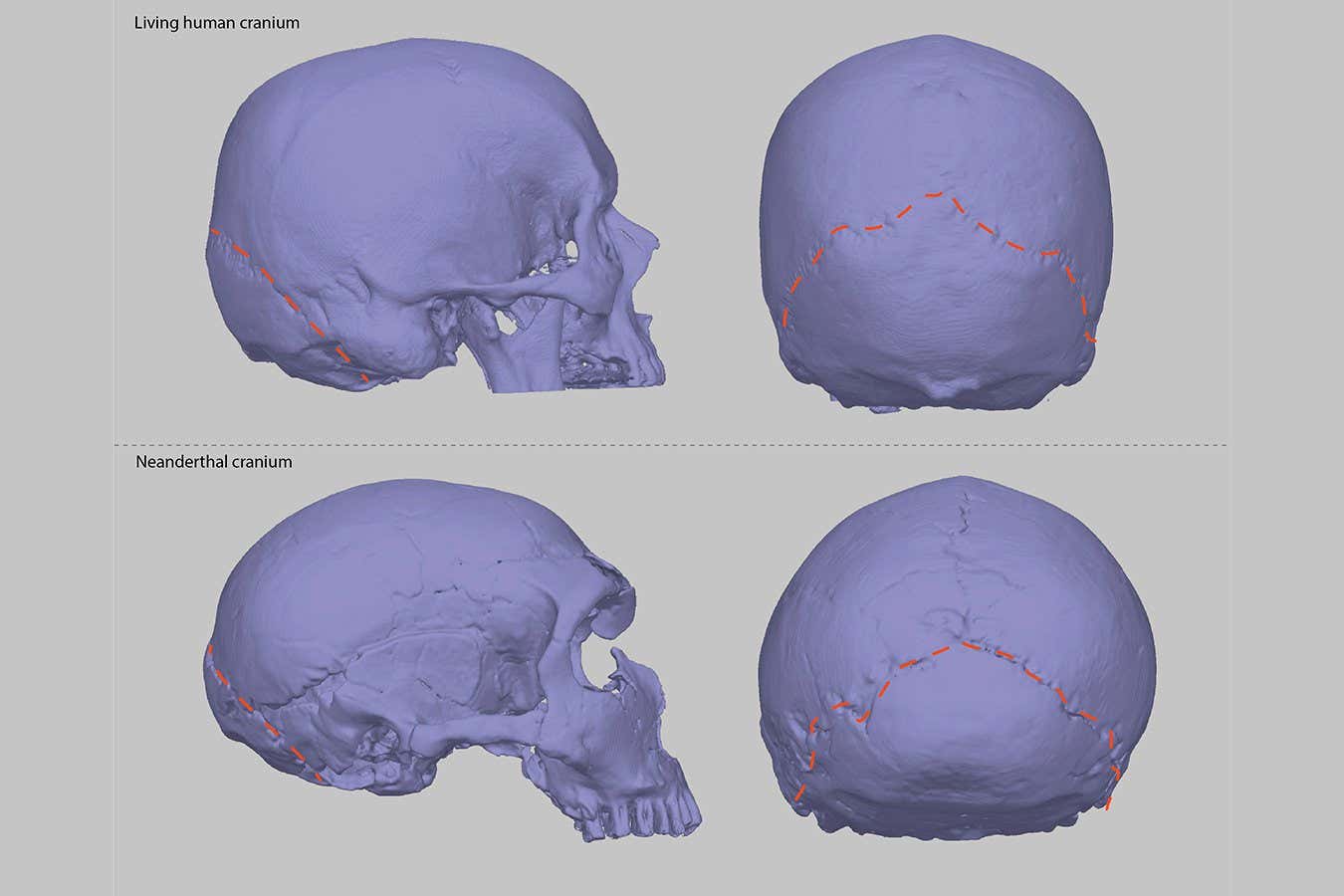
This study found that involvement of the superior cerebellar peduncles is frequent in patients with GAA-FGF14 ataxia (SCA27B)
ObjectivesGAA-FGF14 ataxia (SCA27B) is a recently reported late-onset ataxia caused by a GAA repeat expansion in intron 1 of the FGF14 gene. After the clinical observation of superior cerebellar peduncle (SCP) involvement in some affected patients, we sought to verify the prevalence of this finding in our cohort and 4 additional independent cohorts of patients with SCA27B.