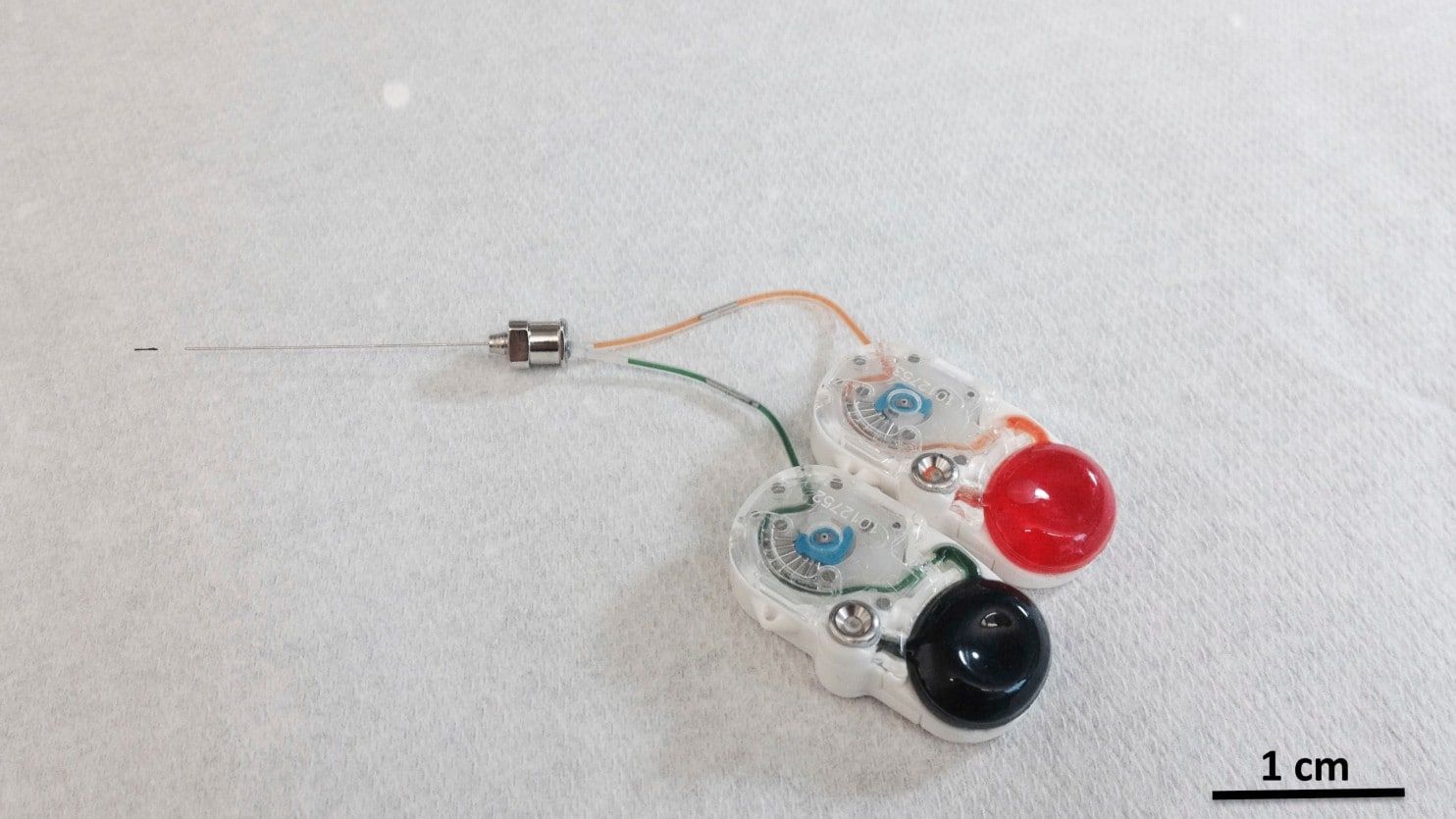
WASHINGTON — Scientists have created a hair-thin implant that can drip medications deep into the brain by remote control and with pinpoint precision.
Tested only in animals so far, if the device pans out it could mark a new approach to treating brain diseases — potentially reducing side effects by targeting only the hard-to-reach circuits that need care.
“You could deliver things right to where you want, no matter the disease,” said Robert Langer, a professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology whose biomedical engineering team reported the research Wednesday.