Scientists found a molecular “kill switch” that could keep cholesterol—and disease—in check.


While glucose, or sugar, is a well-known fuel for the brain, Weill Cornell Medicine researchers have demonstrated that electrical activity in synapses—the junctions between neurons where communication occurs—can lead to the use of lipid or fat droplets as an energy source.
The study, published in Nature Metabolism, challenges “the long-standing dogma that the brain doesn’t burn fat,” said principal investigator Dr. Timothy A. Ryan, professor of biochemistry and of biochemistry in anesthesiology, and the Tri-Institutional Professor in the Department of Biochemistry at Weill Cornell Medicine.
The paper’s lead author, Dr. Mukesh Kumar, a postdoctoral associate in biochemistry at Weill Cornell Medicine who has been studying the cell biology of fat droplets, suggested that it makes sense that fat may play a role as an energy source in the brain like it does with other metabolically demanding tissues, such as muscle.


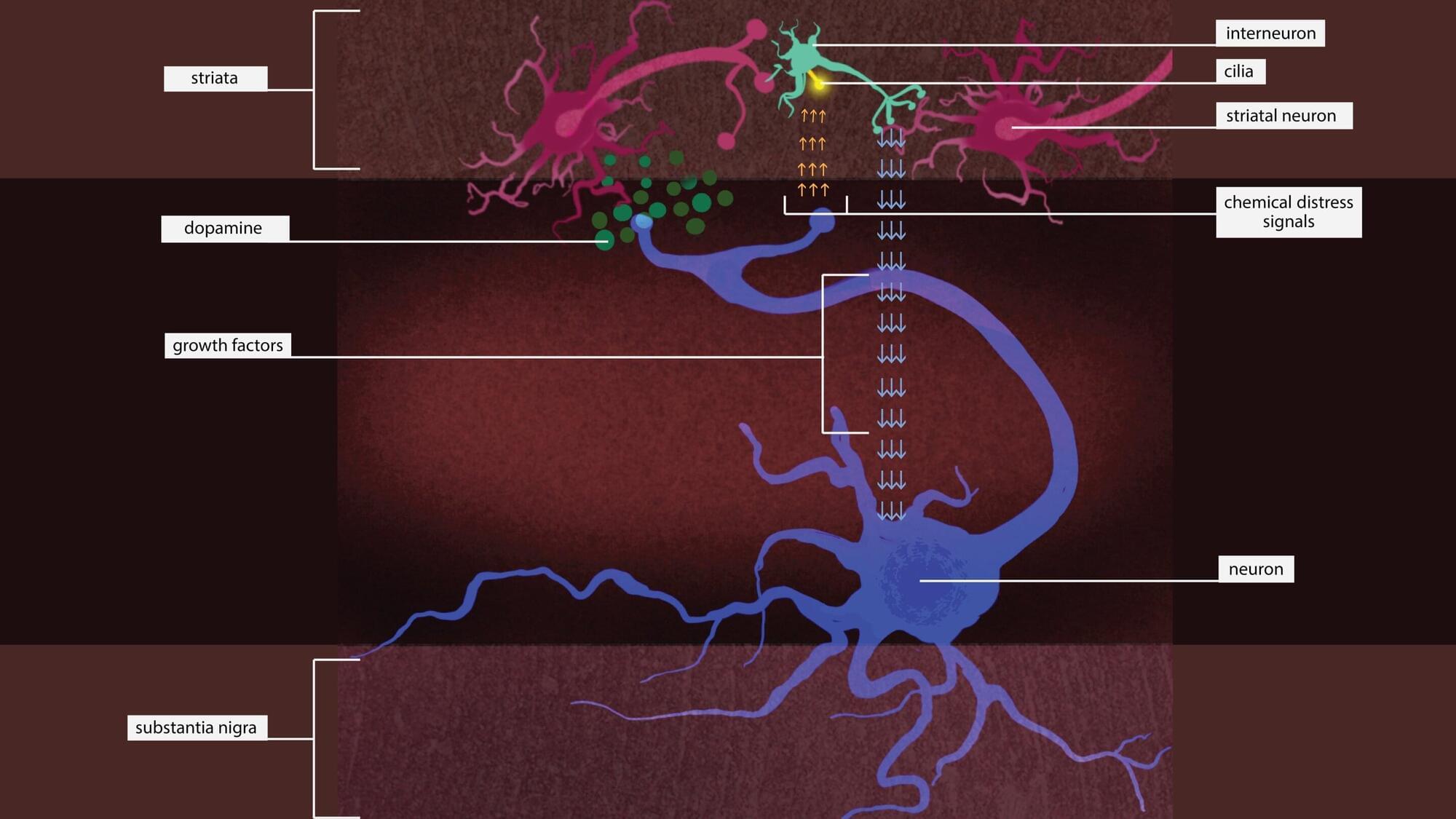
Putting the brakes on an enzyme might rescue neurons that are dying due to a type of Parkinson’s disease that’s caused by a single genetic mutation, according to a new Stanford Medicine-led study conducted in mice.
The study has been published in Science Signaling.
The genetic mutation causes an enzyme called leucine-rich repeat kinase 2, or LRRK2, to be overactive. Too much LRRK2 enzyme activity changes the structure of brain cells in a way that disrupts crucial communication between neurons that make the neurotransmitter dopamine and cells in the striatum, a region deep in the brain that is part of the dopamine system and is involved in movement, motivation and decision-making.
Researchers at UT Arlington have discovered a key enzyme, IDO1, that when blocked, helps immune cells regain their ability to properly process cholesterol—something that breaks down during inflammation. This breakthrough could offer a powerful new way to fight heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and more. By “turning off” this enzyme, the team restored cholesterol absorption in macrophages, potentially stopping disease at the source. Even more promising, they found a second enzyme, NOS, that makes things worse—raising hopes that targeting both could pave the way for transformative treatments for millions suffering from inflammation-driven conditions.

CGT manufacturers need to get better at gathering process data to move manufacturing into the digital age according to a new study [Reptile8488/Getty Images]
Cell and gene therapy (CGT) production will only enter the digital age when the industry gets better at gathering process data, according to researchers, who say closed systems and advanced monitoring technologies will be vital.
Unlike in pharma, the fourth industrial revolution has not reached the CGT sector, according to Aleksander Szarzynski, a researcher at the Vienna University of Technology and co-author of a new study looking at cell and gene therapy production.
To study what happened in the brain during this task, the researchers used functional magnetic resonance imaging, which measures blood flow as a proxy for neural activity. They scanned the brains of 11 participants while they performed the memory task over multiple sessions. By applying a complex decoding model to the imaging data, the researchers were able to estimate not only what participants were remembering but also how uncertain they were about each memory. The model treated neural activity as a probabilistic code, where stronger or more focused patterns of activity reflected more confident memory representations.
The results showed that neural signals in the visual cortex—the area of the brain involved in processing visual information—were more intense for the high-priority memory items. These stronger signals translated to smaller memory errors and greater confidence. On average, participants remembered the high-priority items more accurately and responded more quickly when asked to recall them. Their eye movements were closer to the correct location, and they took less time to respond. These behavioral improvements matched the patterns observed in the brain data.
The study also found that the magnitude of neural activity in the frontal cortex predicted how well participants could distinguish between high-and low-priority memories. This suggests that the frontal cortex plays a regulatory role, sending signals that adjust the strength of memory representations in visual areas depending on how important each item is. In other words, the frontal brain regions help direct the mental spotlight, increasing the “volume” of the memories that matter most.
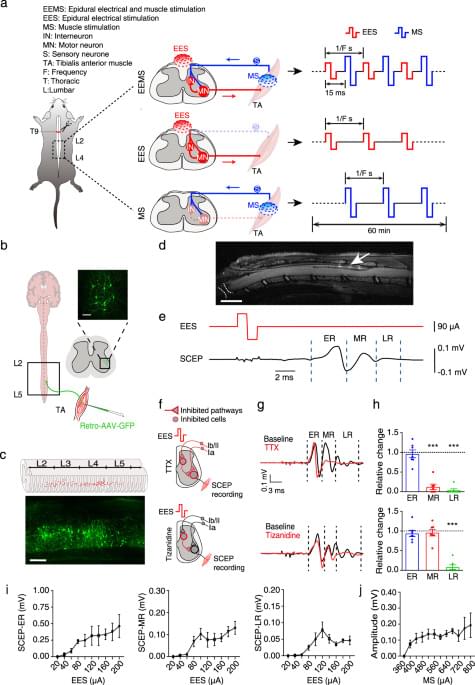
Electrical signals with characteristic parameters for reconstructing neural circuits remain incompletely understood, limiting the therapeutic potential of electrical neuromodulation techniques. Here, the authors demonstrate that dual electrical stimulation at 10–20 Hz rebuilds the spinal sensorimotor neural circuit after spinal cord injury, indicating the characteristic signals of circuit remodeling.