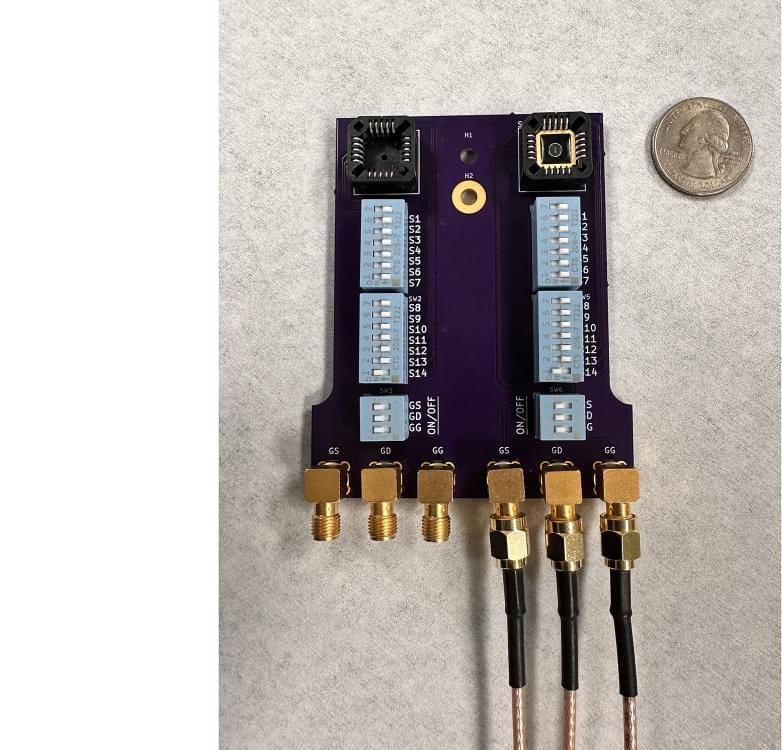
A recently developed electronic tongue is capable of identifying differences in similar liquids, such as milk with varying water content; diverse products, including soda types and coffee blends; signs of spoilage in fruit juices; and instances of food safety concerns. The team, led by researchers at Penn State, also found that results were even more accurate when artificial intelligence (AI) used its own assessment parameters to interpret the data generated by the electronic tongue.
The researchers published their results today (Oct. 9) in Nature.
According to the researchers, the electronic tongue can be useful for food safety and production, as well as for medical diagnostics. The sensor and its AI can broadly detect and classify various substances while collectively assessing their respective quality, authenticity and freshness. This assessment has also provided the researchers with a view into how AI makes decisions, which could lead to better AI development and applications, they said.