For the first time, scientists have witnessed the very moment DNA begins to unravel, revealing a necessary molecular event for DNA to be the molecule that codes all life. A new study from King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), published in Nature, captures the moment DNA begins to unwind, allowing for all the events that follow in DNA replication.
Category: biotech/medical – Page 461
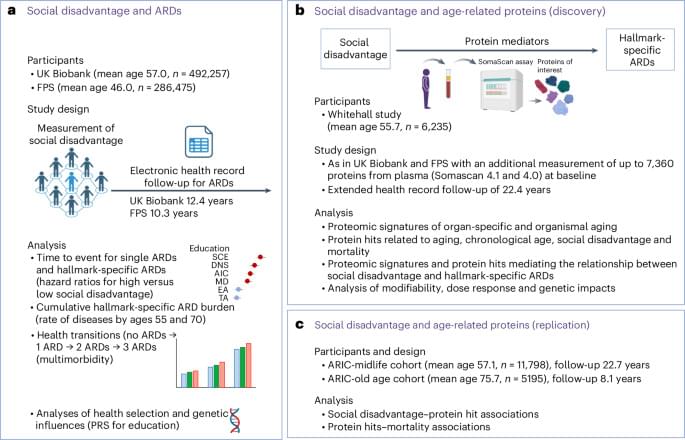
Social disadvantage accelerates aging
As an initial step, we selected ARDs associated with hallmarks of aging. These included a total of 83 diseases linked to one or more hallmarks of aging, based on the taxonomy put forward in ref. 4 (Supplementary Table 2). Support for this taxonomy comes from multiple sources. Analyses of electronic health records from general practice and hospitalizations identified more than 200 diseases with incidence rates increasing with chronological age6,22. Researchers linked a subset of these ARDs to specific hallmarks of aging using several approaches: mining 1.85 million PubMed abstracts on human aging, identifying shared genes in the genome-wide association study catalog, conducting gene set enrichment analysis and analyzing disease co-occurrence networks within each hallmark4.
We confirmed the co-occurrence of ARDs within each hallmark in 492,257 participants from the UK Biobank study23. The presence of one ARD increased the risk of developing another ARD related to the same hallmark, with clustering coefficients ranging from 0.76 for LOP-specific ARDs to 0.92 for SCE-specific ARDs. These findings corroborated the hallmark-specific clustering of ARDs (Extended Data Figs. 3 and 4)23.
In time-to-event analyses of UK Biobank and FPS participants without these ARDs at baseline (n ranging from 477,325 to 492,294 in the UK Biobank and from 278,272 to 286,471 in the FPS, depending on the social disadvantage indicator and ARD), social disadvantage—indicated by education and adult SES (neighborhood deprivation)—was associated with a higher risk of developing ARDs. In the UK Biobank, the age-, sex-and ethnicity-adjusted hazard ratio for developing any ARD was 1.31 (95% confidence interval (CI) 1.29–1.33) for individuals with low compared with high education. For individuals with high versus low adult SES, the hazard ratio was 1.21 (95% CI 1.20–1.23). In the FPS, the corresponding hazard ratios were 1.28 (95% CI 1.25–1.31) and 1.23 (95% CI 1.20–1.27), respectively.
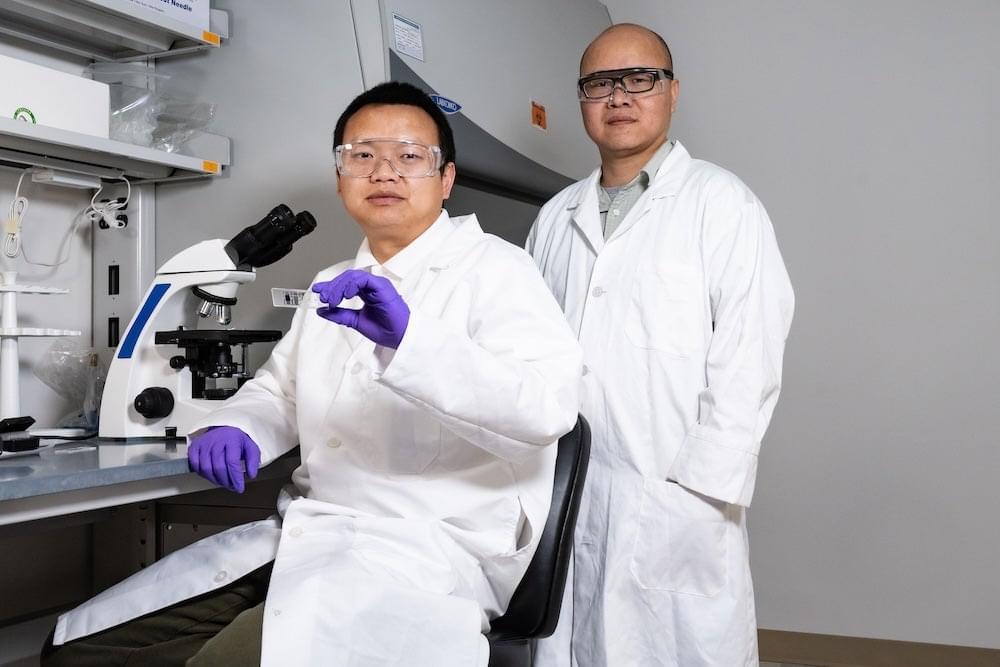

Scientists gain insight into RNA-editing protein that could lead to improved treatment for cancer, autoimmune diseases
A research team led by Rice University’s Yang Gao has uncovered new insights into the molecular mechanisms of ADAR1, a protein that regulates ribonucleic acid (RNA) induced immune responses. Their findings, published in Molecular Cell March 17, could open new pathways for treating autoimmune diseases and enhancing cancer immunotherapy.
ADAR1 converts adenosine to inosine in double-stranded RNA, a process essential for preventing unwarranted immune responses, yet the molecular basis of this editing had remained unclear. Through detailed biochemical profiling and structural analysis, researchers found that ADAR1’s editing activity depends on RNA sequence, duplex length and mismatches near the editing site. High-resolution structures of ADAR1 bound to RNA reveal its mechanisms for RNA binding, substrate selection and dimerization.
“Our study provides a comprehensive understanding of how ADAR1 recognizes and processes RNA,” said Gao, assistant professor of biosciences and a Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (CPRIT) Scholar. “These insights pave the way for novel therapeutic strategies targeting ADAR1-related diseases.”
Mutated DNA Restored to Normal in Gene Therapy Advance
Researchers have corrected a disease-causing gene mutation with a single infusion carrying a treatment that precisely targeted the errant gene.
This was the first time a mutated gene has been restored to normal.
The small study of nine patients announced Monday by the company Beam Therapeutics of Cambridge, Mass., involved fixing a spelling error involving the four base sequences — G, A, C and T — in DNA. The effect was to change an incorrect DNA letter to the right one. The result was a normal gene that functioned as it should, potentially halting liver and lung damage of patients with a rare disorder.
The small study in patients with a rare disorder that causes liver and lung damage showed the potential for precisely targeted infusions.
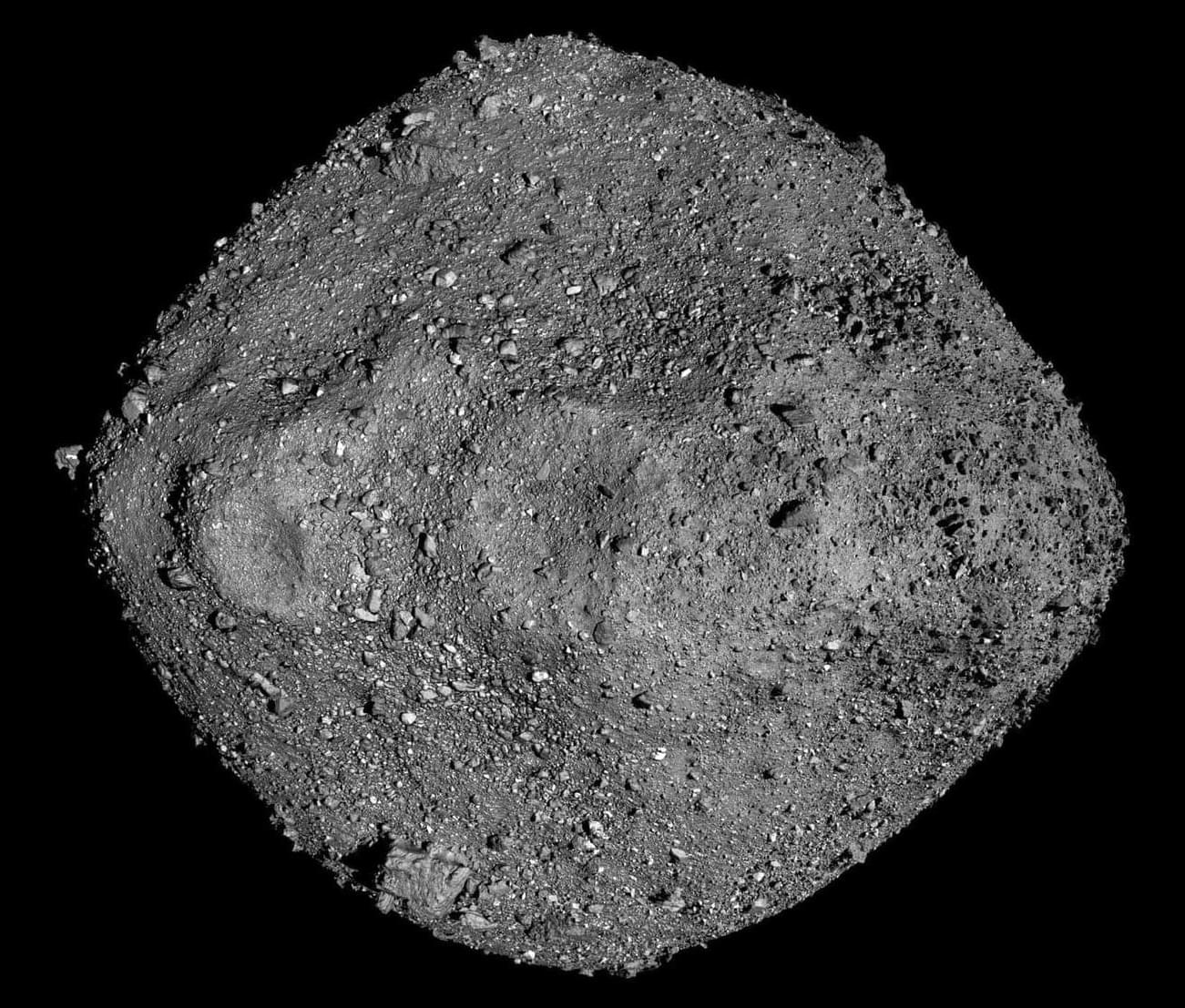

Asteroid Bennu Holds Traces of Ancient Water — And Maybe Life’s Origins
Scientists at Berkeley Lab are unraveling the mysteries of Bennu, a 4.5-billion-year-old asteroid, using cutting-edge technology.
The asteroid harbors traces of ancient briny water, salty minerals, and even organic molecules – potential clues to life’s origins. Researchers are using X-ray and electron microscopy to analyze these space rocks at the atomic level, revealing how early planetary systems formed. Even more exciting, they’ve found amino acids.
<div class=””> <div class=””><br />Amino acids are a set of organic compounds used to build proteins. There are about 500 naturally occurring known amino acids, though only 20 appear in the genetic code. Proteins consist of one or more chains of amino acids called polypeptides. The sequence of the amino acid chain causes the polypeptide to fold into a shape that is biologically active. The amino acid sequences of proteins are encoded in the genes. Nine proteinogenic amino acids are called “essential” for humans because they cannot be produced from other compounds by the human body and so must be taken in as food.<br /></div> </div>
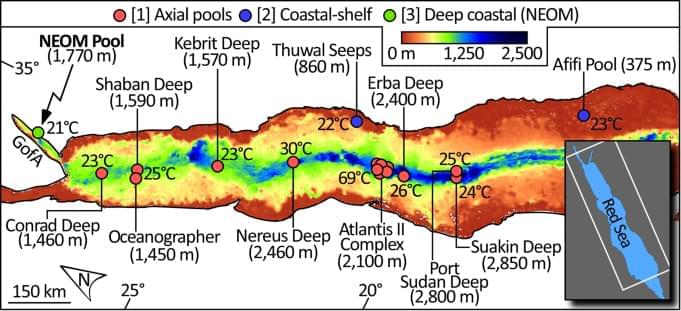
Discovery of the deep-sea NEOM Brine Pools in the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea
Experts just discovered massive pools of water that quickly paralyze and kill anything that enters them.
A team of researchers from the University of Miami has discovered deadly deep-sea brine pools in the Red Sea, uncovering a mysterious underwater world where anything that swims in does not survive.
These extreme habitats, found 1.1 miles below the surface, are so salty and oxygen-deprived that they quickly paralyze or kill marine life.
Despite their lethal nature, the outskirts of these pools support unique microbial life, offering scientists new insights into Earth’s climatic history, the origins of life, and even potential extraterrestrial ecosystems. The discovery, published in Nature Communications Earth and Environment, marks the first time such pools have been found so close to shore, making them an invaluable natural archive of past tsunamis, floods, and earthquakes.
S history, these brine pools may also lead to groundbreaking medical advancements. Similar deep-sea microorganisms have previously yielded antibacterial and anticancer compounds, hinting at the potential for new treatments hidden in these depths. Additionally, studying life in such extreme conditions could help scientists understand how organisms might survive on other planets with water-rich environments. This discovery not only expands our understanding of Earth learn more.
Deep-sea brine pools represent hypersaline environments famed for their extremophile microbes. With anoxia entirely excluding bioturbating megafauna, brine pools are also conducive to the pristine preservation of sedimentary sequences. Here we use bathymetric and geophysical observations to locate a complex of brine pools in the Gulf of Aqaba consisting of one 10,000 m2 pool and three minor pools of less than 10 m2. We further conduct sediment coring and direct sampling of the brine to confirm the sedimentary and environmental characteristics of these pools. We find that the main pool preserves a stratigraphy which spans at least 1,200 years and contains a combination of turbidites, likely resulting from flashfloods and local seismicity, and tsunamigenic terrestrial sediment. The NEOM Brine Pools, as we name them, extend the known geographical range of Red Sea brine pools, and represent a unique preservational environment for the sedimentary signals of regional climatic and tectonic events.
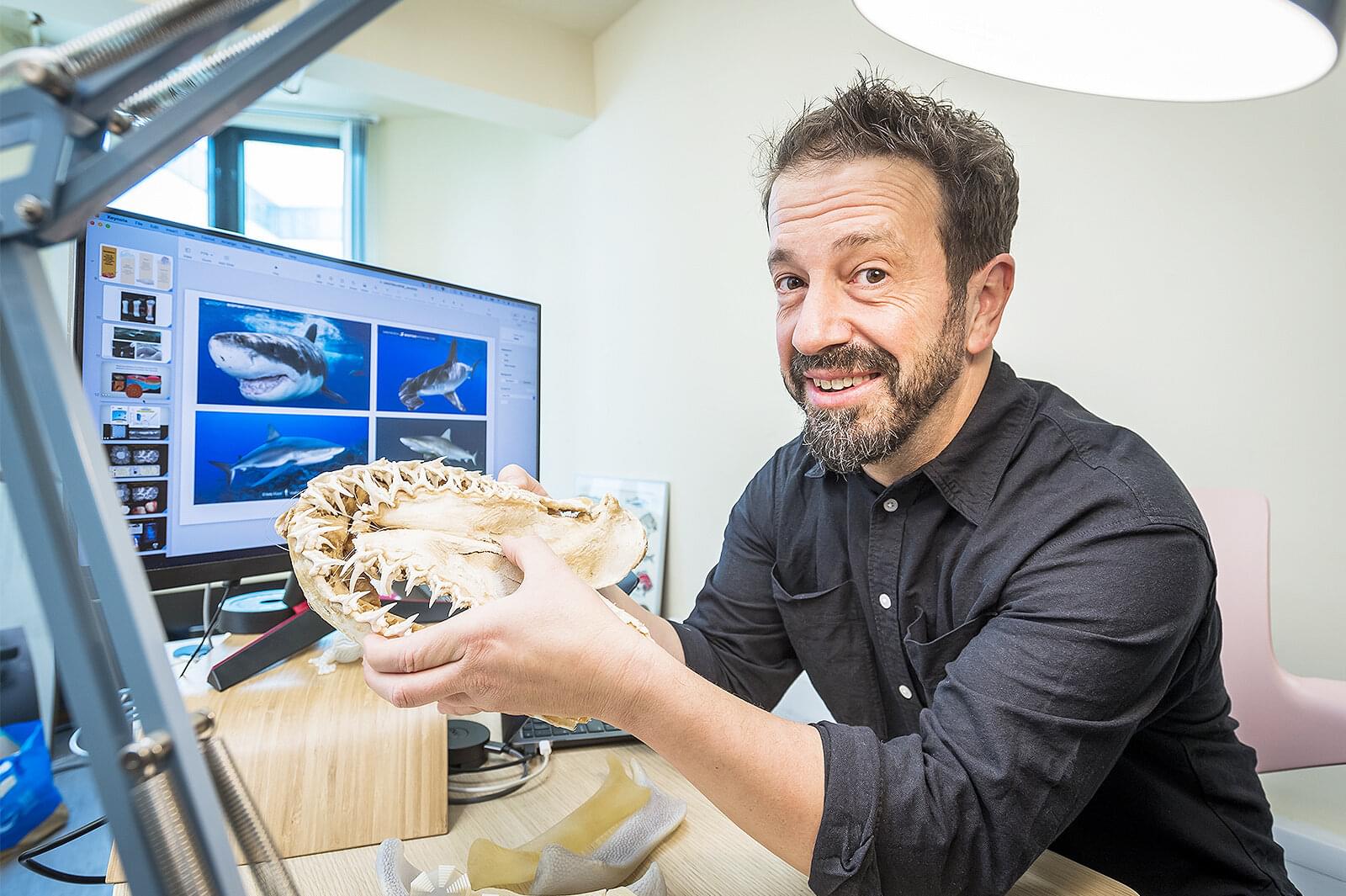

Stingrays reveal nature’s elegant solution to maintaining geometric armor growth
How does the armored tiling on shark and ray cartilage maintain a continuous covering as the animals’ skeletons expand during growth?
This is a question that has perplexed Professor Mason Dean, a marine biologist in the Department of Infectious Diseases and Public Health at City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK) since he was in graduate school.
An expert in skeletal development, structure and function in vertebrate animals, but with a particular focus on (and affection for) sharks and rays, Professor Dean says he was curious about how nature keeps complex surfaces covered while organs and animals are growing, and their surfaces are changing.
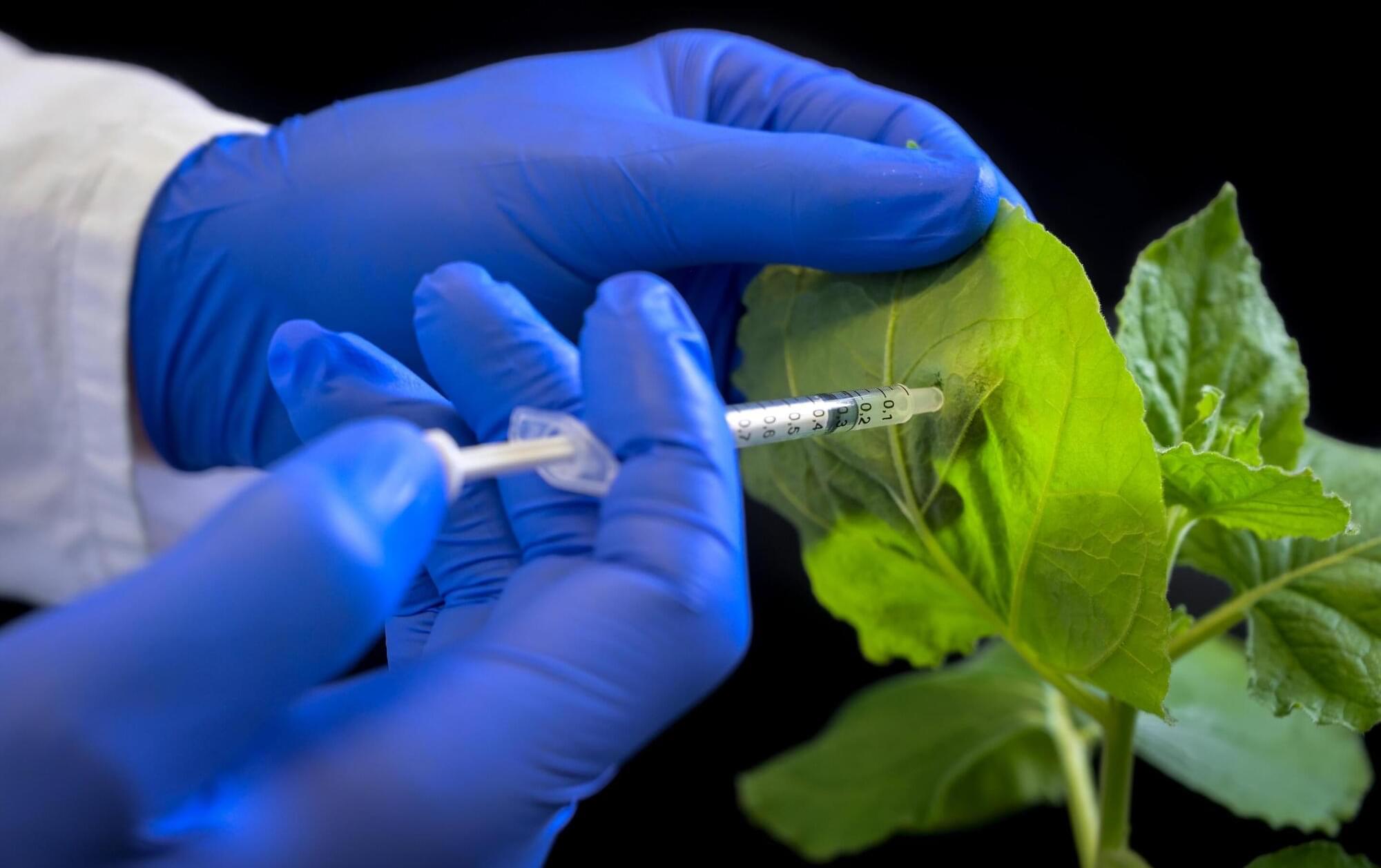

Protecting crops: RNA-based substances open up new avenue to combat a widespread plant virus
New RNA-based active agents reliably protect plants against the Cucumber mosaic virus (CMV), the most common virus in agriculture and horticulture. They were developed by researchers at the Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU).
The active ingredients have a broad spectrum effect; a series of RNA molecules support the plant’s immune system in combating the virus. In laboratory experiments, 80 to 100% of the treated plants survived an infection with a high viral load, as the team reports in Nucleic Acids Research.
Their paper has been selected as a “breakthrough article” by the journal. The researchers are now working on transferring the idea from the laboratory into practice.
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria more vulnerable under body-like fluid flow conditions, study finds
Some notoriously difficult-to-treat infections may not be as resistant to antibiotics as has been thought, according to new research using a microfluidic device that more closely duplicates the fluid flow found in the body than standard cultures.
The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign research team, led by biochemistry professor Joe Sanfilippo, tested antibiotic agents against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, considered one of the most highly resistant pathogens. They introduced the drugs at varying rates of fluid flow and found that, while the bacteria thrived at no or low fluid flow, the antibiotics killed the bacteria at higher flow rates.
“Anytime you take an antibiotic orally or by IV, it’s not immediately in the place it is supposed to be. It will get there by flowing in the bloodstream. Other fluids move throughout the body as well: in the lungs, the urinary tract, the digestive tract. Yet biologists don’t really study the impact of fluid flow when they study pathogens,” Sanfilippo said.
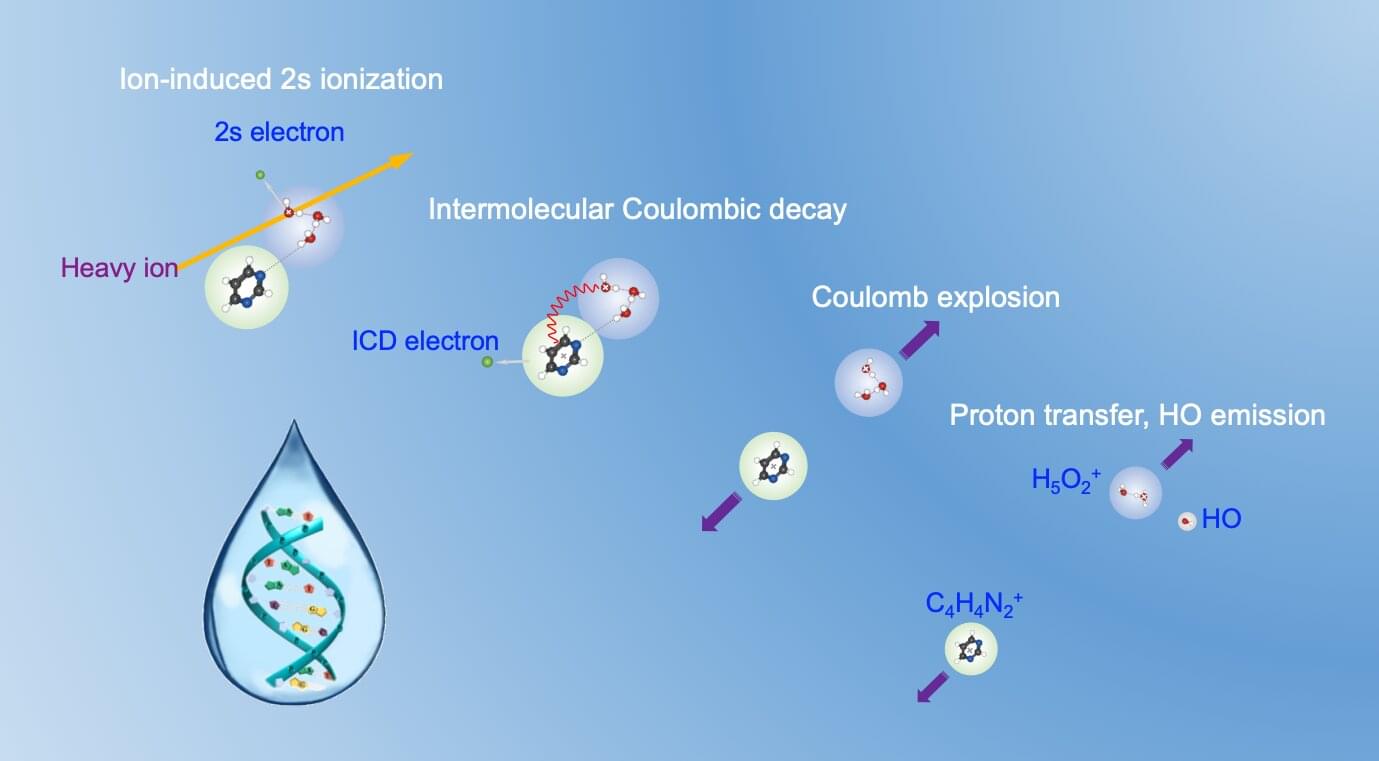
Key decay mechanism behind superior biological effects of heavy-ion cancer therapy uncovered
Heavy-ion therapy, one of the most advanced radiotherapy techniques, has proven to be more effective than conventional X-rays and proton radiation in cancer treatment. However, the mechanisms behind this superior biological effectiveness remain unclear.
Published in Physical Review X on March 11, a new study has uncovered a key mechanism involving intermolecular Coulombic decay (ICD) in aqueous environments initiated by heavy-ion irradiation, providing insights about the effectiveness of such irradiation.
The study was conducted by researchers from the Institute of Modern Physics (IMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), in collaboration with researchers from Russia’s Irkutsk State University, Germany’s Heidelberg University, the University of Science and Technology of China, Xi’an Jiaotong University, and Lanzhou University.