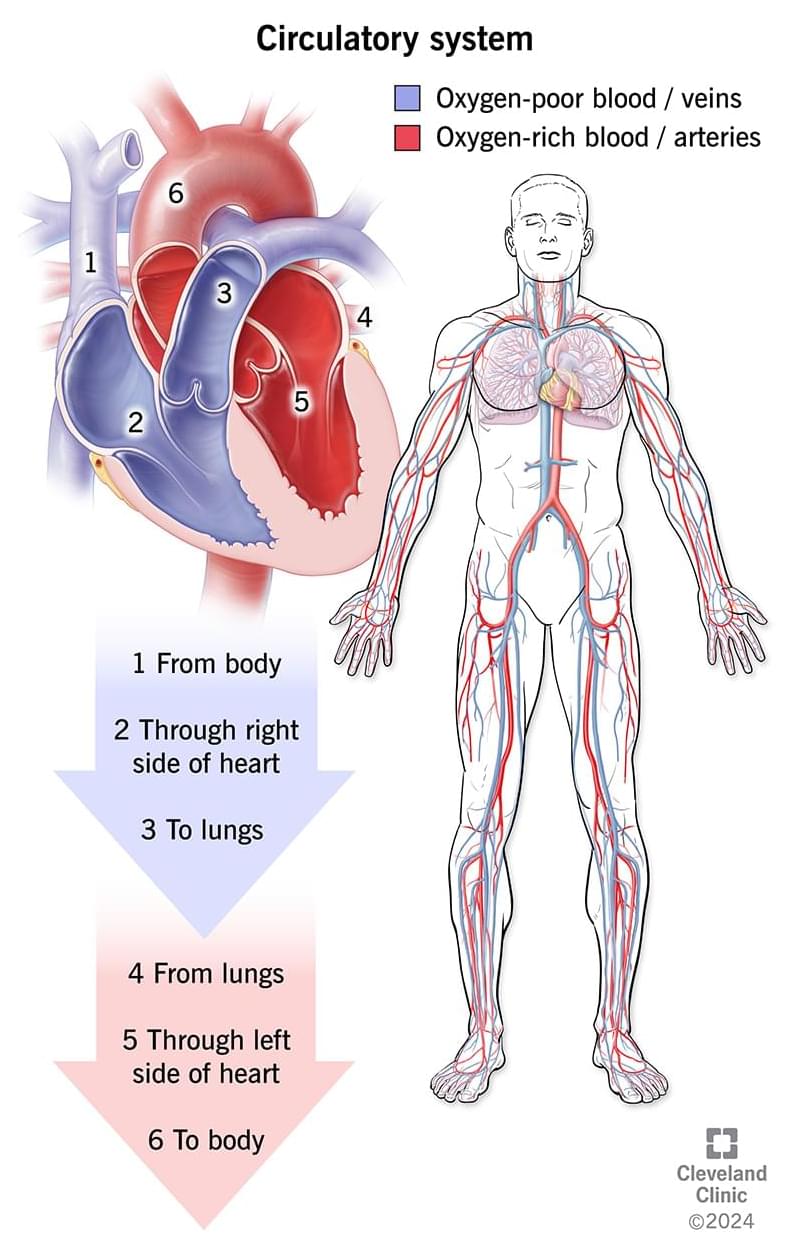
Your circulatory system (cardiovascular system) includes your heart and blood vessels. Your heart pumps oxygen-rich blood after your lungs add oxygen to your blood.