#18 in our top science stories of 2019.
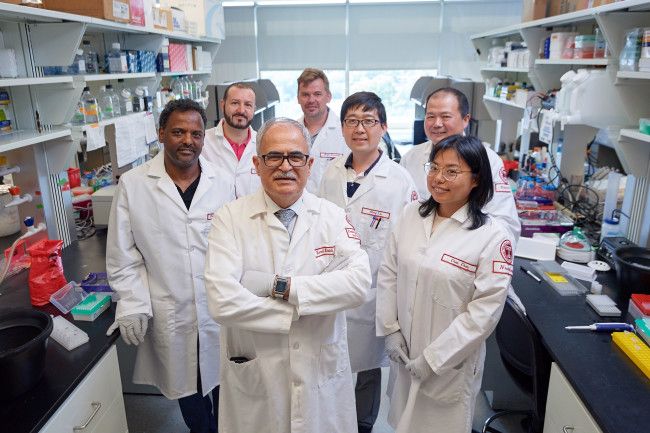



Engineering Food: The Impossible Whopper.
“Now, let’s compare the estrogen hormone in an impossible whopper to the whopper made from hormone implanted beef. The impossible whopper has 44 mg of estrogen and the whopper has 2.5 ng of estrogen. Now let me refresh your metric system. There are 1 million nanograms (ng) in one milligram (mg). That means an impossible whopper has 18 million times as much estrogen as a regular whopper. Just six glasses of soy milk per day has enough estrogen to grow boobs on a male. That’s the equivalent of eating four impossible whoppers per day. You would have to eat 880 pounds of beef from an implanted steer to equal the amount of estrogen in one birth control pill.”
The impossible whopper is being advertised by Burger King as a plant based alternative to the whopper. When food manufacturers started talking about making artificial meat, I, too, thought it would be impossible to make a hamburger cheaply enough to make it competitive. You see, I assumed that they would have to buy the individual amino acids (the building blocks for protein) and chemically string them together in the proper order, then remove the reagents (chemicals needed to cause the chain reactions) and then add something to give it the right textures.
The impossible whopper (made by Impossible Foods) bypassed all of those steps. Let’s compare the two. The impossible whopper patty is made from 24 ingredients. The most important ingredient is soy protein. The whopper patty has just one ingredient. That would be beef.
The impossible whopper has 630 calories, mostly from the added oils. The whopper has 660 calories. So, about 5% less calories, this is not a huge improvement.

Writing in Nature Medicine, an international team headed by researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine describe a new way to effectively deliver a gene-silencing vector to adult amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) mice, resulting in long-term suppression of the degenerative motor neuron disorder if treatment vector is delivered prior to disease onset, and blockage of disease progression in adult animals if treatment is initiated when symptoms have already appeared.
The findings are published in the December 23, 2019 online issue of the journal Nature Medicine. Martin Marsala, MD, professor in the Department of Anesthesiology at UC San Diego School of Medicine and a member of the Sanford Consortium for Regenerative Medicine, is senior author of the study.
ALS is a neurodegenerative disease that affects nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord. Motor neurons responsible for communicating movement are specifically harmed, with subsequent, progressive loss of muscle control affecting the ability to speak, eat, move and breathe. More than 5,000 Americans are diagnosed with ALS each year, with an estimated 30,000 persons currently living with the disease. While there are symptomatic treatments for ALS, there is currently no cure. The majority of patients succumb to the disease two to five years after diagnosis.
Raising hope of effective treatment for age-related macular degeneration (AMD), researchers have found that the brain knows how to integrate natural and artificial vision, while maintaining information processing that is important for vision.
AMD is a common cause of severe vision loss in among those aged 50 and over.
Though there is no cure for AMD, significant recent advancements in artificial retina implants may lead to effective treatment.

When it comes to kefir benefits, there are more than you can shake a well populated gut microbiome at. Because the drink – typically made from cow, goat or sheep milk, that gets the funky, fermented treatment – is resplendent in potential wins for your health.
But it can be a bit of a, erm, challenging concept. Why? Well, the texture can wind up somewhat lumpy, and the taste is distinctly sour. It’s fermented by adding kefir grains, which are colonies of yeast and lactic acid bacteria that look like tiny gel-like beads, similar to those used for sourdough, to milk and leaving for 24 hours, allowing the microorganisms to multiply and ferment the lactose to lactic acid. Bang: you’ve got DIY kefir.
Though — shocker — is isn’t vegan, it is possible to make from non-dairy milks or drinks, like coconut water, but the benefits proven in the same way. It is however low in lactose (the natural sugar in the milk), as the process of making kefir turns the lactose into lactic acid, so often lactose intolerant people can drink it.

Talk with an Alzheimer’s researcher and you’ll likely hear the same lament: Finding a treatment or cure is incredibly challenging because scientists are not even certain what exactly causes the neurological disease in the first place.
In fact, researchers speak of a “web of causation” that can lead to Alzheimer’s. In addition to genetics, scientists look to so-called lifestyle elements such as blood pressure and blood sugar levels. Even the bacteria that live in our mouths are being scrutinized for their potential role in Alzheimer’s.
One element that researchers are completely certain about is that people who carry the apolipoprotein E4 gene — known as APOE4 — are at a greater risk of developing Alzheimer’s.
It turned out that laser can actually regenerate damaged teeth. Credit: Hashem Al-Ghaili.

Lab-grown brain organoids developed from a patient’s own glioblastoma, the most aggressive and common form of brain cancer, may hold the answers on how to best treat it. A new study in Cell from researchers at Penn Medicine showed how glioblastoma organoids could serve as effective models to rapidly test personalized treatment strategies.
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) remains the most difficult of all brain cancers to study and treat, largely because of tumor heterogeneity. Treatment approaches, like surgery, radiation and chemotherapy, along with newer personalized cellular therapies, have proven to slow tumor growth and keep patients disease-free for some periods of time; however, a cure remains elusive.
“While we’ve made important strides in glioblastoma research, preclinical and clinical challenges persist, keeping us from getting closer to more effective treatments,” said senior author Hongjun Song, Ph.D., Perelman Professor of Neuroscience in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. “One hurdle is the ability to recapitulate the tumor to not only better understand its complex characteristics, but also to determine what therapies post-surgery can fight it in a timelier manner.”
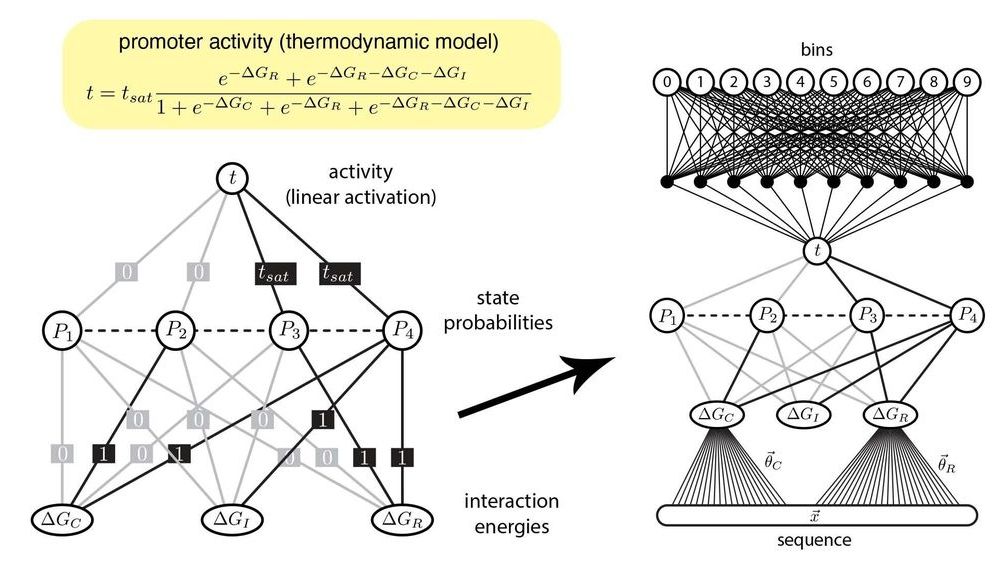
In this age of “big data,” artificial intelligence (AI) has become a valuable ally for scientists. Machine learning algorithms, for instance, are helping biologists make sense of the dizzying number of molecular signals that control how genes function. But as new algorithms are developed to analyze even more data, they also become more complex and more difficult to interpret. Quantitative biologists Justin B. Kinney and Ammar Tareen have a strategy to design advanced machine learning algorithms that are easier for biologists to understand.
The algorithms are a type of artificial neural network (ANN). Inspired by the way neurons connect and branch in the brain, ANNs are the computational foundations for advanced machine learning. And despite their name, ANNs are not exclusively used to study brains.
Biologists, like Tareen and Kinney, use ANNs to analyze data from an experimental method called a “massively parallel reporter assay” (MPRA) which investigates DNA. Using this data, quantitative biologists can make ANNs that predict which molecules control specific genes in a process called gene regulation.