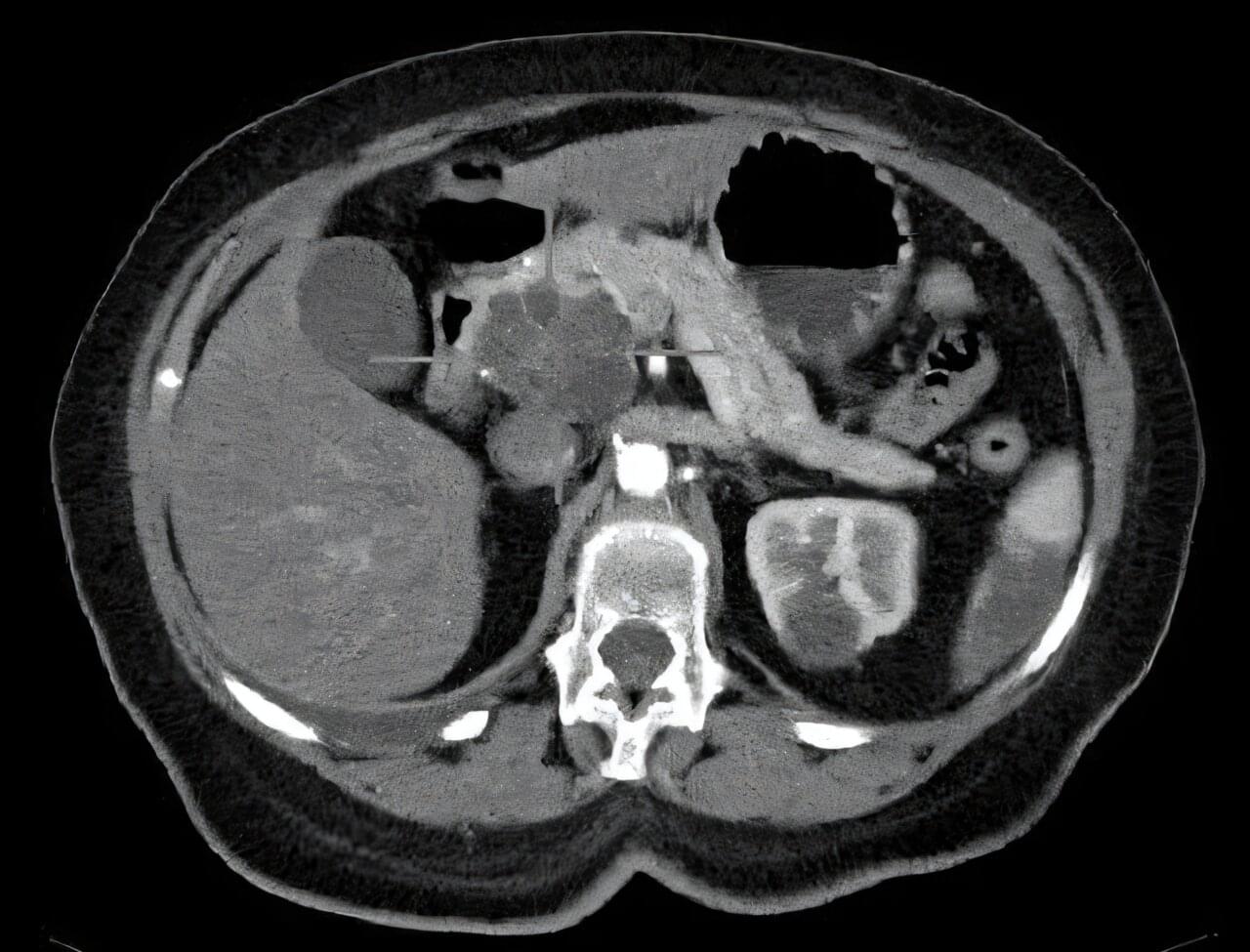
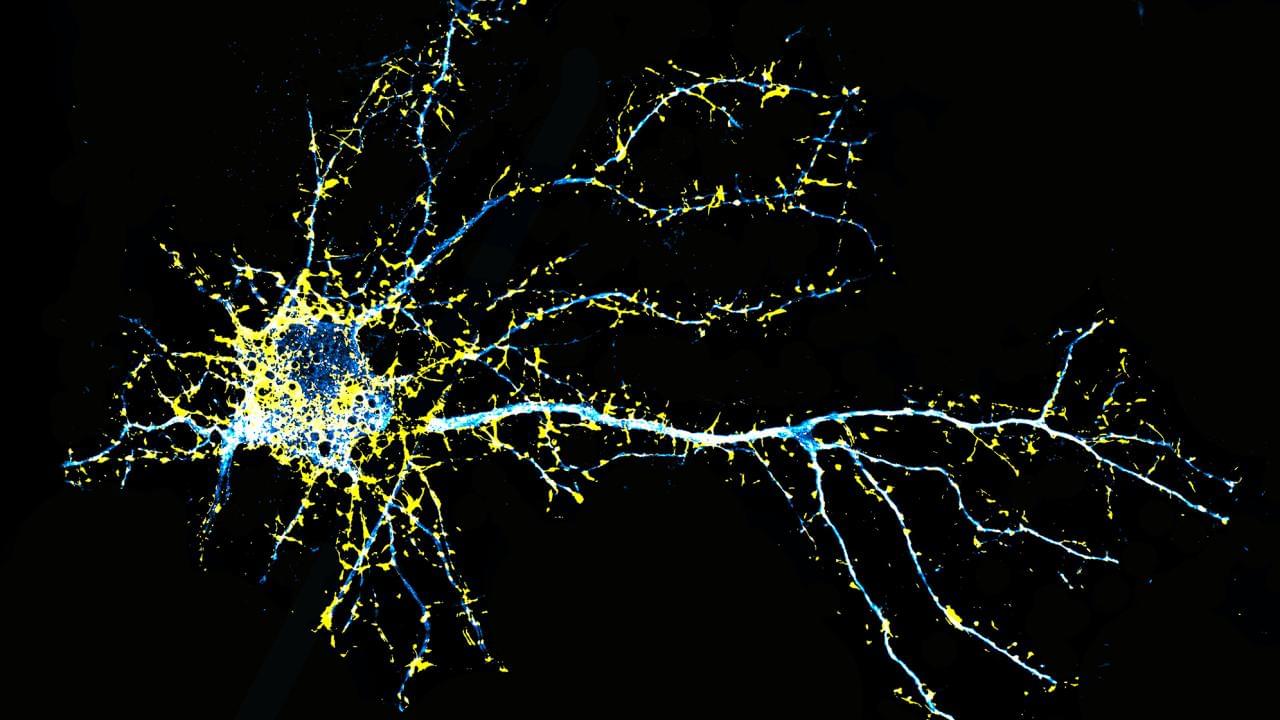
Pancreatic cancer is one of the most aggressive cancers and has one of the lowest survival rates—only 10% after five years. One of the factors contributing to its aggressiveness is its tumor microenvironment, known as the stroma, which makes up the majority of the tumor mass and consists of a network of proteins and different non-tumor cells. Among these, fibroblasts play a key role, helping tumor cells to grow and increasing their resistance to drugs.
Now, a study led by researchers from the Hospital del Mar Research Institute, IIBB-CSIC-IDIBAPS, Mayo Clinic, Instituto de Biología y Medicina Experimental (CONICET, Argentina) and CaixaResearch Institute, has identified a new key factor contributing to this feature of pancreatic cancer: a previously unknown function of Galectin-1 protein inside the nuclei of fibroblasts.
This discovery, published in the journal PNAS, offers new insights into the role of these cells in the progression of pancreatic cancer.