Chromatin remodeling plays a vital role in gene regulation, affecting how DNA is accessed. Disruptions in this process can also lead to cancer and other diseases.
To better understand how chromatin remodeling works, scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital used cryo–electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to obtain fine structural details of a human chromatin remodeler in action.
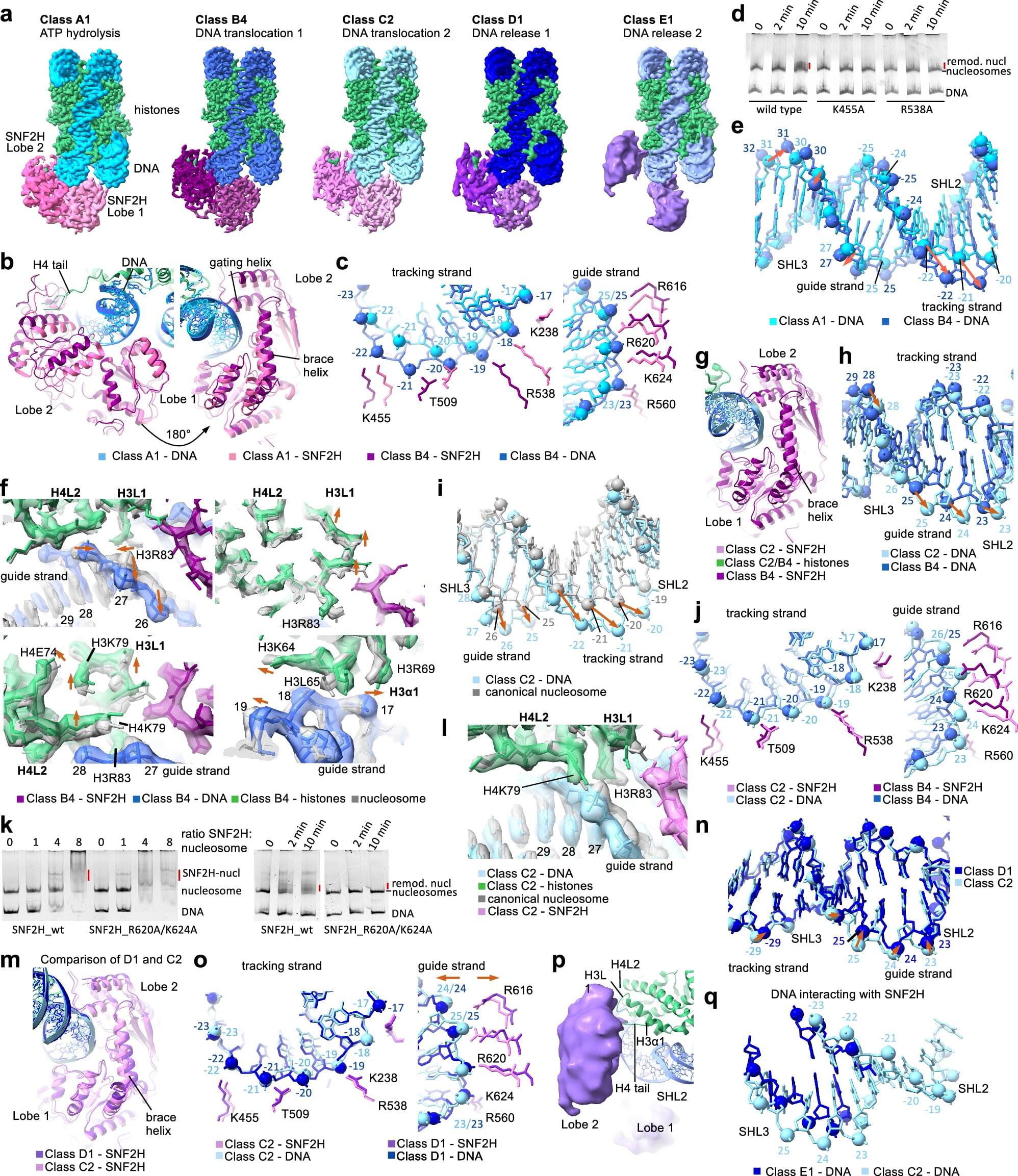
The researchers captured 13 structures that together offer a comprehensive view of how the remodeling enzyme SNF2H works, offering insights that are likely shared across other such enzymes. The work was published today in Cell Research.