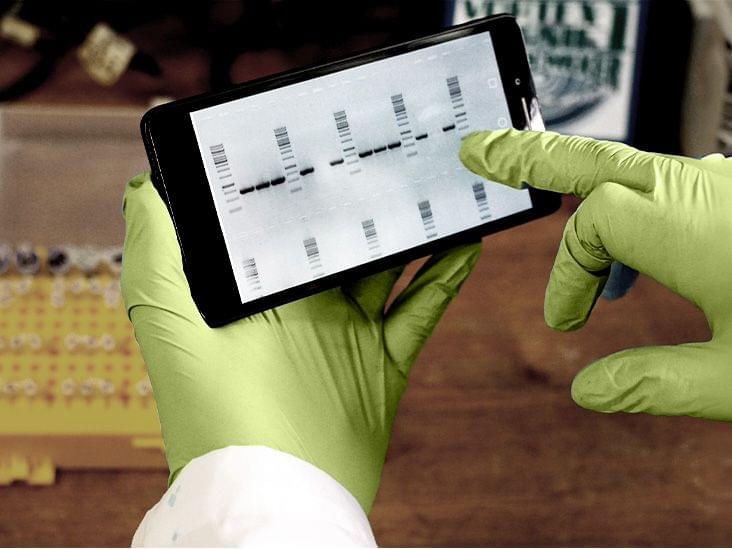
Scientists say that long genes — which are more susceptible to DNA damage — might be a main cause of the body’s aging and could play a role in. the development of diseases like Alzheimer’s.
Category: biotech/medical – Page 463
After decades of slow progress, therapeutic vaccines that direct the immune system to attack tumours could soon become a fixture of cancer treatment.
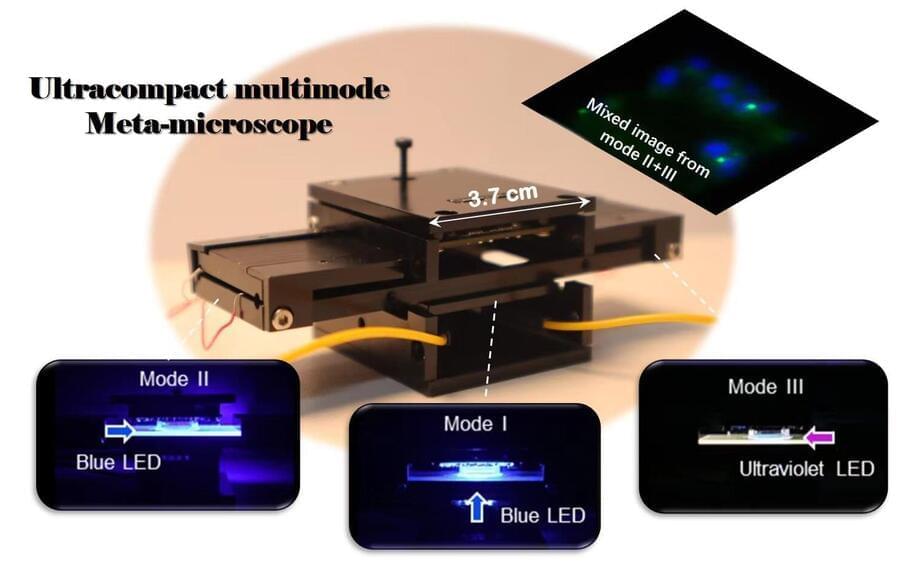
Versatility and miniaturization of imaging systems are of great importance in today’s information society. Microscopic imaging techniques have always been indispensable for scientific research and disease diagnosis in the biomedical field, which is also stepping towards the integration, portable, and multi-functions.
If someone tells you that you have a big head, take that as a compliment.
Humankind’s brains have apparently gotten bigger and bigger over the years, according to a team of scientists, who are surmising that bigger brains may stave off dementia as folks age.
An international team of researchers, led by the University of California Davis Health, arrived at this finding after studying the MRIs of people starting with those born in the 1930s, all the way through the 1970s.
Susannah Fox, former chief technology officer for the HHS, explains how technology can empower a patient-led healthcare revolution.
Thiruvananthapuram: CSIR-National Institute for Interdisciplinary Science and Technology (CSIR-NIIST) has pioneered a groundbreaking technology for the safe, sustainable, and cost-effective management of biomedical waste, marking a significant milestone as the first of its kind in the country.
This innovative technology was unveiled at the Biomedical Waste Management Conclave, a one-day event hosted at the CSIR-NIIST campus in the city on March 26.
According to UNI, Dr M Srinivas, Director, AIIMS New Delhi, inaugurated the meet, which was presided over by Dr N Kalaiselvi, Secretary, DSIR and Director General, CSIR, through videoconferencing.
When Jeff Siewerdsen, Ph.D., joined MD Anderson last year, he finally got the opportunity to work more closely with clinical teams to make advances that would benefit patients and clinicians in the operating room.
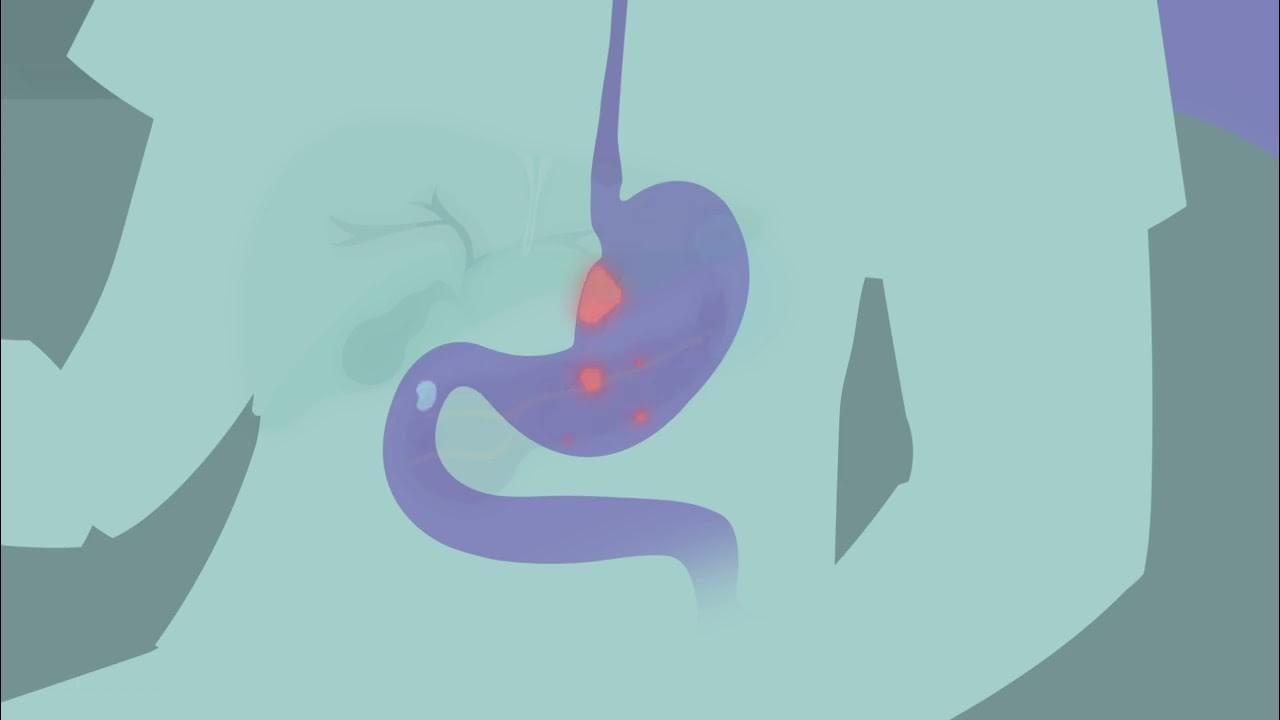
Learn more about the role of your stomach and learn more about the signs and symptoms of stomach cancer that you should be aware of.
The stomach is part of the body’s digestive system, located in the upper abdomen.
It acts as a temporary storage area for food before being mixed and broken down and passed through the rest of the upper gastrointestinal system.
Stomach cancer – sometimes also referred to as gastric cancer – occurs when abnormal cells in the stomach grow out of control. This may also occur in the junction where the stomach meets the oesophagus.
Unlike other cancers, there is no early detection test for stomach cancer.
The symptoms are often vague and can be similar to other medical conditions – so it’s important for you to see your GP for a review if you experience symptoms that are unusual for you or persistent.
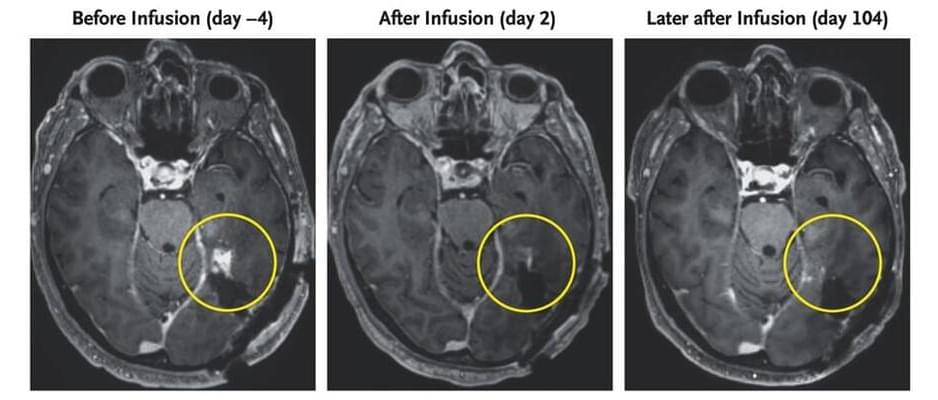
Brain scans of a 72-year-old man diagnosed with a highly aggressive form of cancer known as a glioblastoma have revealed a remarkable regression in his tumor’s size within days of receiving an infusion of an innovative new treatment.
Though the outcomes of two other participants with similar diagnoses were somewhat less positive, the case’s success still bodes well for the search for a way to effectively cure what is currently an incurable disease.
Glioblastomas are typically about as deadly as cancers can get. Emerging from supporting cells inside the central nervous system, they can rapidly develop into malignant masses that claim up to 95 percent of patient lives within five years.
Medical implants such as pacemakers and gastric stimulators have improved our lives, but the batteries in these devices eventually run out and require surgery to replace them.
It raises a futuristic question: what if there was a way to avoid cutting a patient’s body open to replace a battery?
A team of Chinese scientists have come up with a possible method to pull that off by developing an implantable battery that uses oxygen already inside the human body to continuously power itself up.