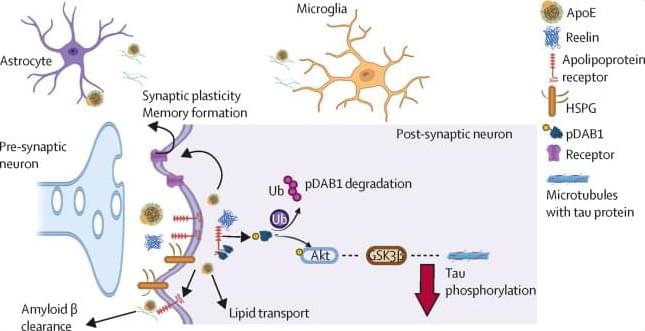
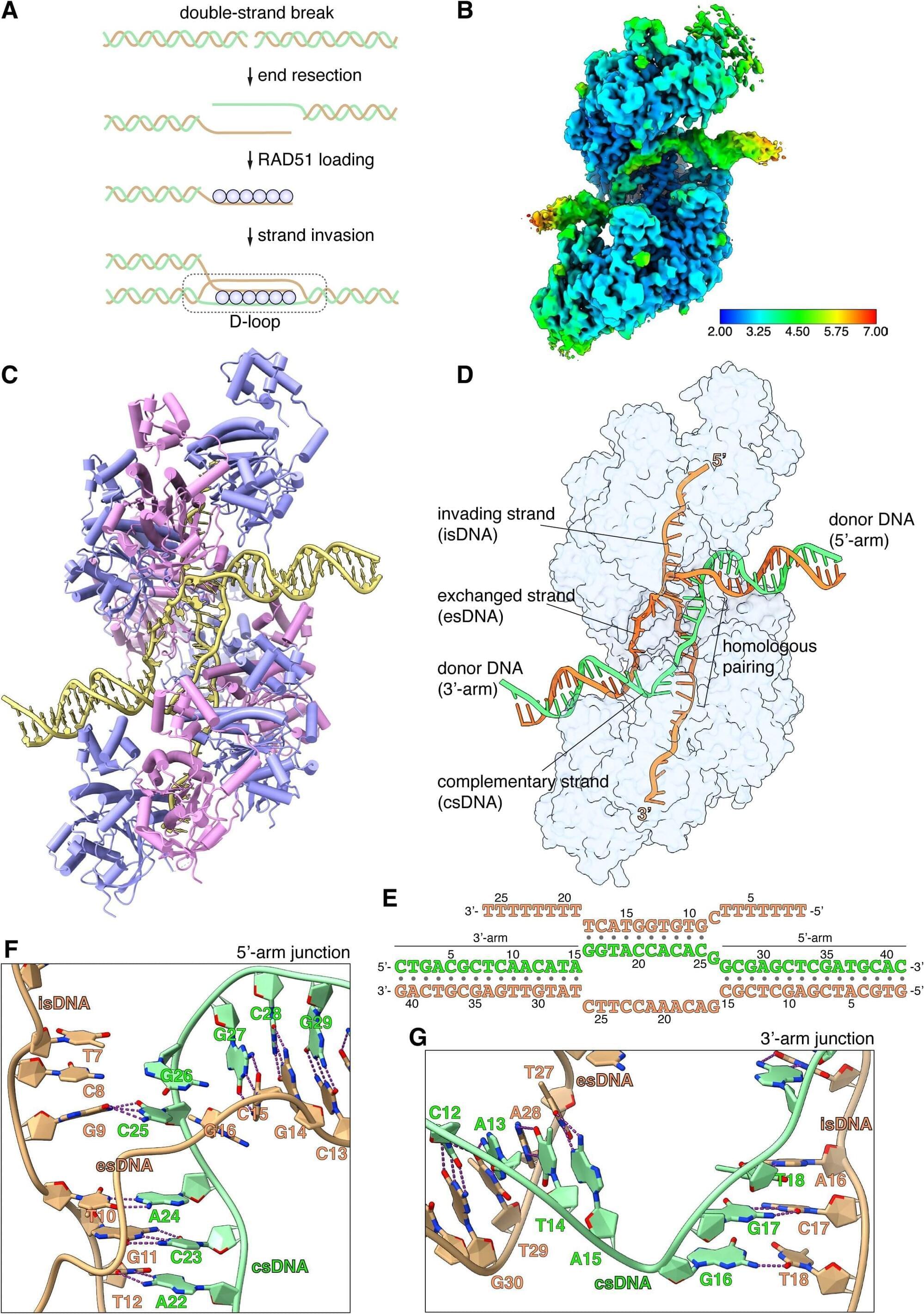
Neuralink did not immediately return requests for comment outside regular business hours.
Semafor’s report corroborates earlier reporting from Bloomberg, which noted in April that the startup was looking to raise $500 million at an $8.5 billion pre-money valuation.
Neuralink last year received “breakthrough device” clearance from the U.S. FDA. Three people have so far received implants made by Neuralink. Earlier this month, a nonverbal patient posted a video about how he uses a Neuralink implant to edit and narrate YouTube videos with just his brain signals.