If we had known in advance of the challenges that were to come, we might never have started the research.
- By Jean Bennett, Katherine A. High on March 8, 2019

If we had known in advance of the challenges that were to come, we might never have started the research.

It won’t be simple. As with the advent of the car, many serious implications will be emergent, and the harshest effects borne by communities with the least powerful voices. We need to move our gaze from individuals to systems to communities, and back again. We must bring together diverse expertise, including workers and citizens, to develop a framework that health systems can use to anticipate and address issues. This framework needs an explicit mandate to consider and anticipate the social consequences of AI — and to keep watch over its effects. That is the best way to ensure that health technologies meet the needs of all, and not just those in Silicon Valley.
Health authorities are overlooking risks to systems and society in their evaluations of new digital technologies, says Melanie Smallman.

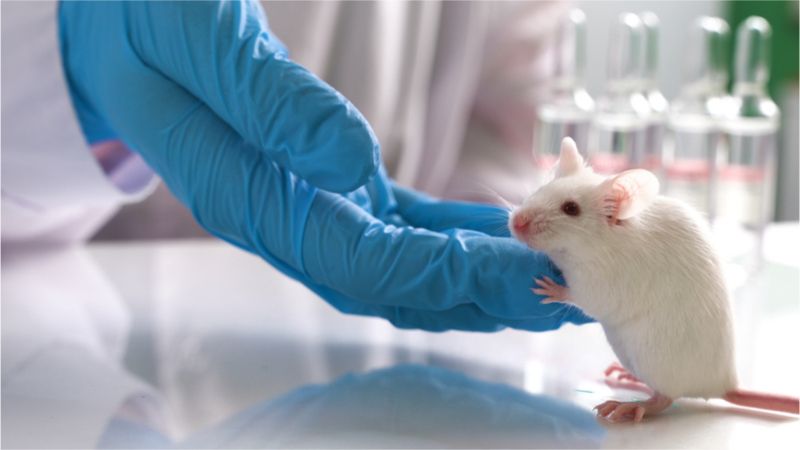
Scientists have shown that the removal of non-dividing senescent cells, which are normally associated with aging, also appears to prevent Type 1 diabetes in diabetic mouse strains.
Clearing senescent beta cells prevents T1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin. Insulin is a hormone that allows sugar (glucose) to enter cells in order to create energy, so it is critical to cellular function and life.
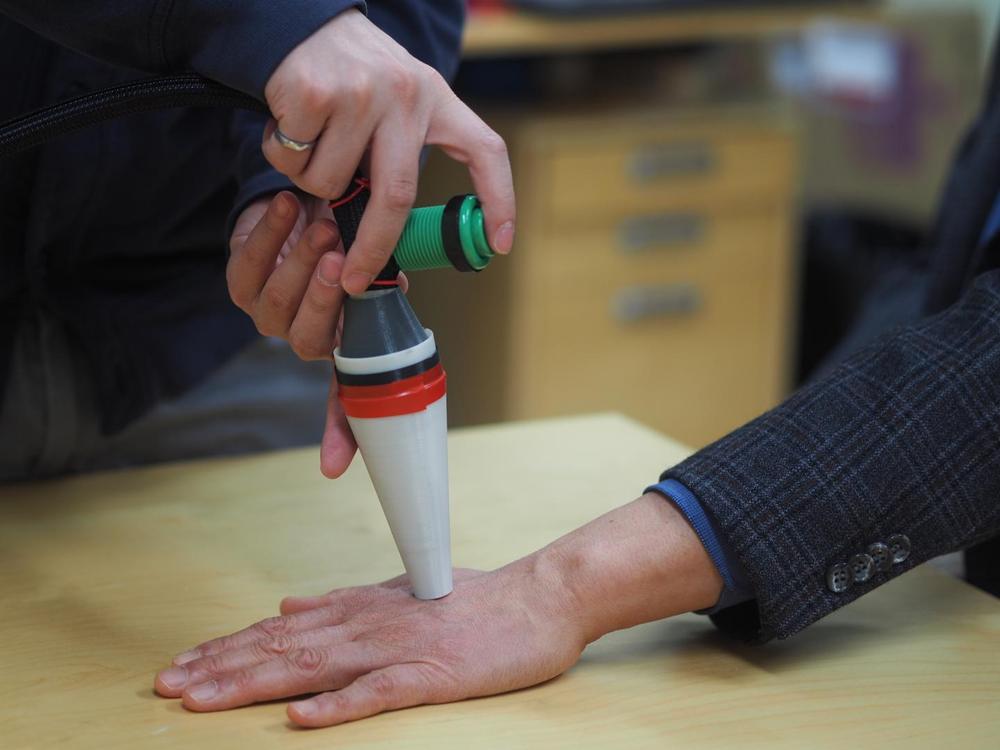

Canadian researchers have developed a laser probe that uses changes in light patterns to detect melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer.
The device works on the principle that light waves change as they pass through objects. Cancerous cells have a different physical profile to healthy cells, and the researchers designed a system that can detect these patterns instantly. By determining the optical polarisation of different skin lesions, the team was able to distinguish cancerous from non-cancerous tissues.
“With skin cancer, there’s a saying that if you can spot it you can stop it – and that’s exactly what this probe is designed to do,” said researcher Daniel Louie, a PhD student who constructed the device as part of his studies in biomedical engineering at the University of British Columbia (UBC).


In the world of things we already know.
MooDFOOD, the largest randomized clinical trial to study the effects of nutritional strategies on the prevention of major depressive disorder concludes that daily intake of nutritional supplements cannot prevent depression.

The products of wastewater treatment have been found to contain trace amounts of antibiotic resistant DNA. These products are often reintroduced to the environment and water supply, potentially resulting in the spread of antibiotic resistance. As such, researchers at the University of Southern California Viterbi School of Engineering have been studying the development of these potentially harmful and dangerous genes in wastewater treatment processes. Their findings, published in Environmental Science & Technology, indicate that even low concentrations of just a single type of antibiotic leads to resistance to multiple classes of antibiotics.
“We’re quickly getting to a scary place that’s called a “post-antibiotic world,” where we can no longer fight infections with antibiotics anymore because microbes have adapted to be resilient against those antibiotics,” said Adam Smith, assistant professor of civil and environmental engineering at USC and lead investigator of the study. “Unfortunately, engineered water treatment systems end up being sort of a hot-bed for antibiotic resistance.”
The majority of the antibiotics we consume are metabolized in our bodies. However, small amounts pass through us in our waste, which are then carried to wastewater treatment plants. At these plants, one of the common ways in which the wastewater is treated is with a membrane bioreactor, which uses both a filtration system and a biological process where microscopic bacteria consume waste products.
A startup called CogitAI has developed a platform that lets companies use reinforcement learning, the technique that gave AlphaGo mastery of the board game Go.
Gaining experience: AlphaGo, an AI program developed by DeepMind, taught itself to play Go by practicing. It’s practically impossible for a programmer to manually code in the best strategies for winning. Instead, reinforcement learning let the program figure out how to defeat the world’s best human players on its own.
Drug delivery: Reinforcement learning is still an experimental technology, but it is gaining a foothold in industry. DeepMind has talked of using it to optimize the performance of data centers and wind turbines. Amazon recently launched a reinforcement-learning platform, but it is aimed more at researchers and academics. CogitAI’s first commercial customers include those working in robotics for drug manufacturing. Its platform lets the robot figure out the optimal way to process drug orders.